- Submissions

Full Text
Advancements in Civil Engineering & Technology
Research on Urban Biodiversity Network Construction of Riverside Greenway: A Case of Administrative Office Area of Beijing Municipal Administrative Center
Yang Xin1*, Li Tongyu1, and Zhang Qi2
1School of Architecture and Art, North China University of Technology, China
2View Unlimited Landscape Architecture Studio of China Urban Construction Design &Research Institute Co., Ltd., China
*Corresponding author:Yang Xin, School of Architecture and Art, North China University of Technology, Beijing 100144, China
Submission: December 16, 2022;Published: December 22, 2022

ISSN: 2639-0574 Volume5 Issue3
Abstract
In this study, the biodiversity of riverside greenway in the administrative office area of Beijing Municipal Administrative Center was investigated by field observation and data statistical analysis. The information and status quo of typical plants and animals was surveyed from June 28 to July 23, 2021, to study and analyze the construction of urban greenway habitat, food chain, food web and ecological chain.
Keywords:Riverside greenway; Biodiversity; Food web; Ecological chain
Research Review
The 15th Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity on 18 July 2021 called for greater awareness of biodiversity conservation, especially in cities. Urban biodiversity survey focuses on the biological resources and related ecological chain structure of the site and explores whether the site has sufficient animal and plant resources and the ability of nature science popularization and education. Meantime, it propagates and enhances the awareness of nature conservation and promotes the construction of urban biodiversity [1-2].
In this study, the species along the riverside greenway in the administrative office area of Beijing Municipal Administrative Center was recorded through field investigation and natural observation; through data statistics, the investigation content was summarized and sorted out to construct food web and ecological chain; and the biodiversity of the site was comprehensively evaluated and analyzed. Three field surveys were conducted from June 28, 2021 to July 23, 2021 to record the biodiversity status of the site. According to the publicity of the project, there were about 90 species of native plants. The plants with good landscape effect during the survey period included more than 30 species of trees and medium-sized trees, more than 20 species of shrubs, 8 species of ground cover plants and 8 species of aquatic plants. Besides, there were 13 species of insects and 12 species of birds.
Analysis and Application of Biodiversity Network Construction
Habitat construction
Dragonflies are known as “water quality detectors”. As indicators, dragonflies can be used for biodiversity detection and environmental assessment, because dragonfly nymphs live in water, and areas with good water quality will have more dragonfly resources. D. phaon and P. zonata prefer habitats with fertile silt and high organic matter content. Therefore, a certain number of dragonflies such as D. phaon and P. zonata along the riverside greenway indicate good water quality and fertile silt.
Different water birds have different living habits, but basically all need a habitat rich in aquatic plants and good water quality. Different plants along the riverside greenway will provide space for a variety of birds. For example, T. ruficollis prefer the environment with P. australis and A. calamus; G. chloropus perches in the reeds or lotus pond; I. sinensis likes the environment with large area of P. australis and A. calamus. Organisms and habitats can confirm mutually, so in the landscape environment animals can judge whether the environment is good or not [3,4].
Food web construction
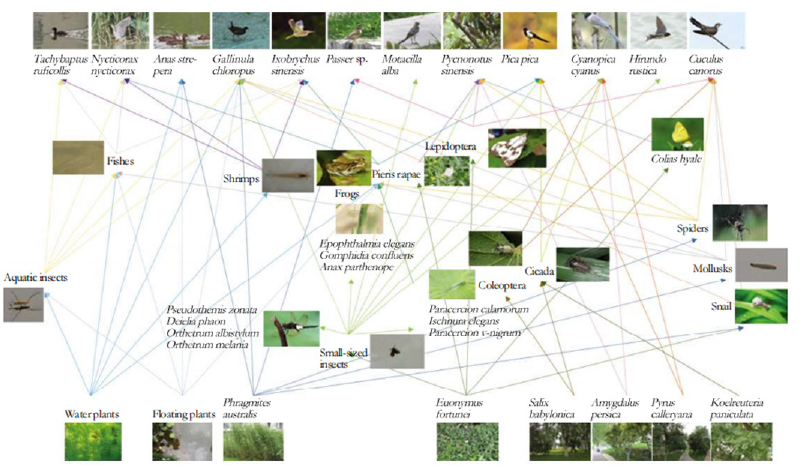
The food web was constructed for the plant and animal species investigated along the riverside greenway. The more complex the food web, the more stable the ecology. When selecting plant materials for urban greenway, plants that are more suitable for providing regional animal habitat, animal food source and insect hosts would be planted, so as to make the ecology of the whole area more stable. The macro-level food web construction can reflect the dependency of organisms in large categories, and the detailed food web structure based on each species can reflect the basis of building the biodiversity network chain between plant species and animal species. Based on the analysis of these two levels, the biological species investigated along the riverside greenway were carried out in detail, and the food web structure of the site was constructed. Through the food web relationship between macroscopic species, the plant and animal species along the riverside greenway were further searched, and then each species of plants and animals were identified to find out which species are scarce along the riverside greenway and which levels of species and number of organisms need to be increased, thereby optimizing the habitat and improving the biodiversity of the riverside greenway (Figure 1).
Figure 1:Food web structure of plants and animals
Ecological chain construction
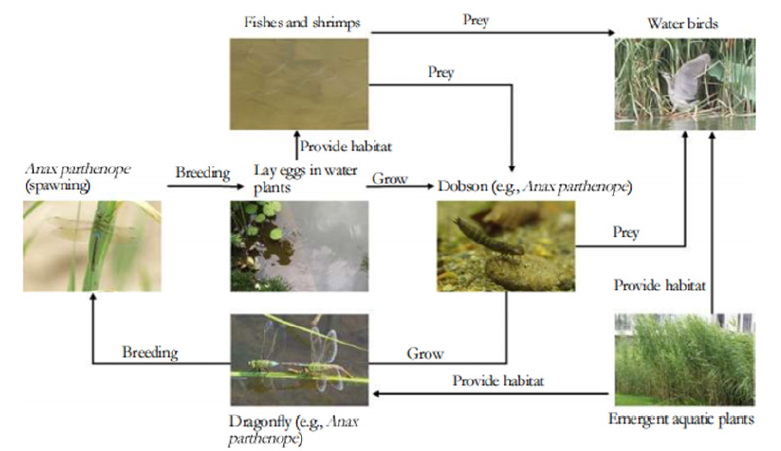
Plants, insects and birds are interconnected to form an ecological chain structure. Abundant natural space can provide better habitat for animals and plants, while abundant animal and plant resources can also reflect the good state of local ecology. The riverside greenway in the administrative office area of Beijing Municipal Administrative Center is rich in animal and plant resources. Relying on scientific and effective construction of landscape ecological space, they jointly form a stable ecological chain network and provide the city with a real oasis of biological coexistence, with excellent ecological value [5,6] (Figure 2).
Figure 2:Relatively stable ecological chain constituted by animals, plants and natural environment.
Conclusion
The survey report on urban biodiversity in riverside greenway in the administrative office area of Beijing Municipal Administrative Center completed the basic status survey of main plants and animals. There are all kinds of connections between plants and animals, e.g., providing habitat, food chain, food web, environmental monitoring, ecological chain and so on, constituting the basis of biodiversity along the riverside greenway.
Through the implementation of greenway project, the site pays attention to building habitat and improving ecological level, and the biodiversity and ecological environment have been well protected. With abundant species diversity, the site provides a good habitat for animals, and different animals can be found in all types of subdivisions. The site has a good level of species diversity, including most of the dragonflies and birds that can be seen in the urban area of Beijing in summer and are used as indicator animals reflecting good ecological level of the site. There are many types of habitats which can accommodate more types and quantities of animals. Birds and insects can perch and prey on the water surface, thickets and hard sites.
The more food chains there are, the more complex the food web will be, the more stable the ecology is, and the less impact it will have on the ecology of the site in case of special circumstances. Through the construction of food web structure, it can be seen that the site has corresponding plant and animal species at each level of the food web structure to play corresponding functions, and the ecosystem is relatively stable. The site has abundant plant growth and abundant species and quantities of animals, indicating that the site has good soil, water and other natural resources and high ecological level. When judging the ecological level of the site, the species, quantity and habits of the site organisms can be sorted out and summarized to build a food web structure. The more complex the structure, the more stable the ecology of the site.
References
- Zhou NX, Yu KJ, Huang ZF (2006) Perspectives on greenway development. Acta Ecologica Sinica 9:3108-3116.
- Zeng MZ, Di J (2021) Comprehensive landscape approaches to realize urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement. Chinese Landscape Architecture 37(7): 101-106.
- Huang Y (2015) The methodology of bird habitats’ making and planning at Beijing urban green spaces (Doctoral thesis). Retrieved from China National Knowledge Infrastructure.
- Xie SL, Lu F, Cao L, Zhou W, Ouyang Z (2016) The effect of landscape patterns on avian communities during summer months in Beijing urban parks. Landscape Architecture Frontiers 4(3): 10-21.
- Zhang XY (2020) Analysis on the importance of modern urban landscape design under the concept of ecological priority. Contemporary Horticulture (35): 115-116.
- Zhao Q (2012) The studies on the biodiversity conversation planning of urban green space under the background of urbanization (Master’s thesis). Retrieved from China National Knowledge Infrastructure.
© 2022 Yang Xin. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






