- Submissions

Full Text
Advances in Complementary & Alternative medicine
Medicinal Properties of Polymers
Smita Singh*, Praween Surin and S K Sengupta
Faculty of Science, Gossner College, India
*Corresponding author:Smita Singh, Faculty of Science, Gossner College, India
Submission: April 10, 2025;Published: April 24, 2025

ISSN: 2637-7802 Volume 8 Issue 4
Introduction
Antibacterial properties in polymers are developed by the incorporation of antimicrobial additives or through modification of the preformed polymer’s chemical structure. This property tends to fight microbial infections and are being studied for wider range of applications. These useful polymers are able to kill bacteria’s or inhibit their growth, ensuring their significance in areas like packaging, healthcare, food and textiles. Controlled drug release into the body is performed by the delivery systems that are Polymer-based. Targeting of drugs into the sites of tumours and imflammation are efficiently done by the polymers. Conjugation of polymers that are biocompatible with suitable drugs successfully forms the polymeric drugs. The conjugated macromolecules so synthesized usually positively accumulate in tumours. For these tumour cells, the cell permeability is higher than normal cell. Natural and synthetic polymers in medicine depends on the biocompatible nature, mechanical resistance, and sportive character. Several significant applications served by polymers are in producing haemodialysis and gynaecology products, catheters, tooth reconstruction, etc.
[2-(Methacryloyloxy) Ethyl] Trimethylammonium Chloride (MAETMAC), an amphiphilic, biocompatible, stable, physiologically inert, functional synthetic monomer, has remarkably important properties and finds several uses in various industries such as coatings, plastic paints, rubber and ink production, leather industries, cosmetics and soaps industries, plastics and paper industry, adhesives, etc. The monomer consists of Quarternary Ammonium Salt (QAS) having a reactive methacryloyl group on account of which this monomer gets easily subjected to radical polymerization [1] and has gained wider acceptance. The materials safety data sheet (MSDS) report confirms MAETMAC to be non-carcinogenic and having no acute and ecological toxicity. In the toxicity test conducted by the hatano research institute, food and drug safety centre, Japan, its Lethal Dose (LD50) value was found to be more than 2000mg/kg (oral toxicity test) which is comparable with that of NaCl (LD50 3000mg/kg) as given in MSDS. These data confirm the nontoxic nature of this monomer. MAETMAC containing materials have found to possess antibacterial and antifungal properties [2,3] and also providing long term efficacy. Also, MAETMAC containing products are indeed safer alternatives promoting environmentally sound materials. The grafting of positively charged polyMAETMAC side chains provides neutralization ability to the graft copolymer making it a promising candidate for diverse applications.
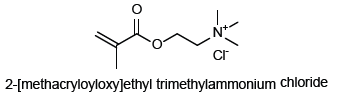
Considering the short alkyl chain length of MAETMAC, the antimicrobial property is derived from the charged nitrogen atom of quaternary ammonium group, that concentrates the positive charge. Considering the amphiphilic structure, the polymer chain includes both water-repelling (hydrophobic) region and water-attracting (hydrophilic), which causes interaction with bacterial membranes, causing disruption. QAS similar to MAETMAC has chances of causing lysis of bacterial membranes. The electrical balance of the cell membrane is likely to be disturbed by the positively charged sites of quaternary ammonium in contact with the negatively charged bacterial sites. The bacteria could then be damaged or killed through cytoplasmic leakage. Studies have shown that the MAETMAC monomer presents antimicrobial properties against 31 kinds of Candida albicans (C. albicans). The cotton grafting poly (MAETMAC) shows antimicrobial properties against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, and this effect increases with the amount of grafted poly (MAETMAC). No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). MAETMAC as per the acquired desired properties is used in wound dressings and drug delivery systems. Also it is utilized in tissue engineering and bone regeneration. Another medicinal properties of this monomer is yet to be explored and demands extensive research for the same.
References
- Stopiglia CDO, Collares FM, Ogliari FA, Piva E, Fortes CBB, et al. (2012) Antimicrobial activity of [2-(methacryloyloxy) ethyl] trimethylammonium chloride against Candida Rev Iberoam Micol 29(1): 20-23.
- Goel NK, Rao MS, Kumar V, Bhardwaj YK, Chaudhari CV, et al. (2009) Synthesis of antibacterial cotton fabric by radiation-induced grafting of [2-(Methacryloyloxy)Ethyl]Trimethylammonium Chloride (MAETC) onto cotton. Radiat Phys Chem 78(6): 399-406.
- Hassan MM (2015) Binding of a quaternary ammonium polymer-grafted-chitosan onto a chemically modified wool fabric surface: Assessment of mechanical, antibacterial and antifungal properties. RSC Adv 5: 35497-35505.
© 2025 Smita Singh*. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






