- Submissions

Full Text
Techniques in Neurosurgery & Neurology
Artificial Intelligence and Parkinson’s Disease
Ghassan George Haddad*
Serhal Hospital, Lebanon
*Corresponding author: Ghassan George Haddad, Consultant Neurologist and Clinical Neurophysiologist, Serhal Hospital, Lebanon
Submission: November 11, 2019;Published: November 22, 2019
ISSN 2637-7748
Volume3 Issue1
Introduction
Computer-aided diagnosis is emerging to improve treatment strategies for neurological diseases. Multiple Artificial Intelligence systems (AIS) have been developed to classify patients with diseases such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease and recently Parkinson’s disease [1].
The goal of AIS is to provide a more precise diagnosis and assessment of patients with PD. AIS extract the features unique to various neurological diseases from the data and surpass human ability to classify that data. This AIS system will improve the treatment of neurological diseases by reducing the doctor’s burden and increasing the accuracy of diagnosis using a large volume and high dimension of gait analysis data.
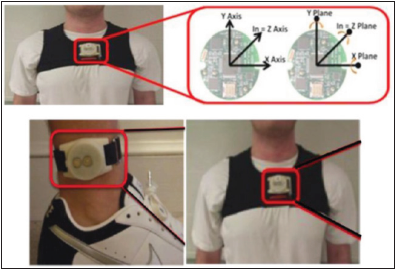
Scientists has shown that gait analysis [2] as shown in Figure 1 and simple wearable instrumentation as shown in Figure 2 in combination with supervised machine learning algorithms such as Artificial neural networks can provide significant diagnostic support and discriminate between PD patients and healthy subjects with accuracy above 90% and can assess response to current treatment and advice change in medications dosage and timing.
Figure 1:A typical gait cycle.
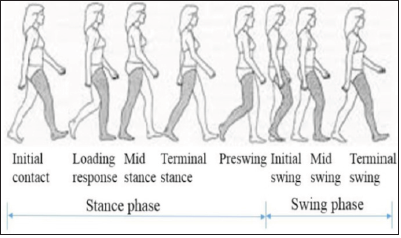
Figure 2:Picture of sensor located on one participant.
Artificial neural networks [3] (Figure 3) are computing systems
that are inspired by the normal brain network. Machine learning
applications in this field can be divided into two subgroups:
A. Diagnostic support and
B. Disease monitoring and assessment.
Artificial Neural Network proved to be the most successful
algorithm for early diagnostics, reporting accuracy above 95%
using features extracted from gait force patterns. This is especially
important, since in early disease stages motor symptoms are not
clearly visible and with delayed diagnostics the progression of
the disease is unbridled High-accuracy results are also obtained
for detection of motor symptoms, disease stage and severity.
Prediction of symptoms severity was successfully applied using
various algorithms and sensors.
Figure 3: The ANN “learn” to perform tasks and solve problems in the same way that a human brain would.
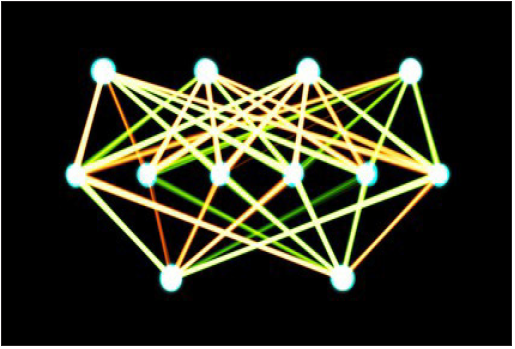
Figure 4: The ultimate goal is to develop a closed loop detection at two levels.
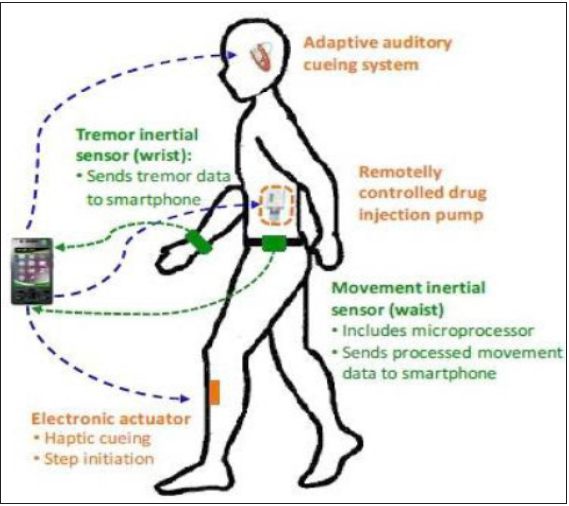
At the first level, (Figure 4) the wearable monitoring system
consisting of a waist belt, a wrist band and patch electrodes
on the leg all connected by Wifi to an iphone application .The
Neurologist will be able to process in real time the motor status of
the PD patients, and evaluate the ON/OFF/Dyskinesia status during
ambulatory conditions and will also perform a gait guidance system
able to direct the patient in real time during their daily activities.
At a second level, the AIS provided by the first level, supported
with a disease management protocol will allow the monitoring neurologist in charge to access accurate and reliable information
to decide about the treatment that best suits the patient at different
time during the day and improve the management of their disease,
in particular to adjust the so called therapeutic window thru a
remotely controlled subcutaneous injection pump.
References
- Siuly S, Zhang Y (2016) Medical big data: Neurological diseases diagnosis through medical data analysis. Data Sci Eng 1(2): 54-64.
- Gil D, Johnsson M (2009) Diagnosing parkinson by using artificial neural networks and support vector machines. Glob J Comput Sci Technol 9(4): 63-71.
- Dreyfus SE (1990) Artificial neural networks, back propagation, and the Kelley-Bryson gradient procedure. Journal of Guidance Control and Dynamics. 13(5): 926-928.
© 2019 Ghassan George Haddad. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






