- Submissions

Full Text
Research & Investigations in Sports Medicine
The Effect of Psychological Well-Being on the Self-efficacy of Sports Science Students
Seyed Hossein Alavi1* and Abolfazl Arij2
1Associate Professor of Department of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, National University of Skill (NUS), Tehran, Iran
2Ph.D. Student in Sport Management, University of Guilan, Rasht, Iran
*Corresponding author:Seyed Hossein Alavi, Associate Professor of Department of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, National University of Skill (NUS), Tehran, Iran
Submission: October 10, 2024;Published: January 08, 2025

ISSN: 2577-1914 Volume11 Issue1
Abstract
People will proceed with a decision that they believe in their ability to do and this decision is parallel to their self-efficacy level, which can be affected by several factors. In this way, the aim of the present study is to investigate the effect of psychological well-being on the self-efficacy of sports science students. This applied research has been done in a survey manner. The statistical population of this research was consisting of sports science students in Master and Bachelor degrees; According to the sampling approaches in Smart PLS software for partial squares method, 136 samples from the statistical population were examined, the results showed that the coefficient of the effect of psychological well-being on students’ self-efficacy is equal to 0.796 and has a t-value equal to 30.267. As a result, it can be concluded that by creating psychological well-being, students’ beliefs are improved regarding their abilities and they can appear more successful in learning sports skills.
Keywords: Psychological well-being; Self-efficacy; Sports science students
Introduction
Self-efficacy refers to a person’s belief in his abilities to organize and perform a set of activities necessary to achieve a certain goal. These abilities include not only physical performance, but also all processes, emotional states and activities required for environmental changes [1]. Therefore, in sports psychology the term result is widely used to refer to the outcomes of competitive events such as winning and losing or defeating a particular competitor. For example, in the sports psychology literature, goals are standards based on outcomes such as winning and outcome orientation is a personality trait that people have to define success or failure based on winning and losing. Still, in self-efficacy theory, achievement is not the result of expectation, but it is the cause of performance [2]. Expectations are the result of perceived consequences (e.g., social status, pride and psychological well-being) that arise through the successful performance. Psychological well-being expresses how people feel about themselves and includes people’s emotional responses and life satisfaction [3]. Mental well-being is an important structure that leads to depression and social isolation at a low level and causes a lack of satisfaction and self-esteem, and leads to a decrease in mental and physical health [4]. According to the surveys conducted by various researches, sports science students have an unfavourable level of self-efficacy to advance educational activities in the university, and to advance educational affairs, they always suffer from functional weaknesses, doubt in learning skills and lack of belief in their athletic abilities. In this regard, one of the factors that lead to the development of self-efficacy and has been able to have a significant impact on the development of self-efficacy in past researches is psychological well-being. In fact, mental peace and positivity, the satisfaction of training and helping athletes’ talents identification, should convey the belief that the ability to use and develop skills is possible. In this regard, the main question of research is that whether psychological well-being has a significant effect on the self-efficacy of sports science students?
Materials and Methods
This applied research has been done in a survey manner. The statistical population of this research was consisting of sports science students in Master and bachelor degrees in Iran. Regarding the sample size, it should be stated that according to the number of variables observed and hidden in the model, the expected effect size and the desired probability and statistical power levels are calculated for the partial least squares method [5]. Considering the effect size of 0.25, the power of the test 0.8, hidden variable 2 and 35 obvious variables and the significance level 0.05 was estimated equal to 136 people. Data collection in this research was done using the self-efficacy questionnaire of Sherer et al. [6] and the psychological well-being questionnaire of Raf and Signer [7]. The self-efficacy questionnaire consists of 17 questions and the psychological well-being questionnaire consists of 6 factors (autonomy, environmental mastery, personal growth, positive relations with others, purpose in life, and self-acceptance) and 18 questions. The validity of this questionnaire was confirmed by experts and its reliability was obtained using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient. SPSS26 and SmartPLS3 software were used for data analysis.
Result
According to the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, the significance level of most of the components is less than α=0.05, so the data distribution is non-normal. As a result, it is better to use the structural equation model method using PLS software to check the relationship of statistical hypotheses related to them, because one of the capabilities of this software is to check non-normal data. The values of the tests reported in Table 1, the value of the Rho coefficient is above 0.7, the average extracted variance is above 0.5, Cronbach’s alpha is above 0.7 and the combined reliability is above 0.8, which shows the reliability and validity of the presented structure. In the following, the fitting of the communication model of the research is discussed (Figure 1).
Table 1:Construct reliability and validity.

Figure 1:Path coefficient analysis.
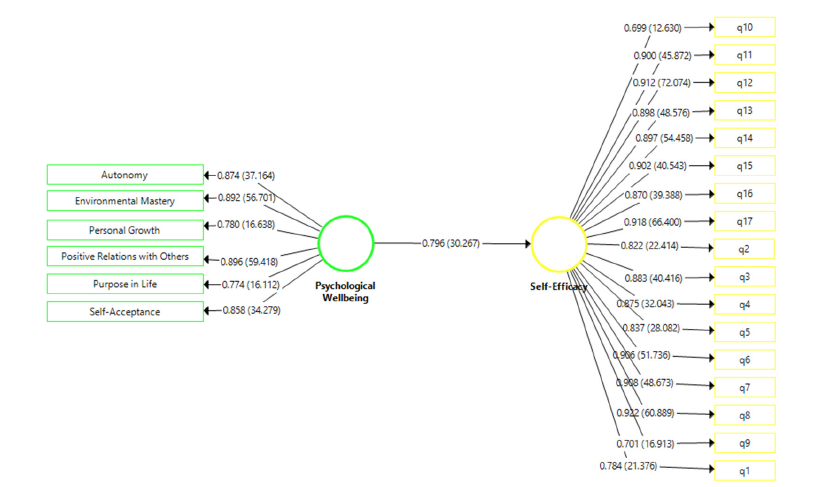
According to the above graph, it was found that the loading factors (standardized regression coefficients) and the t statistic have significance values at the levels of P<0.05. These indicators show that the measured observational variables were a good reflection of the hidden variables (psychological well-being and self-efficacy).
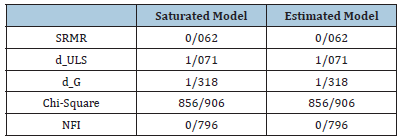
Based on the results of Table 2, it is clear that the coefficient of the effect of psychological well-being on students’ self-efficacy is equal to 0.796 and has a t value equal to 267.30. Therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected with 95% confidence. That means, there is a significant relationship between psychological well-being and students’ self-efficacy. According to the results of Table 3, to check partial least squares fit indices in Smart PLS 3 software, from Standard Root Mean Square Residual Index (SRMR), true model fit criterion d_ULS and d_G, Normalized Fit Index (NFI) and chi square (Chi²) was used and all tests were estimated to be appropriate.
Table 2:Total effect.
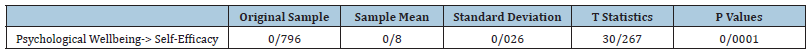
Table 3:Model fit.
Discussion
In fact, the psychological well-being of a student is affected by practicing in sports fields and learning sports theoretical courses, teachers help the athletes’ abilities flourish with the help of basic education and providing a suitable educational environment and this peace of mind and satisfaction leads to the growth and development of student athletes’ self-efficacy. According to Bandura’s theory, people will proceed with a decision that they believe in their ability to do and this decision is parallel to their level of self-efficacy. For this reason, a capable person may not use his ability optimally due to lack of confidence in his ability and competence. Therefore, if the athletes believe in their ability to achieve their goals in sports, they will try harder to achieve them and move forward with more strength and effort in the direction of achieving goals and in the end, the possibility of success is greater. According to this finding, if a person with a favourable level of psychological well-being can lead to an improvement in the level of self-efficacy and participates more decisively in the educational programs of the university, he would have more dynamism and shows more effort in learning.
Conclusion
It is concluded that psychological well-being has a significant effect on the self-efficacy of sports science students, psychological well-being leads to an improvement in the level of self-efficacy of students, Students with a strong sense of self-efficacy do not experience feelings of helplessness when progressing through their curriculum and practice programs. Their elevated psychological well-being fosters confidence in their capabilities, leading to improved performance.
References
- Law FM, Guo GJ (2016) Correlation of hope and self-efficacy with job satisfaction, job stress and organizational commitment for correctional officers in the Taiwan prison system. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology 60(11): 1257-1277.
- Mosca LL, Continisio GI, De Lucia N, Gigante E, Guerriera C, et al. (2023) A scoping review on innovative methods for personality observation. Frontiers in Psychology 14: 1112287.
- Cegarra B, Cattaneo G, Ribes A, Solana-Sánchez J, Saurí J (2023) Independent living, emotional well-being and quality of life in people with disabilities: The mediator role of self-determination and satisfaction with participation. Frontiers in psychology 14: 1279014.
- Lyyra N, Thorsteinsson EB, Eriksson C, Madsen KR, Tolvanen A, et al. (2021) The association between loneliness, mental well-being and self-esteem among adolescents in four Nordic countries. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18(14): 7405.
- Soper DS (2022) A-priori sample size calculator for structural equation models. Free Statistics Calculators.
- Sherer M, Maddux JE, Mercandante B, Prentice-Dunn S, Jacobs B, et al. (1982) The self-efficacy scale: Construction and validation. Psychological Reports 51(2): 663-671.
- Ryff CD, Singer BH (2006) Best news yet on the six-factor model of well-being. Social Science Research 35(4): 1103-1119.
© 2025 Seyed Hossein Alavi. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






