- Submissions

Full Text
Gastroenterology Medicine & Research
Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Regeneration Processes of the Stomach and Colon in the Rat
Abdulatipova ZM and Trubitsyna IE*
Department of Health, Russia
*Corresponding author:Trubitsyna IE, Department of Health, Moscow, Russia
Submission: December 02, 2019;Published: December 09, 2019

ISSN 2637-7632Volume4 Issue2
Summary
In experimental studies, the effect of MSCs on regeneration processes in mechanical damage to the gastric mucosa and colon ulcers after toxic and immune damage to the colon mucosa was studied. It is established that MSCs have a positive effect on regeneration processes. Double injection of MSCs is more effective than a single one. MSCs have an immunomodulatory effect, in the acute period of inflammation MSCs are less effective, so you need a second injection of MSCs.
Keywords:Mesenchymal stem cells; Surgery; Gastric mucosa; Colon ulcer
Introduction
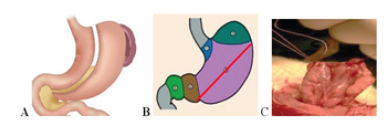
Surgical treatment of obesity has become widespread, which led to the formation of an independent section of surgery, bariatric surgery. The number of stomach surgeries has increased. Of these, the most common is “sleeve” (vertical, longitudinal) resection. The removal of 80% of the stomach of the patient suffering from obesity. During the “sleeve” gastroplasty, the body and the bottom of the stomach are removed the area where the largest number of secretory cells are located (Figure 1). There remains a narrow passage-a sleeve along the small curvature of the gastric. After resection, the operating wound is sewn in layers, an operating seam is formed. The stomach has a fairly “strong” wall, anastomosis’s rarely occurs. However, there is a considerable risk of strictures, which disrupt the motility and evacuation of stomach contents. Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), which include ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD), represent one of the most serious and unresolved problems in modern gastroenterology. In terms of morbidity, IBD are significantly more than other diseases of the digestive system, but in terms of severity, frequency of complications and mortality, they occupy one of the leading positions in the structure of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract worldwide. In the study of the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), some progress has been made, but despite the achievements of fundamental medicine and a wide range of medicines used, there is an increase in the incidence of IBD [1,2].
Aim
Aim of our experimental studies was to study the healing processes of defects of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. In the first case, a model of postoperative gastric wound was created, second case, toxic damage colon.
Figure 1:The stomach is: A. man B. Rat: 1. Cardiac part 2. The rumen; 3. Body; 4. Gatehouse cave; 5. Pyloric part. Schemes of departments and line of operative intervention. C. layer-by-Layer suturing of the stomach stump in rats.
Material and Methods
Part 1:
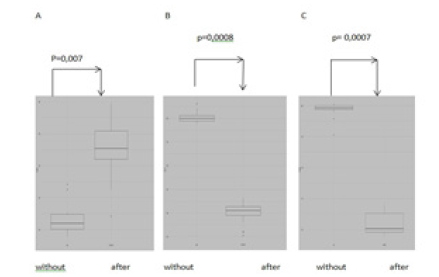
Surgery on the stomach, used white rats of line Wistar 40 animals. (Figure 2). The mononuclear cell fraction was obtained from rat bone marrow aspirate [3]. For the experiment, cells of the 8th and 9th passage (cell material suitable for transplantation, with preserved population activity and the absence of dead cells) were used on the 3rd day after surgery once in a dose of 3,5x106 on the 3rd day after surgery. In the second series of experiments, allogeneic cells were administered to rats twice, the first introduction in a dose of 3, 5x106 cells on the 3rd day after surgery, the second introduction in the same dose was carried out on the 8th day. In the serum of rats were measured by ELISA method was used to determine IL-4, IL - 1β, TNF. The control series of experiments were intact animals, which underwent surgery on the stomach, after which one or two times injected saline solution in equal volumes with the experimental series (0.5ml). We found that in the blood serum of rats trough 24hours after suturing the surgical wound sharply increased the concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNFa), the content of anti-inflammatory interleukin- 4 (IL- 4) is low (Figure 3). These shifts in the control group operation + saline solution was detected both during inflammation and regeneration. With the introduction of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells in serum to 10 days decreased the content of TNFa, IL-1β and increased IL-4. We associate the positive dynamics of regenerative processes in the surgical wound area under the influence of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells with the positive immunomodulatory effect of these cells, which we observed during dynamic observation. The balance between Th1 and Th2 The obtained data indicate an upcoming decrease in the systemic inflammatory response in the body under the influence of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells, creating favorable conditions for restoring the balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines (Figure 3) and activation of morphogenetic function of immunocytes. A reflection of these processes is the absence of complications (ulcers and erosions, strictures) in the area of the surgical suture (Figure 2). 2 series of experiments were performed: with single and double introduction of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). In the second series of experiments, allogeneic cells were administered to rats twice, the first introduction in a dose of 3, 5x106 cells on the 3rd day after surgery, the second introduction in the same dose was carried out on the 8th day. The introduction of allogeneic bone marrow MSCs, and saline solution were carried out intraperitoneally. The control series of experiments were intact animals, which underwent surgery on the stomach, after which one or two times injected saline solution in equal volumes with the experimental series (0.5ml).
Figure 2:The mucous membrane of the rat’s stomach in the area of the surgical suture. A. Without the introduction of MSC; B. After the introduction of MSC
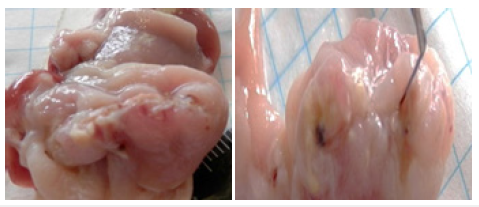
Figure 3:Diagrams of the concentration of cytokines ng / ml: А. IL -4; B. IL-1β C. TNFα (without MSC; after MSC).
Results and Discussion
So, found that in the blood serum of rats trough 24hours after suturing the surgical wound sharply increased the concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNFa), the content of antiinflammatory interleukin- 4 (IL-4) is low (Figure 3). These shifts in the control group operation + saline solution was detected both during inflammation and regeneration. With the introduction of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells in serum to 10 days decreased the content of TNFa, IL-1β and increased IL-4. We associate the positive dynamics of regenerative processes in the surgical wound area under the influence of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells with the positive immunomodulatory effect of these cells, which we observed during dynamic observation. The balance between Th1 and Th2 The obtained data indicate an upcoming decrease in the systemic inflammatory response in the body under the influence of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells, creating favorable conditions for restoring the balance of pro - and anti-inflammatory cytokines (Figure 3) and activation of morphogenetic function of immunocytes. A reflection of these processes is the absence of complications (ulcers and erosions, strictures) in the area of the surgical suture (Figure 2). 2 series of experiments were performed: with single and double introduction of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). In the second series of experiments, allogeneic cells were administered to rats twice, the first introduction in a dose of 3, 5x106 cells on the 3rd day after surgery, the second introduction in the same dose was carried out on the 8th day. The introduction of allogeneic bone marrow MSCs, and saline solution were carried out intraperitoneally. The control series of experiments were intact animals, which underwent surgery on the stomach, after which one or two times injected saline solution in equal volumes with the experimental series (0.5ml). We associate the positive dynamics of regenerative processes in the surgical wound area under the influence of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells with the positive immunomodulatory effect of these cells, which we observed during dynamic observation. The balance between Th1 and Th2 is restored. (Rice. 3). The obtained data indicate an upcoming decrease in the systemic inflammatory response in the body under the influence of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells, creating favorable conditions for restoring the balance of Pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines (Figure 3) and activation of morphogenetic function of immunocytes. A reflection of these processes is the absence of complications (ulcers and erosions, strictures) in the area of the surgical suture (Figure 2).
Conclusion
The positive dynamics of regenerative processes in the area of the operating wound under the influence of MSCs was established. These processes are associated with the positive immunoregulatory effect of MSCs. After administration of MSCs, the ratio of pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines is restored and the morphogenetic function of immunocytes is activated [4].
2 PART
Figure 4:A. Diffuse leukocytic infiltration of the lamina propria, destruction of the epithelium basal parts of the crypts. N&E x250. B. epithelial Cells in a state of severe dystrophy and necrobiosis. In the lumen of the crypts are clusters of white blood cells H&E x250
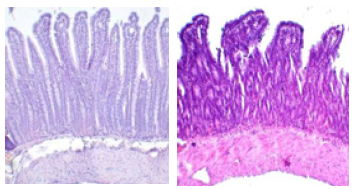
Ulcer colon, for obtain acute forms destruction sufferers rats received with drinking 10% water care solution Dextran sulfate (DS) in for weeks. To obtain the chronic forms of intestinal injury in rats received with drinking a 10% aqueous solution of DS during the week, followed by 2 weeks break and the procedure repeated twice or the more. In the mucosa of the ileum: there was a sharp decrease in the height of intestinal villi, in some cases, the intestinal villi were absent in crypt depth increased, there was increase in the number interepithelial lymphocytes and increased lymphoplasmacytic infiltration of lamina propria. In some animals, dilation of vessels of the submucosal layer was observed, epithelial cells were in a state of severe dystrophy and necrobiosis [5]. In the lumen of the crypts in some cases found clusters of white blood cells (Figure 4). The introduction of MSCs in the series with chronic destruction significantly the histological picture of the ileum mucosa: the height of the intestinal villi, although in some cases reduced, but in more situations to condition analogous in the control group. Nevertheless, changes in epithelial cells were noticeable: there was no brush border of enterocytes, lymphocytic infiltration of the own plate was preserved (Figure 5). In a series of experiments with chronic solution dextran sulfate, compared with ulcer colon 2 months after the introduction of MSCs histological picture has improved significantly. The normal structure of the mucous membrane of the ileum, caecum and ascending intestine was practically restored, and the crypts were much higher than in the control group (Figure 4). The introduction of MSC dramatically activated proliferative processes and led to hyperplasia of the caecum epithelium and increased the formation of small and large follicles in the mucosa and submucosal layer, increased the number of goblet cells in the epithelium, as well as the height and number of intestinal villi of the mucosa [6].
Results and Discussion
Thus, it was demonstrated that MSCs have high proliferative activity and high reparative potential. The introduction of MSCs led to complete recovery and reduction of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cecum and ascending intestine. The most pronounced reparative processes were observed in a series of experiments with chronic priming 2 months after the introduction of MSC (Figure 5), Mesenchymal stromal cells, as already follows from the experience of the studies, demonstrated the prospects of this method in the field of medical use of MSCs for the treatment of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. Without MSCs, the bottom of the ulcer is covered with granulation tissue, but there are vascular disorders under the granulation tissue, which does not provide quality healing (Figure 5). After the introduction of MSCs, the bottom of the ulcer is also covered with newly formed granulation tissue, vascular disorders are absent, healing is qualitative (Figure 5). Without MSCs, the bottom of the ulcer is covered with granulation tissue, but there are vascular disorders under the granulation tissue, which does not provide quality healing (Figure 5). After the introduction of MSCs, the bottom of the ulcer is also covered with newly formed granulation tissue, vascular disorders are absent, healing is qualitative (Figure 5).
Conclusion
Thus, it was demonstrated that MSCs have high proliferative activity and high reparative potential. The introduction of MSCs led to complete recovery and reduction of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cecum and ascending intestine. The most pronounced reparative processes were observed in a series of experiments with chronic priming 2 months after the introduction of MSCs. The introduction of mesenchymal stromal cells, as already follows from the experience of the studies, demonstrated the prospects of this method in the field of medical use of MSCs for the treatment of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases and the surgical suture.
References
- Allgayer H (2003) Review article: mechanisms of action of mesalazine in the prevention of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel diseases. Food Pharmacol Ther 18: 10-14.
- Asano TK, McLeod RS (2004) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and aspirin for the prevention of colorectal adenomas and cancer: A systematic review. Dis Rectum Colon 47(5): 665-673.
- Trubitsyn E, Abdulatipova Z, Orlova Yu M, Vasnev OS, Gulyaev AS (2017) Participation of MSCs in postoperative wound healing of stomach. Genes and Cells 12(3): 246-247.
- Trubitsyna I, Onishchenko N, Lundup A, Knyazev O, Parfenov A (2016) Immunomodulatory effects of stem cells in the book: abstracts on cell technologies of the region. Research and Practice (Kterp) pp. 121.
- Knyazev V, Trubitsyna I, Khomeriki SG, Fadeeva NA, Kagramanova AV, et al. (2018) Dynamics of cytokine level in the intestinal mucosa after transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 7(1): A66-67.
- Knyazev V, Khomeriki SG, Trubitsyna IE, Konoplyannikov AG (2017) Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells on the model of ulcerative colitis. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 8(144): 62-66.
© 2019 Trubitsyna IE. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






