- Submissions

Full Text
Developments in Anaesthetics & Pain Management
Segmental Thoracic Spinal Anesthesia with Ultrasound Guided Erector Spinae Plane Block for Cholecystectomy in Patient with Severe Lung Disease
Prajapati SK1*, Chudasama P2, Patel M3 and Anandu M4
1Post Diploma DNB 2nd Year Resident Student, GMERS Medical College, India
2Associate Professor, GMERS Medical College, India
2Senior Resident, GMERS Medical College, India
2DNB 2nd Year Resident Student, GMERS Medical College, India
*Corresponding author:Shweta Kamleshbhai Prajapati, Post Diploma DNB 2nd Year Resident Student, GMERS Medical College, Himmatnagar, India
Submission:August 16, 2023;Published: August 31, 2023

ISSN: 2640-9399 Volume2 Issue4
Abstract
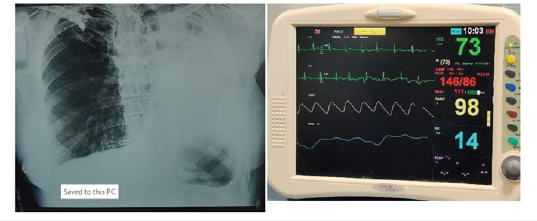
General anesthesia is associated with a risk for postoperative pulmonary complications. The risk is even higher in patients with chronic respiratory failure, and post-operative morbidity and mortality rates are also high. Proper peri-operative anesthetic management is important in such patients. Therefore, it is essential to optimize the patient’s physical status before anesthesia and perform optimal anesthesia technique based on the pre-anesthetic evaluation of the patient’s pulmonary function. Regional anesthesia is considered a favorable modality in selected patients and is becoming more popular day by day. In this regard, we are presenting a case report of 60-year-old female patient with post Koch’s sequelae-left sided destroyed lung, who needed surgery to remove a gall-bladder due to acute calculous cholecystitis. After discussion with the surgical faculties, and proper pre-op optimization of the patient, segmental thoracic spinal anesthesia along with ultrasound guided right side erector spinae plane block was planned, and the patient underwent an open cholecystectomy awake with spontaneous respiration. Although not routinely used, this procedure has shown advantage in maintaining hemodynamic stability for this patient, and we could avoid the morbidity associated with general anesthesia. Moreover, this study has shown that erector spinae plane block at T8 level has delayed the need of post-operative rescue analgesia (Figure 1).
Figure 1:Pre-operative chest x-ray of the patient-showing homogenous opacity with calcification in the left middle and upper zone, suggesting post infective fibro calcifiedchanges with shift of mediastinum towards left sidesuggesting fibrotic collapse. Fibro calcified lesions in right paper zone.
Keywords:Plane block; Lung disease; Anesthesia; Erector spinae; Cholecystectomy
© 2023 Prajapati SK. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






