- Submissions

Full Text
Psychology and Psychotherapy: Research Studys
A Cognitivist Framework on Behaviorism Interventions
Yang I Pachankis*
Universal Life Church, USA
*Corresponding author: Yang I Pachankis, Universal Life Church, Headquarters 601 3rd St, Modesto, CA 95351, USA
Submission: May 26, 2023; Published: July 12, 2023

ISSN 2639-0612Volume7 Issue2
Abstract
The meta-scientific analysis in psychiatry seeks to reconcile the theoretical differences between behaviorism and cognitive psychology from a neuronal perspective. It develops from Butler’s biopolitics concept and the environmental determinants of public health and biology in general. In the broader perspective, behaviorism is taken as the reflexive contents from consciousness in cognitive psychology, and the multivariable in psychodynamics is outlined in the framework. The methods introduce external nucleons as the psychiatric element in bridging the theoretical gaps between behaviorism and cognitive psychology.
Keywords:Cognitive behavioral therapy; Environmental agents; Environmental physiology; Extremal nucleons; Gestalt psychology; Neurodiversity; Psychodynamics
Abbreviations:ASD: Autism Spectrum Disorder; ANS: Autonomous Nervous System; CNS: Central Nervous System; CBT: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Introduction
The research takes behaviorism and cognitive psychology in a neurological framework of individuality, biopolitical framework of sociostructural determinants, and environmentalist framework in the content matters of a psychologist’s ego. The multivariable framework takes neurodiversity as the basis for the behaviorists’ limitations in theoretical premise, and for cognitive psychologists’ limitations in the metaphysical interpretations in biophysical sources of diversity. As a balanced way to proceed to the methodological developments, behaviorists’ theoretical premise can be understood in terms of reflexive contents of neural physiology, i.e. Autonomous Nervous System (ANS), and the cognitivists’ theoretical premise in terms of the conscious exercise of one’s autonomy, i.e., Central Nervous System (CNS). The psychological science’s focus is predominantly on intersubjectivity within given sociostructural determinants. The focus largely determined the psychologists’ professional ethics, and the concentration of individualistic determinants of psychological and mental health. The disciplinary limitations can be meta-scientifically interpreted in terms of social Darwinist perspective in anthropology, which Butler, from an inter-species competition perspective, defined as violence and proposed the concept of biopolitics [1]. In the methodological development, the concept of biopolitics is further categorized into the domains in: 1) cross-species strategies from the original Darwinist interpretations of evolution; 2) inter-species strategies broadly defined as culture in the civilizational development of the human species; and 3) the existential strategies of life forms as to the natural environment. with categorization, current psychological science mainly concentrates on the second category.
The natural environment’s influences on human behaviors either on an individual or group basis, or either on the human behaviors or behaviors of other species, can be as subtle as the weather, and as tremendous as extinction events. The behavioral consequences from the environmentalist framework mainly act on the third category of biopolitics and affect the other two thereafter. Global Sustainment Development and Carbon Neutrality can be seen as the human behaviorist consequences from the environmentalist framework.
Thereon, the intersubjective scope of psychological science’s sociostructural-determinant content matters can be expanded to the causal reflex stimulated by the environmentalist framework. Even though methodological development mainly purposes to bridge behaviorism and cognitive psychology, it substantially falls into psychiatry. Neurology mainly specializes in the biochemical and biophysical matters of the neural sciences. However, with more than millions of nerves in the human nervous systems, psychiatry provides a better explanatory perspective to psychodynamics than the neurologically robotic perspectives. If we are to acknowledge the conscious autonomies of neurologically diverse individuals, and the cognitive contents’ roles in the evolution of human species, not only the tasks are insurmountable by the neurological science, but also it is nearly impossible to predict the behavioral or cognitive change of any individual from the multivariable framework. However, the interplay still exists between psychiatry and neurological evidences.
The key problem for the research originated from the definition in threats in the context of ill-treatment and torture by Sales P [2], as a form of communication between perpetrator and victims that entails a message of coercion or punishment. With the digital extensions of the torture environment, the fundamental texts of the International Criminal Court (ICC) are seen to be the existing legal texts that outlined the framework against social Darwinist realities [3,4]. However, the cognitive element does not serve well for the torture victims’ rehabilitation in the sociostructural environment of torture, where the jurisdiction of the ICC is limited and the only global entity having theoretical universal jurisdiction, the International Court of Justice (ICJ), originates from the de facto territorial controls of the entities that provide immunity indefinitely for the perpetrators. There is no remedy for injustice except for the justification of social Darwinism. Inter-species competition of humanity is an anthropological fact, regardless of value orientations. As Butler [1] suggests, an ethics of nonviolence cannot be predicated on individualism, and it must take the lead in waging a critique of individualism as the basis of ethics and politics alike. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), or more accurately the intervention thereof, serves the exact role in the ethical [re] orientations. Therefore, the broader environmentalist framework serves as an alternative to the nature of violence as to the nature of life.
Methods
Extremal nucleons in behaviorism
The concept of extremal nucleons is broadly defined. The particles of light that enable vision, molecular microbes, viral RNAs, cosmic rays, nuclear proliferation, etc. All share the same basic properties not dissimilar to the basic components organized into human physiology. Selective attention in persons with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), with extremal nucleon explanatory paradigm, causally infers to hypersensitivity [5]. Genetic mutations under the scope of cosmological nuclear environment also offer an alternative explanatory behavioral paradigm to lives on earth, namely the epigenetics of cognitive contents [6]. The visualization on the kinematics from the cosmic environment is seen in Figure 1 [7]. Apart from the lethal nucleon concentrations, behaviorist interventions change the epigenetic responses on an interpersonal basis. Pure medical interventions and objectives in neural science treats the standard in population mean, and largely marginalize the inter-species mutations. This cognitive element from biopolitics is also the basis for the wording “Extremal” in the concept. Genetic divergence within the human species necessarily predicts Neurodivergence, however, the cognitive matters and social cognitive consequences have been substantially ignored by behaviorist paradigms. If life forms are seen in the recipient end of extremal nucleons, hypersensitivity in ASD can be advantaged in the reflexive cognitions of environmental agents compared to neurotypical persons, which is explanatory of high functioning ASD.
Figure 1: The cosmic environment’s thermonuclear kinematics exemplified by the black hole phenomenon on NGC 3034.
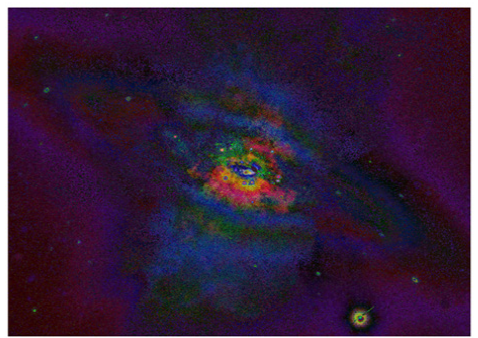
The introduction of extremal nucleons to behaviorism furthers the punishment-award scopes from sociostructuralism to neurological adaptation. For example, market incrementalism has been considered a strategy for social justice in multilateral debates, but the neurological implications of wiring the punishmentaward responses socially to the ANS only further intensify interspecies competition [8]. Threats can be easily made from the sociostructural level such as power political and realpolitik uses of economic sanctions, wherefore, shaping mass psychological repetitive behaviors. Such behavioral threats from the power advantage points further marginalize victims from therapeutic providers sociostructurally, especially in dictatorial regimes, and risk of societal collapse not only from the structural inter-species competition itself, but also from the polarity created against individual conscious control of ANS by CNS for disseminated strategic input..
Cognitive entropies from extremal nucleons
After fetal development, human brains can be seen as entropic systems. It is exactly the medium conductive process from white matter to grey matter that constitute as biophysical and biochemical entropy and shape the mental faculties. Entropy further expands and diversifies by psychiatric and psychological developments, along with social and professional activities. The environmentalist perspective to such an entropic scope of neurodiversity is characterized by Vazza & Feletti [9]. However, the cognitive perspective’s influence to environmentally imposed entropic dynamics has no other comparable explorative or experimental research or paradigm rather than psychodynamics. Humanism and human-centrism have substantially limited the paradigmatic perspectives to neurodiversity [10,11]. There is a risk in “Curing” ASD that can ASD be similar to sexuality? Psychodynamics, however, are individually focused in depth, and do not categorize according to the systematic statistics of similarities or differences. By normal distribution, a 1% long tail for ASD can only be analyzed properly in longitudinal analysis within the anthropological development in human race in correlation to global changes.
Cognitive entropy is also behavioral on a civilizational level. Human security is a precursor to cognitive entropy. Kaldor M [12] correlated from an inter-species competition perspective on civilizational levels in cognitive paradigm shifts [12,13]. Just as nuclear sciences developed from the 1900s, its profound influences on the environmental determinants such as astronomy and cosmology, and to the medical sciences, in turn, also created another destructive tendency that can be considered “Entropic” to the positive changes rendered possible by scientific developments. In further quantifying such a human security paradigm in cognition with both the manmade and natural nucleons entropic to the brain development and brain evolution, a hypothesis-testing trial has been preregistered on bioinformatic entropy [14].
Behavioral changes from cognition
Cognition-driven behavioral changes have been the key characteristic in human civilization, linking biopolitics and environmentalism. Cognition-driven civilization-environment interactions differ from the punishment-award incentives and animal intelligence stimulated by survival instincts. The Gateway Process document assessed the biofeedback associated with advanced meditation [15]. Not only the document has implied the anti-entropic capabilities of cognition-driven behavioral changes, but also has outlined the methodological criteria substantially descriptive of ASD traits between Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). This psychological characteristics also correspond with clinical evidence on vagus nerve’s correlations to the blood flow in both right and left thalamus [16].
If neurological knowledge were derived from neurotypical persons, without further assumptions in behavioral diversity’s justification, just as sexuality, is it possible that ASD potentially leads to a new paradigm for immunology concerning the environmental, anthropological, and evolutionary determinants? This hypothesis takes the “Born Equal” clause in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights literally. It can be progressive if only considered in terms of the medical sciences, but multidisciplinary approaches do not totally falsify, although falsifiable with a sociological paradigm with structural economics, the hypothesis. What if the immunological presumptions on neurodiverse persons are biased, whereby the limitations of cytokine production exactly have prevented ASD persons from severe COVID-19 lung fibrosis [17].
Result
The evidence assessment under the conceptual framework corroborates with each other cohesively. With the research difficulties for physical evidences, further experimental design is needed. Due to the potential conflict of interests, the element of affect in cognitive-affective behavioral therapy has not been included [18].
Discussion
The research implies that epistemology is at the core of CBT. CBT intervenes on the psychodynamic behaviors of the visitors, and the visitors’ epistemic orientations are critical to therapeutic outcomes. The autonomy of the visitors from behavioral interventions cannot be protected without full respect to the visitors’ mindsets. The cognitive elements in CBT need to be discretely examined, while not intervened unless foreseeable harms can result from them. However, the definitions of foreseeable harms are substantially sociological. It is with this regard, the article only outlines the cognitivist framework with relation to psychiatry and neurology. This has also limited the application values of the research.
Conclusion
The theoretical gaps between behaviorism and cognitive psychology are created by therapeutic relationships. The cognitivist framework has proposed an interlinkage from psychiatry with extremal nucleons. The framework has mapped an analytic strategy in CBT practices, and its supplementary role for the medical perspectives in neurology. The framework has taken the sociological and anthropological factors into consideration. Nonviolence and biopolitics are addressed in the cognitivist framework of analysis.
Acknowledgment
Yang I. Pachankis thanks for John Pachankis’ semi-intervention that shaped the basis of his mental resilience. It is by the generous grant in Open Access publication from Crimson Publishers the research is made available to the public.
Conflict of Interest
Yang I. Pachankis has self-diagnosed to be autistic. The methods section in the article was accepted and intended to be presented in the 31st European Congress of Psychiatry, but Yang I. Pachankis did not make it to the meeting due to financial constraints. The contents of the research are summarized from Yang I. Pachankis’ self-healing experience from complex PTSD. Yang I. Pachankis’ personal relationship may have contributed to the improvement of expressive and scientific writing skills.
Data Availability
The preregistration for future empirical studies is accessible on Open Science Framework with the Doi: 10.17605/OSF.IO/KP53U. The pilot research’s data, from which the figure originated, can be accessed on Open Science Framework with the Doi: 10.17605/OSF. IO/WT5Z2.
References
- Butler J (2020) The force of nonviolence. Verso, New York, USA.
- Sales PP (2021) Defining and documenting threats in the context of ill-treatment and torture. Torture Journal 31(1): 3-18.
- Sales PP (2022) The future is here: Mind control and torture in the digital era. Torture Journal 32(1-2): 280-290.
- Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (1998) International Criminal Court, Netherlands.
- Marco EJ, Hinkley LB, Hill SS, Nagarajan SS (2011) Sensory processing in autism: A review of neurophysiologic findings. Pediatr Res 69(5 Pt 2): 48R-54R.
- Pachankis YI (2023) Natural mutation and human catalysis-philosophy after the big bang theory. Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research 48(3): 39784-39786.
- Pachankis YI (2022b) A multiwavelength data analysis with multimission space telescopes. International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology 7(1): 701-708.
- Hettne B (1997) The double movement: Global market versus regionalism. In: Cox RW (Ed.), The New Realism, pp. 223-242.
- Vazza F, Feletti A (2020) The quantitative comparison between the neuronal network and the cosmic web. Frontiers in Physics 8: 525731.
- Haro PAD, Mombelli D (2020) Humanism and humanitarianism: The language of the deaf. Introduction to the Spanish Universalist School, Spain, pp. 83-92.
- Garrett C (2022) There is beauty in diversity in all areas of life including neurological diversity (Bella): A mixed method study into how new thoughts on neurodiversity are influencing psychotherapists’ practice. Zeitschrift für Psychodrama und Soziometrie 21(S1): 147-161.
- Kaldor M (2011) War and economic crisis. In: Calhoun C (Ed.), The deepening crisis, New York University Press, Social Science Research Council, New York, US, pp. 109-134.
- Kitchin R (2014) Big data, new epistemologies and paradigm shifts. Big Data & Society 1(1):
- Pachankis YI (2022a) Bioinformatic entropy in cosmoconsciousness. OS Framework, America.
- McDonnell WM (1983) Analysis and assessment of Gateway process. (CIA-RDP96-00788R001700210016-5). Central Intelligence Agency, USA.
- Bento RRSD (2021) Hemispheric side and vagal nerve activity: A systematic review Catholic University Portuguesa. Lisboa, Portugal.
- Amin BJH, Kakamad FH, Ahmed GS, Ahmed SF, Abdulla BA, et al. (2022) Post COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis, a meta-analysis study. Ann Med Sur 77: 103590.
- Pachankis JE (2007) The psychological implications of concealing a stigma: A cognitive-affective-behavioral model. Psychological Bulletin 133(2): 328-345.
© 2023 Yang I Pachankis, This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






