- Submissions

Full Text
Research in Medical & Engineering Sciences
Protection of Very Small Particles Such as Viruses and Bacteria by Washable and Wearable Z-Nanofiber Sheet Mask
Akihiko Tanioka*, Mitsuhiro Takahashi and Tsuneo Hanada
Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan
*Corresponding author: Akihiko Tanioka, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan
Submission: February 24, 2021Published: March 08, 2021

ISSN: 2576-8816Volume9 Issue2
Opinion
sol diameter containing it by cough about 300nm. Usually, masks are indispensable for preventing both virus spread and inhalation. There are various types of masks from woven to nonwoven fabrics on the market, and the protective effect to virus varies from a few percent to over 99%. In general, the performance of a mask can be represented by the Particle Filtration Efficiency (PFE) and Pressure Drop (PD) similar to an air filter. PFE corresponds to a measure of virus protection and PD to ease of breathing. Therefore, better performing masks have higher PFE and lower PD. PFE and PD are in a strong relationship with each other, that is, whenever we try to increase PFE, PD will increase. Generally, electrets are given to increase PFE in keeping PD low such as HEPA and ULPA. The electret, however, loses the effectiveness by water vapor in air, etc. Z-nanofiber sheet mask, which is produced by Z-melt spinning method (1) of polypropylene (PP), can solve those problems, because nanofiber can adsorb virus and bacteria by the van der Waals force without giving electrical properties, that is so-called hydrophobic bond, which induces the washable property of the mask. Table1 shows the PFE and the PD of seven Nanofiber sheet samples of PP. PFE was measured by using the NaCl particles whose diameters are from 25nm to 131nm, where measurement conditions are 100cm2 of measurement area, 31.8L/min of ventilation volume, and 5.3cm/sec of flow velocity, respectively. PFE and PD of each sample are more than 99% and less than 70Pa, respectively, which means that we can prepare the non-suffocating mask with high virus capture efficiency [1].
Table 1:
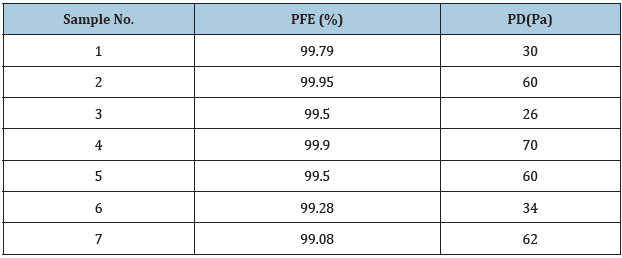
Table 2:
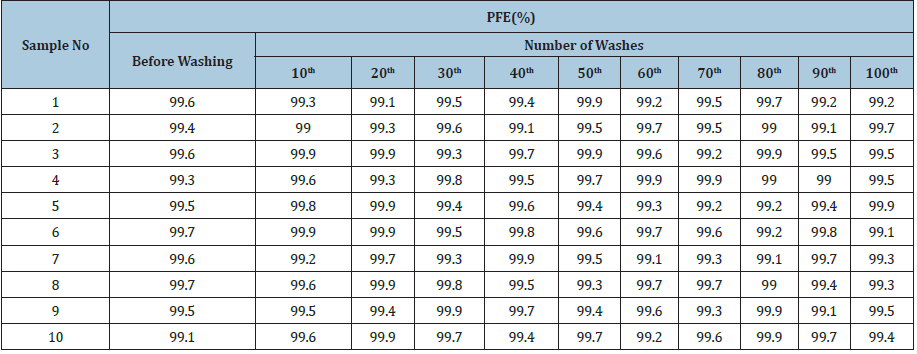
Table 2 shows the PFE of ten different Z-nanofiber sheets of PP before and after washing. For after washing the data of every 10 times are listed and it is repeated 100 times by soak washing for 10min in adding the commercial laundry detergent of 0.35g/L. After drying at 37 °C the PFE was measured at the same condition in Table 1 and the most important thing is PFE keep almost the same value after 100 times washing.
Figure 1:
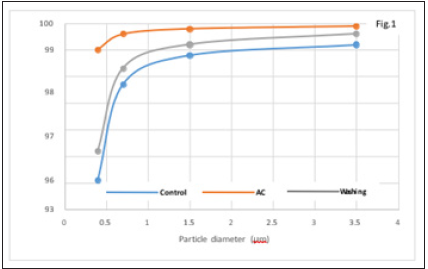
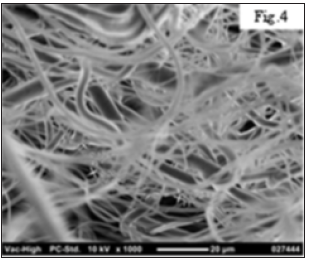
Figure 2 shows the mask made from the Z-nanofiber sheet of PP whose density is about 60g/m2 and thickness is about 5mm as shown in Figure3, and Figure 4 is the SEM image of Nanofiber sheet where the fiber diameter is varied from ca. 100nm to 5 μm. The variation of fiber thickness plays the important role of increasing PFE and keeping PD low while maintaining mechanical strength. Finally, since the Z-nanofiber sheet mask is composed of PP nanofibers, it can be concluded that it can capture more than 99 % of COVID-19 virus, be easy to breathe, and be washed and used repeatedly.
Figure 2:

Figure 3:
Figure 4:
References
© 2021 Akihiko Tanioka. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






