- Submissions

Full Text
Research in Medical & Engineering Sciences
Antifungal Drugs and their Resistance Mechanism
Alemayehu Reta*
*Corresponding author: Alemayehu Reta, Department of Medical Laboratory Science, College of Health Sciences, Debre Markos University, PO Box: 269, Debre Markos, Ethiopia
Submission: July 15, 2017; Published: August 18, 2017

ISSN : 2576-8816Volume1 Issue1
Introduction
Antifungal drugs are distinct in terms of effectiveness, spectrum of activity, therapeutic index, resistance mechanism, and mode of use. An important factor in the practicality of a compound is the mechanism by which it attacks the structure and function of the fungal cell. The target organelles have been established for most antifungal drugs [1].
Conventional Antifungal Drugs with Mechanism of Action and Drug Resistance
Depending on the drug and the Candida species, the mechanism of antifungal resistance can be inherent (without previous exposure) and acquired (with previous exposure) [2]. There are around 4 groups of antifungal drugs.
A. Polyenes: e.g. Amphotericin B- mechanism of action is through disruption of fungal cell membrane and resistance mechanism is by defective ergosterol biosynthesis, due to mutation in the ERG3 gene.
B. Azoles: Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Voriconazole, Posoconazole, Ravuconazole- inhibit ergosterol biosynthesis and resist this action by modifications in target enzymes due to point mutations in ERG11 and active efflux of the drug out of the cell via the activation of efflux transport proteins [1,3].
C. Flucytosine: Inhibit DNA and protein synthesis, fungi resist by alterations in the target enzymes (cytosine permease and cytosine deaminase), or increased production of pyrimidines.
D. Echinocandins: e.g. Caspofungin- inhibit b1, 3-D-glucan synthesis and drug resistance mechanism is by generating insufficient target enzyme b-1, 3-D-glucan synthase [2,4].
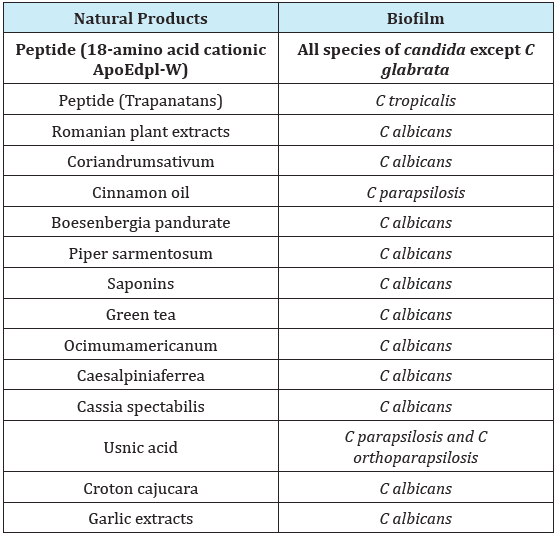
Emerging resistance to antifungal agents & toxicity of existing antifungal compounds leads the current science to search for highly effective with low toxicity natural products. Plants are good options for obtaining a wide variety of drugs [5,6] (Table 1). Another promising antifungal strategies are Silver nano particles (interfere with microbial DNA replication within bacteria and fungi), Anti-Candida antibodies (can reduce the binding of Candida to various surfaces), Photodynamic therapy (inactivation of the fungus) and Gold nano particle conjugate (mediated photodynamic therapy may be used against nosocomially acquired refractory C albicansbiofilms) [7-10].
Table 1: Antifungal activity of natural products against a variety of biofilms.
References
- Bogers M (1980) Mechanism of action of antifungal drugs, with special reference to the imidazole derivatives. Rev infect dis 2 (4): 520-534.
- So´nia S, Melyssa N, Mariana H, Ros´ario O, DW Williams, et al. (2012) Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis and Candida tropicalis: biology, epidemiology, pathogenicity and antifungal resistance. FEMS Micro boil Rev 36 (2): 288-305.
- Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ, Procop GW, Rinaldi MG (2007) Multicenter comparison of the VITEK 2 antifungal susceptibility test with the CLSI broth micro dilution reference method for testing Amphotericin B, flucytosine, and voriconazole against Candida spp. J clin microbiol 45(11): 3522-3528.
- Sanglard D, Odds FC (2002) Resistance ofCandida species to antifungal agents: molecular mechanisms and clinical consequences. Lancet infect dis 2(2): 73-85.
- De Oliveira LF, Jorge AO, Dos Santos SS (2006) In vitro minocycline activity on super infecting microorganisms isolated from chronic periodontitis patients. Braz oral res 20(3): 202-206.
- Sardi JC, Almeida AM, Mendes Giannini MJ (2011) New antimicrobial therapies used against fungi present in sub gingival sites -A brief review. Arch oral biol 56(10): 951-959.
- Percival SL, Bowler PG, Russell D (2005) Bacterial resistance to silver in wound care. J hosp infect 60(1): 1-7.
- Bujda´ kova´ H, Paulovicova´ E, Borecka´ -Melkusova´ S, Gasperı ́k J, Kucharı ́kova S, et al. (2008) Antibody response to the 45 kDa Candida albicans antigen in an animal model and potential role of the antigen in adherence. J med microbiol 57: 1466-1472.
- Coleman JJ, Okoli I, Tegos GP, Holson EB, Wagner FF, et al. (2010) Characterization of plant derived saponin natural products against Candida albicans. ACS Chem Biol 5(3): 321-332.
- Khan S, Alam F, Azam A, Khan AU (2012) Gold nano particles enhance methylene blue-induced photodynamic therapy: a novel therapeutic approach to inhibit Candida albicans biofilm. Int J Nano medicine 7: 3245-3257.
© 2017 Alemayehu Reta. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






