- Submissions

Full Text
Academic Journal of Engineering Studies
Removal of Heavy Metals from Industrial Effluent using Electrogravimetric Technique
Raghavendra Bakale1*, Santosh S Pawar1, Sushant SK2, Shridhar N Mathad2*, Shivalingsarj V Desai3, Beerappa S Maranur4 and Abhishek S Devarushi4
1Department of Chemistry, Jain College of Engineering Belagavi, India
2Department of Engineering Physics, KLE Institute of Technology, India
3Department of Biotechnology, KLE Technological University, Karnataka
4Department of Electronics and Communications, Jain College of Engineering Belagavi, Karnataka
*Corresponding author:Shridhar N Mathad, Department of Engineering Physics, KLE Institute of Technology, India
Submission: October 15, 2024;Published: March 27, 2025
.jpg)
ISSN:2694-4421 Volume3 Issue5
Abstract
Heavy metal pollution due to industrial effluents poses significant environmental and health risks. To address this issue, various techniques have been employed, among them electrogravimetric technique has emerged as a promising solution, effectively removing heavy metals through electrochemical precipitation. This review critically evaluates the technique’s principles, advantages, and applications, highlighting its effectiveness in removing most common heavy metals from various industrial effluents. The technique has demonstrated impressive removal efficiencies of above 90% under optimal operating conditions, as evidenced by case studies. However, challenges such as scaling up, electrode corrosion, and competing ions must be addressed to enhance its feasibility. Future research directions include exploring novel electrode materials, optimizing operating conditions, developing hybrid treatment approaches, and designing modular systems. The integration of electrogravimetric technique with emerging trends, such as sustainable technologies, water reuse, and advanced oxidation processes, holds great potential. By addressing the challenges and capitalizing on these trends, electrogravimetric technique can become a leading technology for heavy metal removal from industrial effluents, ensuring environmental protection, human health protection, industrial sustainability, and compliance with regulatory frameworks. Overall, this review underscores the significance of electrogravimetric technique in mitigating heavy metal pollution and highlights areas for future research and development. Recommendations include conducting thorough economic analyses, developing novel electrode materials, optimizing operating conditions, exploring hybrid treatment approaches, and establishing industry-wide standards.
Keywords:Electrogravimetry; Heavy metal removal; Industrial effluent treatment; Electrochemical precipitation, Wastewater remediation
Introduction
Heavy metals, a byproduct of industrial activities, have become a pervasive environmental pollutant, posing severe risks to Human Health [1], Ecosystems [2], and the Economy [3]. Industrial effluents contaminated with toxic heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, chromium, copper, nickel, zinc, and mercury, are released into water bodies, soil, and air, causing irreversible damage [4]. The consequences of heavy metal pollution are far-reaching and multifaceted. Human health is compromised through increased risk of Cancer [5], neurological damage [6], Kidney Dysfunction [7], and reproductive issues [8]. Environmental degradation occurs as heavy metals accumulate in ecosystems, harming aquatic life, contaminating food chains, and altering ecosystem dynamics [9]. Furthermore, heavy metal pollution has significant economic impacts, affecting agriculture, fisheries, and tourism [10]. Traditional treatment methods, including chemical precipitation, adsorption, and membrane filtration, often struggle to effectively remove heavy metals from industrial effluents due to limitations in efficiency, high operational costs, generation of secondary pollutants, and inability to target specific heavy metals [11]. In response, electrogravimetric technique, or electrochemical precipitation, has emerged as a promising solution [12]. This innovative approach leverages electrical energy to precipitate heavy metals, offering numerous advantages, including high removal efficiency, selectivity for specific heavy metals, energy efficiency, compact design, and costeffectiveness [13]. This review provides a comprehensive evaluation of electrogravimetric technique for heavy metal removal from industrial effluents. The discussion encompasses the principles, advantages, and parameters influencing its performance, as well as applications in various industrial settings, to assess its effectiveness and potential for widespread adoption (Figure 1).
Figure 1:Schematic aim of proposed work.
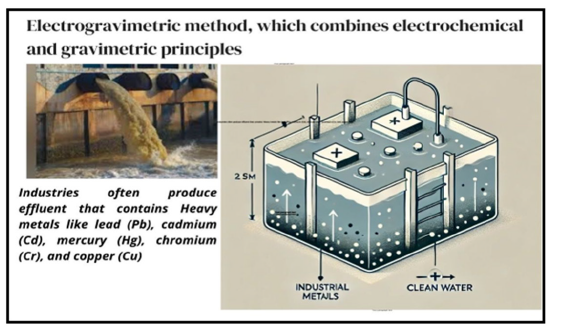
Principle of Electrogravimetric Technique
Electrogravimetric technique, also known as electrochemical precipitation, is a process that utilizes electrical energy to remove heavy metals from industrial effluents. The principle involves the application of an electric potential between two electrodes immersed in the effluent, inducing electrochemical reactions that precipitate heavy metals.
Electrochemical reactions
Cathodic reaction: At the cathode (negatively charged electrode), heavy metal ions (Mn+ ) in the effluent are reduced to their elemental form (M) through electron transfer..
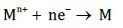
Anodic reaction: At the anode (positively charged electrode), water is oxidized, releasing oxygen gas and hydrogen ions.
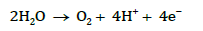
Understanding the principle of electrogravimetric technique is crucial for optimizing its performance, scaling up applications, and exploring new electrode materials and configurations [14-20] (Table 1).
Table 1:Heavy metals removed, removal efficiencies and effluent sources.

Process Mechanism
Electromigration
Heavy metal ions in the effluent migrate towards the cathode under the influence of the electric field.
Electrochemical reduction
At the cathode, heavy metal ions are reduced to their elemental form, precipitating out of solution.
Nucleation and growth
Precipitated heavy metals form nuclei, which grow into larger particles, facilitating easy separation.
Key Factors Influencing Electrogravimetry Technique
a. Electrode Material: Cathode material affects removal efficiency,
with materials like graphite [21], Stainless Steel [22], and
Titanium [23] showing promise.
b. Electrode Potential: Optimal potential range for heavy metal
precipitation.
c. Current Density: Influences precipitation rate and efficiency.
d. pH: Affects heavy metal speciation and precipitation [24].
e. Temperature: Impacts reaction kinetics and efficiency [25].
Advantages
a. High removal efficiency [26]
b. Selectivity for specific heavy metals [27]
c. Energy efficiency [28]
d. Compact design [29]
e. Cost-effective [30]
Electrogravimetric technique varisations
a. Direct Current (DC) electrogravimetry: Traditional method
using constant DC.
b. Pulsed Current electrogravimetry: Uses pulsed current to
enhance removal efficiency.
c. Alternating Current (AC) electrogravimetry: Utilizes AC to
reduce electrode corrosion.
Electrogravimetric technique has achieved impressive removal efficiencies for heavy metals (Figure 2):
Figure 2:Factor Influencing removal efficiency.
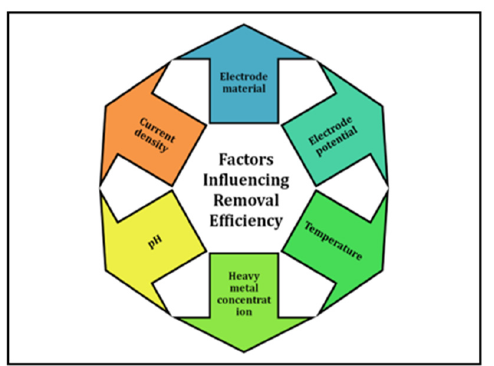
Factors influencing removal efficiency
a. Electrode material
b. Electrode potential
c. Current density
d. pH
e. Temperature
f. Heavy metal concentration
Industrial applications
Electro gravimetric technique has been applied in various
industries:
a. Electroplating [31]
b. Textile manufacturing [32]
c. Tannery [33]
d. Mining [34]
e. Chemical processing [35]
f. Battery manufacturing [36]
g. Printed circuit board manufacturing [37]
By effectively removing heavy metals, electrogravimetric technique helps mitigate environmental pollution, protects human health, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards (Figure 3).
Figure 3:Industrial applications.
Case Studies
Case study 1
i. Removal of Pb and Cd from Textile Industry Wastewater [38]
ii. Location: Textile mill in Gujarat, India
iii. Effluent characteristics: pH 6.5-7.5, Pb 50-70mg/L, Cd 30-
50mg/L
iv. Electrogravimetric technique: DC electrogravimetry with
graphite cathode and stainless steel anode
v. Operating conditions: Current density 20mA/cm², electrolysis
time 2 hours
vi. Results: Pb removal 95%, Cd removal 92%
vii. Conclusion: Electrogravimetric technique effectively removed
Pb and Cd from textile industry wastewater.
Case study 2
i. Electrogravimetric Treatment of Electroplating Industry
Effluent [39]
ii. Location: Electroplating unit in Tamil Nadu, India
iii. Effluent characteristics: pH 4.5-5.5, Cu 100-150mg/L, Ni 50-
70mg/L
iv. Electrogravimetric technique: Pulsed current
electrogravimetry with titanium cathode and stainless-steel
anode
v. Operating conditions: Current density 30mA/cm², pulse
frequency 100Hz, electrolysis time 3 hours
vi. Results: Cu removal 98%, Ni removal 95%
vii. Conclusion: Electrogravimetric technique efficiently removed
Cu and Ni from electroplating industry effluent.
Case study 3
i. Heavy Metal Removal from Mining Industry Wastewater [40]
ii. Location: Mining site in Australia
iii. Effluent characteristics: pH 3.5-4.5, Zn 500-700mg/L, Pb 200-
300mg/L
iv. Electrogravimetric technique: AC electrogravimetry with
graphite cathode and stainless steel anode
v. Operating conditions: Current density 40mA/cm², frequency
50Hz, electrolysis time 4 hours
vi. Results: Zn removal 90%, Pb removal 92%
vii. Conclusion: Electrogravimetric technique successfully
removed Zn and Pb from mining industry wastewater.
Case study 4
i. Removal of Cr from Tannery Effluent [41]
ii. Location: Tannery unit in Italy
iii. Effluent characteristics: pH 4.5-5.5, Cr 150-200mg/L
iv. Electrogravimetric technique: DC electrogravimetry with
stainless steel cathode and titanium anode
v. Operating conditions: Current density 25mA/cm², electrolysis
time 2.5 hours
vi. Results: Cr removal 95%
vii. Conclusion: Electrogravimetric technique effectively removed
Cr from tannery effluent.
Case study 5
i. Treatment of Battery Manufacturing Wastewater [42]
ii. Location: Battery manufacturing unit in China
iii. Effluent characteristics: pH 6.5-7.5, Pb 100-150mg/L, Cd 50-
70mg/L
iv. Electrogravimetric technique: Pulsed current
electrogravimetry with graphite cathode and stainless-steel
anode
v. Operating conditions: Current density 30mA/cm², pulse
frequency 100Hz, electrolysis time 3 hours
vi. Results: Pb removal 98%, Cd removal 95%
vii. Conclusion: Electrogravimetric technique efficiently removed
Pb and Cd from battery manufacturing wastewater.
viii. These case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of
electrogravimetric technique in removing heavy metals from
various industrial effluents, showcasing its potential as a
reliable and efficient treatment technology.
Challenges
Despite its effectiveness, the electrogravimetric technique faces several challenges that must be addressed to fully harness its potential. One of the primary challenges is scaling up, transitioning from laboratory-scale to industrial-scale operations, which requires significant design and operational adjustments [43]. Additionally, electrode corrosion remains a concern [44], reducing efficiency and increasing maintenance costs. The presence of competing ions in complex effluents also interferes with the technique’s performance, necessitating strategies to mitigate their impact. Furthermore, optimizing energy consumption is crucial to enhance the technique’s energy efficiency and reduce operational costs. The capital and operating costs associated with electrogravimetric technique must also be minimized to make it a viable solution for industries. Ensuring stability and reliability is another critical aspect, as consistent performance is essential for industrial applications. Lastly, navigating varying regulatory frameworks poses a challenge, requiring compliance with diverse standards and guidelines. Addressing these challenges will be essential to overcome the limitations of electrogravimetric technique and unlock its full potential for heavy metal removal from industrial effluents. By tackling these hurdles, researchers and industries can work together to develop more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable solutions.
Future Directions
To overcome the challenges and enhance the electrogravimetric technique, several future directions can be pursued. One key area of focus is the development of novel electrode materials with improved corrosion resistance [45], which would significantly enhance the technique’s efficiency and longevity. Additionally, optimizing operating conditions by investigating the effects of pH, temperature, and current density can lead to improved performance [46]. Another promising approach is the integration of electrogravimetry with other technologies to create hybrid treatment approaches, leveraging the strengths of multiple methods [47]. Modular design is also essential, enabling the development of compact, scalable, and flexible systems suitable for various industrial settings. Furthermore, implementing advanced monitoring and control systems through automation and control will ensure seamless operation and maximize efficiency [48]. Conducting thorough economic analyses is also crucial to understand the cost-benefit dynamics of electrogravimetric technique and identify areas for improvement. Finally, establishing industry-wide standards through standardization and certification will facilitate widespread adoption and ensure consistency across applications. By exploring these future directions, researchers and industries can work together to advance electrogravimetric technique and create a more effective, efficient, and sustainable solution for heavy metal removal from industrial effluents.
Research Opportunities
Research Opportunities abound in the field of electrogravimetric technique, offering avenues for advancement and innovation. Fundamental studies are needed to investigate the underlying electrochemical mechanisms, shedding light on the technique’s intricacies. Material science research can focus on developing new electrode materials with enhanced properties, while process modelling can simulate and optimize electrogravimetric processes to improve efficiency. Pilot-scale testing is crucial to validate laboratory results and demonstrate scalability. Industrial collaborations are also vital, enabling partnerships with industries to apply electrogravimetric technique in real-world settings. By bridging the gap between research and practice, these collaborations can inform the development of practical solutions.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends are poised to shape the future of electrogravimetric technique. Integrating sustainable technologies with renewable energy can minimize environmental footprint. Adopting circular economy principles enables the recovery of valuable metals and reuse of treated effluent. Water reuse strategies can treat effluent for reuse in industries, conserving resources. Furthermore, combining electrogravimetry with advanced oxidation processes can unlock synergies and enhance treatment efficacy. By embracing these trends, researchers and industries can unlock new possibilities and propel electrogravimetric technique toward widespread adoption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the electrogravimetric technique has demonstrated significant potential in effectively removing heavy metals from industrial effluents, offering a promising solution to a pressing environmental concern. By addressing the existing challenges, such as scaling up, electrode corrosion, and competing ions, and exploring future directions, including novel electrode materials, optimization of operating conditions, and hybrid treatment approaches, the efficiency, scalability, and costeffectiveness of this technique can be substantially enhanced. Ongoing research and development are crucial to ensure the continued relevance and improvement of electrogravimetric technique in industrial wastewater treatment. As the technology advances, its integration with emerging trends, such as sustainable technologies, circular economy, and water reuse, will further solidify its position as a leading solution for heavy metal removal. The successful implementation of electrogravimetric technique has far-reaching implications, including improved environmental protection, enhanced human health, and reduced economic burdens associated with heavy metal pollution. Ultimately, this innovative technology has the potential to transform industrial wastewater treatment, providing a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable future for generations to come.
Recommendations
To fully harness the potential of electrogravimetric technique for heavy metal removal from industrial effluents, several key recommendations must be implemented. Firstly, conducting thorough economic analyses is crucial to understand the costbenefit dynamics and identify areas for improvement. Additionally, developing novel electrode materials with enhanced properties can significantly boost efficiency and longevity. Optimizing operating conditions, such as pH, temperature, and current density, is also vital to maximize performance. Furthermore, exploring hybrid treatment approaches that combine electrogravimetry with other technologies can unlock synergies and enhance treatment efficacy. Finally, establishing industry-wide standards through standardization and certification will facilitate widespread adoption and ensure consistency across applications. By addressing the challenges and capitalizing on emerging trends, electrogravimetric technique can overcome its limitations and become a leading technology for heavy metal removal from industrial effluents, driving innovation and sustainability in environmental remediation. Effective implementation of these recommendations will pave the way for electrogravimetric technique to make a significant impact in mitigating heavy metal pollution.
References
- Hembrom S, Singh B, Gupta SK, Nema AK (2019) A comprehensive evaluation of heavy metal contamination in foodstuff and associated human health risk: a global perspective. Contemporary Environmental Issues and Challenges in Era of Climate Change, pp. 33-63.
- Alengebawy A, Abdelkhalek ST, Qureshi SR, Wang MQ (2021) Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 9(3): 42.
- Malviya P, Verma AK, Chaurasia AK, Parmar H, Thakur LS, et al. (2023) Heavy metals contaminants threat to environment: it’s possible treatment. Transportation Energy and Dynamics, pp. 323-341.
- Kumari S, Mishra A (2021) Heavy metal contamination. Soil Contamination Threats and Sustainable Solutions.
- Bonfiglio R, Sisto R, Casciardi S, Palumbo V, Scioli MP, et al. (2023) The impact of toxic metal bioaccumulation on colorectal cancer: unravelling the unexplored connection. Science of the Total Environment, p. 167667.
- Zuhra N, Tayyaba Akhtar, Rizwan Yasin, Iqra Ghafoor, Muhammad Asad, et al. (2024) Human health effects of chronic cadmium exposure. Cadmium Toxicity Mitigation, p. 65-102.
- Acharya S (2024) Heavy metal contamination in food: sources, impact, and remedy. Food Safety and Quality in the Global South, pp. 233-261.
- Dar BA, Yaqoob A, Mir GJ (2023) Effect of environmental contaminants on female reproductive health: a narrative review: environmental contaminants & female reproductive health. BME Horizon 1(3).
- Hameed M, Dijoo ZK, Bhat RA, Qayoom I (2020) Concerns and threats of heavy metals contamination on aquatic ecosystem. Bioremediation and Biotechnology 4: 1-19.
- Adibrata S, Yusuf M, Firdaus M (2021) Contamination of heavy metals (pb and cu) at tin sea mining field and its impact to marine tourism and fisheries. Indonesian Journal of Marine Sciences 26(2): 79-86.
- Kumar M, Seth A, Singh AK, Rajput MS, Sikandar M (2021) Remediation strategies for heavy metals contaminated ecosystem: A review. Environmental and Sustainability Indicators 12: 100155.
- Dave S, Dave S, Das J (2021) Electrochemical monitoring as an emerging technology for detection of environmental pollutants with special reference to pesticides. The Future of Effluent Treatment Plants, pp. 183-198.
- Ayach J, El Malti W, Duma L, Lalevee J, Al Ajami M, et al. (2024). Comparing conventional and advanced approaches for heavy metal removal in wastewater treatment: an in-depth review emphasizing filter-based strategies. Polymers 16(14): 1959.
- Rafique M, Hajra S, Tahir MB, Gillani SSA, Irshad M (2022) A review on sources of heavy metals their toxicity and removal technique using physico-chemical processes from wastewater. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 29(11): 16772-16781.
- Ayub S, Mohammadi AA, Yousefi M, Changani F (2019) Performance evaluation of agro-based adsorbents for the removal of cadmium from wastewater. Desalination and Water Treatment 142: 293-299.
- Nur Alam EM, Mia MAS, Ahmad F, Rahman MM (2020) An overview of chromium removal techniques from tannery effluent. Applied Water Science 10(9): 205.
- Liu Y, Wang H, Cui Y, Chen N (2023) Removal of copper ions from wastewater: a review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20(5): 3885.
- Avili FG (2021) Removal of heavy metals (Lead and Nickel) from water sources by adsorption of activated alumina. Anthropogenic pollution 5(2).
- Shrestha R, Ban S, Devkota S, Sharma S, Joshi R, et al. (2021) Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 9(4): 105688.
- Sylwan I, Thorin E (2021) Removal of heavy metals during primary treatment of municipal wastewater and possibilities of enhanced removal: A review. Water 13(8): 1121.
- Ren G, Zhou M, Su P, Liang L, Yang W, et al. (2018) Highly energy-efficient removal of acrylonitrile by peroxi-coagulation with modified graphite felt cathode: influence factors possible mechanism. Chemical Engineering Journal 343: 467-476.
- Rusli SFN, Bakar MHA, Loh KS, Mastar MS (2019) Review of high-performance biocathode using stainless steel and carbon-based materials in microbial fuel cell for electricity and water treatment. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 44(58): 30772-30787.
- Zhai H, Xia BY, Park HS (2019) Ti-based electrode materials for electrochemical sodium ion storage and removal. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 7(39): 22163-22188.
- Zhang Y, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Liu C, Sun C, et al. (2018) pH effect on heavy metal release from a polluted sediment. Journal of Chemistry 1: 7597640.
- Perwitasari DS, Muryanto S, Jamari J, Bayuseno AP (2018) Kinetics and morphology analysis of struvite precipitated from aqueous solution under the influence of heavy metals: Cu2+, Pb2+, Zn2+. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 6(1): 37-43.
- Halim EM, Demir Cakan R, Perrot H, El Rhazi M, Sel O (2022) Interfacial charge storage mechanisms of composite electrodes based on poly (ortho-phenylenediamine)/carbon nanotubes via advanced electrogravimetry. The Journal of Chemical Physics 156(12): 124703.
- El Mahdi H (2019) Electrogravimetric and electrochemical studies on new nanostructured materials based on carbon nanomaterials, conducting polymers and metal nanoparticles: Application for energy storage and conversion.
- Lemaire P, Dargon T, Alves Dalla CD, Sel O, Perrot H, et al. (2020) Making advanced electrogravimetry as an affordable analytical tool for battery interface characterization. Analytical Chemistry 92(20): 13803-13812.
- Musa DE, Sha Ato R, Eneji IS, Itodo AU (2018) Electrogravimetric determination of copper using a constructed compact electrolytic cell. Open Access Library Journal 5: 1-14.
- Nisiewicz MK, Gajda A, Kowalczyk A, Cupriak A, Kasprzak A, et al. (2022) Novel electrogravimetric biosensors for the ultrasensitive detection of plasma matrix metalloproteinase-2 considered a potential tumor biomarker. Analytica Chimica Acta 1191: 339290.
- Serdiuk V, Sklabinskyi V, Bolshanina S, Ableyev A, Dychenko T (2020) Prevention of hydrosphere contamination with electroplating solutions through electromembrane processes of regeneration. Journal of Ecological Engineering 21(4): 61–69.
- Simon P, Gogotsi Y (2020) Perspectives for electrochemical capacitors and related devices. Nature materials 19(11): 1151-1163.
- Festus B, Tella TA (2025) Quantification of toxic organic pollutants by electrochemical methods. Smart Nanomaterials for Environmental Applications, pp. 257-289.
- Csorba B, Farkas L, Mihalko A, Boros RZ, Gresits IL (2023) Photometric determination of trace amounts of aluminum in nearly saturated rock salt solutions used by chlor-alkali industry. Periodica Polytechnica Chemical Engineering 67(3): 442-451.
- Qafsaoui W, Taouil AE, Kendig MW, Cachet H, Joiret S, et al. (2018) Coupling of electrochemical, electrogravimetric and surface analysis techniques to study dithiocarbamate/bronze interactions in chloride media. Corrosion Science 130: 190-202.
- Link S, Dimitrova A, Krischok S, Bund A, Ivanov S (2020) Electrogravimetry and structural properties of thin silicon layers deposited in sulfolane and ionic liquid electrolytes. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 12(51): 57526-57538.
- Palin EJ (2019) An in-situ Study of Buried Metal Interfaces Using Electrochemical and Neutron Scattering Techniques. (Doctoral dissertation, University of Leicester).
- Turksoy R, Terzioglu G, Yalcin IE, Turksoy OT, Demir G (2021) Removal of heavy metals from textile industry wastewater. Frontiers in Life Sciences and Related Technologies 2(2): 44-50.
- Serdiuk V, Sklabinskyi V, Bolshanina S, Ableyev A, Dychenko T (2020) Prevention of hydrosphere contamination with electroplating solutions through electromembrane processes of regeneration. Journal of Ecological Engineering 21(4): 61-69.
- Qasem NA, Mohammed RH, Lawal DU (2021) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. Npj Clean Water 4(36): 1-15.
- Nur Alam EM, Mia MAS, Ahmad F, Rahman MM (2020) An over.
- Yu Y, Wu B, Jiang L, Zhang XX, Ren HQ, et al. (2019) Comparative analysis of toxicity reduction of wastewater in twelve industrial park wastewater treatment plants based on battery of toxicity assays. Scientific Reports 9(1): 3751.
- Le T (2018) Fundamental insights into dynamic ionic exchange in vertically-oriented nanostructured materials via fast electrogravimetric methods. Applications to energy storage mechanisms.
- Vivier V, Orazem ME (2022) Impedance analysis of electrochemical systems. Chemical Reviews 122(12): 11131-11168.
- Garcia Jareno JJ, Agrisuelas J, Vicente F (2023) Overview and recent advances in hyphenated electrochemical techniques for the characterization of electroactive materials. Materials 16(12): 4226.
- Unal A, Hillman AR, Ryder KS, Cihangir S (2021) Electrogravimetric analysis of poly (aniline-co-o-toluidine) copolymer films in the presence of fluoride ions. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 895: 115519.
- Shaukat H, Ali A, Bibi S, Altabey WA, Noori M, et al. (2023) A review of the recent advances in piezoelectric materials, energy harvester structures and their applications in analytical chemistry. Applied Sciences 13(3): 1300.
- Oluyisola OE, Bhalla S, Sgarbossa F, Strandhagen JO (2022) Designing and developing smart production planning and control systems in the industry 4.0 era: a methodology and case study. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 33(1): 311-332.
© 2025 Raghavendra Bakale. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






