- Submissions

Full Text
Peer Review Journal of Solar & Photoenergy Systems
Influence of Wind and Solar Power Plants on the Reliability of the Functioning of Power Systems
Vladimir A Nepomnyashchiy*
Professor of Economics, Saint Petersburg, Russial
*Corresponding author: Vladimir A Nepomnyashchiy, Professor of Economics, Academician of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences, Saint Petersburg, Russia
Submission: December 9, 2020;Published: December 22, 2020

Volume1 Issue4 December, 2020
Opinion
Until recently, it was considered one of the most effective directions in the development of the electric power industry to increase the share of renewable energy sources (RES) in the balance of power and electricity of power systems in the form of wind and solar power plants (wind turbines and solar power plants), the main advantages of which are considered to be the economy of fossil fuel (coal, gas, fuel oil) and reducing environmentally harmful emissions into the atmosphere. However, at the same time, the influence of renewable energy sources on the controllability of the modes of operation of electric power systems and on the reliability of the functioning of the RES remains completely unexplored. This brief analysis is devoted to the last question.
Keywords: Power system; Wind and solar power plants; Rotating reserve; Power supply reliability; Accident; Damage
Introduction
Currently, the world energy uses 318 million kW of wind turbines and about 142.4 million kW of solar power plants, of which the main countries of Western Europe account for about 227 million kW, or 49.3% (for the location of these power plants by country, see Table 1).
Table 1:Use of wind and solar power plants in Western Europe in 2018.
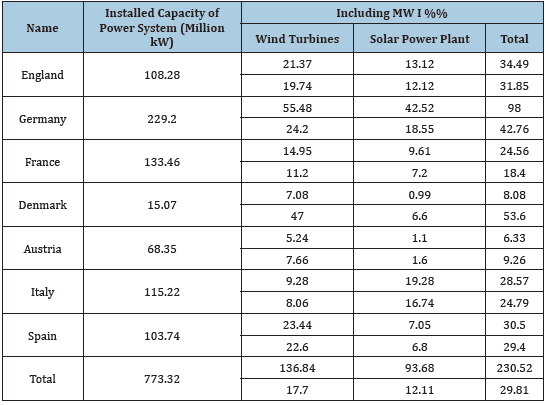
From the presented data, it can be seen that on average in Western Europe, wind and solar
power plants account for almost 30% of the total generating capacity, with the largest share of wind turbines in Denmark (47%), and the highest share of solar
power plants (18.6%) belongs to Germany.
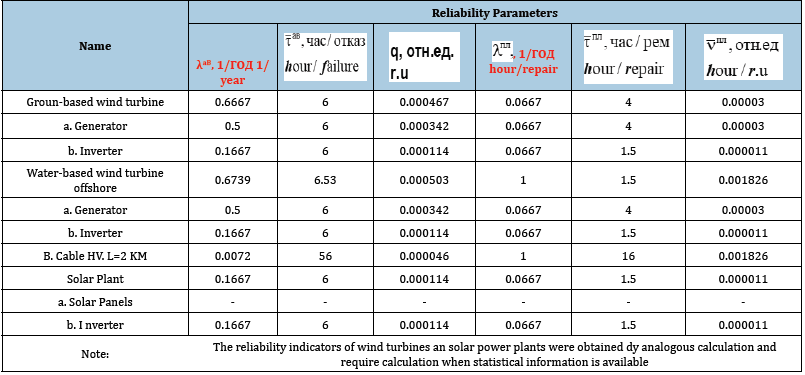
A modern wind turbine contains a direct generator, an energy
storage device (battery) and an inverter. If the offshore wind
turbine is provided, then the power plant includes a HV cable for
connecting the generator with the high-voltage electrical network
of the power system. When assessing the reliability of wind power
plants and solar power plants, it was taken into account that wind
turbines, as a rule, must operate without maintenance continuously
for at least 15 years. The same rule was conditionally extended to
the RES. Reliability indices of wind turbines and solar power plants
obtained by the analogous calculation method are shown in Table 2.
Table 2:Estimated indicators of reliability of wind and solar power plants.
To study the influence of wind and solar power plants on the
reliability of the functioning of power systems, the author’s model
of the reliability of power systems “SATURN” in version 3.3 was
used.
The studies conducted allow us to draw the following
conclusions:
A. An increase in the share of wind and solar power plants in
energy systems determines the economy of fossil fuel and reduces
harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
B. The same factor causes a decrease in the reliability of
the power system, increases the likelihood of systemic accidents
with disconnecting consumers and causing them serious economic
damage, reaching 1% of the produced GDP
C. This damage can be prevented by increasing the rotating
reserve within the available EPS reserve, which will require
an increase in funds for its maintenance due to additional fuel
consumption.
The ratio of reducing the probable damage to consumers
and the cost of additional fuel consumption to maintain the
necessary rotating reserve in the power system makes it possible
to economically substantiate the strategy and scale of introducing
renewable energy sources into the electric power industry.
© 2020 Vladimir A Nepomnyashchiy. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






