- Submissions

Full Text
COJ Technical & Scientific Research
Revolutionizing Supermarket Checkout: A Comprehensive Review of RFID-Enabled Shopping Carts for Automatic Payments and Real-Time Inventory Tracking
Marios Vlachos*
Institute of Communication and Computer Systems, Greece
*Corresponding author:Marios Vlachos, Institute of Communication and Computer Systems, 15773 Athens, Greece
Submission: August 07, 2024:Published: September 25, 2024

Volume5 Issue1September 25, 2024
Abstract
This paper presents a comprehensive review of RFID-enabled shopping carts, an innovative solution designed for automatic payments and real-time inventory tracking in supermarkets. By integrating RFID technology into shopping carts, these systems automatically update the cart’s contents as products are inserted, streamlining checkout processes and enhancing operational efficiencies. This review examines the underlying technology, benefits, challenges, and potential applications of RFID-enabled shopping carts in the retail industry, offering insights into implementation considerations and future research directions.
Keywords:RFID; Shopping cart; Internet of Things (IoT); Inventory tracking; Supermarket; Retail
Introduction
The retail sector is undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements aimed at enhancing customer experiences and optimizing operational processes [1]. In the dynamic landscape of supermarkets, traditional checkout procedures often pose challenges such as long waiting times and manual errors, leading to inefficiencies and customer dissatisfaction. To address these challenges, supermarkets are increasingly exploring innovative solutions, with Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology emerging as a promising option [2,3]. RFID technology offers a viable solution for automating payment processes and enabling real-time inventory tracking in supermarkets. By embedding RFID readers directly into shopping carts [4], supermarkets can revolutionize the shopping experience by automating the updating of cart contents as products are added or removed. This transformative approach eliminates the need for manual scanning and ensures that the cart accurately reflects the items selected by the shopper, thereby streamlining checkout processes and enhancing operational efficiencies. This paper presents a comprehensive review of RFID-enabled shopping carts, focusing on their functionality, benefits, challenges, and potential applications in the retail industry. By examining the underlying technology, integration considerations, and implications for both customers and supermarkets, this review aims to provide valuable insights into the transformative potential of RFID technology in supermarket checkout processes. Additionally, key considerations for implementation and future research directions will be explored to offer a holistic understanding of the implications of adopting RFID-enabled shopping carts in supermarkets.
Method
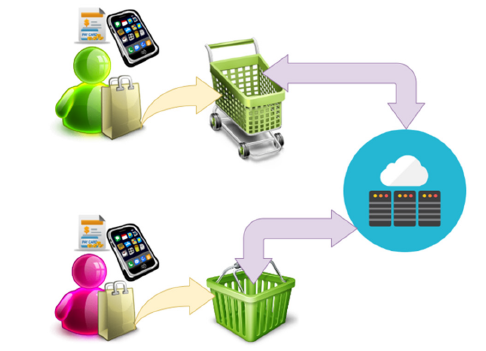
The project involved a comprehensive examination of existing literature, industry reports, and case studies to explore the applications of RFID-enabled shopping carts in the retail sector. The focus was on understanding the components, functionality, and benefits of RFID-enabled shopping cart systems, with particular emphasis on integrating IoT equipment such as RFID tags, gateways, mobile apps, and cloud platforms. The methodology encompassed a thorough analysis of RFID technology, including tag identification, data transmission, and integration with shopping carts. This involved exploring the characteristics and capabilities of RFID tags, which are embedded in product packaging and contain unique identifiers readable by RFID readers. Additionally, the role of RFID gateways as intermediate devices for collecting data from RFID readers and transmitting it to backend systems was investigated. The operational dynamics of RFID readers installed on shopping carts were examined, particularly their ability to detect RFID tags embedded in product packaging. These readers, acting as IoT devices, interact with RFID tags to automatically update the cart’s contents in real-time. The integration of mobile apps into the RFID-enabled shopping cart system allowed shoppers to interact with the system, view real-time cart contents, and initiate checkout processes from their smartphones. In addition to exploring technological aspects, the project assessed the implications of RFIDenabled shopping carts for both customers and supermarkets. This included analyzing potential benefits such as streamlined checkout processes, reduced waiting times, and enhanced convenience for shoppers facilitated by the integration of IoT equipment. Moreover, the project delved into challenges associated with implementing RFID-enabled shopping carts, including technology integration, infrastructure compatibility, and cost considerations. The synthesis of insights from literature and industry perspectives aimed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the transformative potential of RFID-enabled shopping carts in supermarkets, with a specific focus on integrating IoT equipment. Furthermore, the project identified key considerations for successful implementation, including selecting appropriate RFID tags, gateways, mobile apps, and cloud platforms. It also proposed avenues for future research to advance the adoption and optimization of RFID technology in the retail sector. A high-level structure of an automatic IoT system utilizing RFID technology for realizing a new method of payment in supermarkets advancing retailer experience shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1:High-level structure of an automatic IoT system utilizing RFID technology for realizing a new method of payment in supermarkets.
Results
The integration of RFID technology into shopping carts offers several advantages for both customers and supermarkets. By automatically updating the cart’s contents as products are inserted, RFID-enabled shopping carts streamline checkout processes, reduce waiting times, and enhance convenience for shoppers. Additionally, real-time inventory tracking enables supermarkets to monitor stock levels, identify out-of-stock items, and optimize replenishment strategies. Moreover, RFID technology provides insights into consumer shopping behaviors, allowing supermarkets to personalize marketing efforts and improve product placement. However, the implementation of RFID-enabled shopping carts presents challenges related to technology integration, infrastructure compatibility, and cost considerations. Supermarkets must invest in RFID readers, tags, and backend systems to support automatic updates and real-time inventory tracking. Furthermore, concerns about data security, privacy, and consumer acceptance must be addressed to ensure successful deployment of RFID-enabled shopping carts. Future research should focus on addressing these challenges and exploring opportunities to enhance the functionality and usability of RFID technology in retail environments.
Conclusions and Future Work
RFID-enabled shopping carts have the potential to revolutionize the retail experience by automating checkout processes and enabling real-time inventory tracking. By leveraging RFID technology, supermarkets can improve operational efficiency, enhance customer satisfaction, and gain valuable insights into consumer behavior. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, investment, and collaboration between stakeholders. Future research should focus on addressing technological challenges, refining system usability, and exploring novel applications of RFID technology in the retail industry.
References
- Brij BG, Akshat G, Prabin KP (2023) Analysis of retail sector research evolution and trends during COVID-19. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 194: 122671.
- Hingley M, Taylor S, Ellis C (2007) Radio frequency identification tagging: Supplier attitudes to implementation in the grocery retail sector. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management 35(10): 803-820.
- Jones P, Clarke HC, Hillier D, Comfort D (2005) The benefits, challenges and impacts of Radio Frequency Identification Technology (RFID) for retailers in the UK. Marketing Intelligence & Planning 23(4): 395-402.
- Shahroz M, Mushtaq FM, Ahmad M, Ullah S, Mehmood A, et al. (2020) IoT-based smart shopping cart using Radio Frequency Identification. IEEE 8: 68426-68438.
© 2024 Marios Vlachos. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






