- Submissions

Full Text
Modern Concepts & Developments in Agronomy
Quercetin- A Mini Review
Muhammad FM1, Ahsan M2 and Abdul W3
1South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China
2Department of Chemistry, Government College University Faisalabad, Pakistan
3Government College University Faisalabad-38000, Pakistan
*Corresponding author: Muhammad Faisal Manzoor, School of Food Science and Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China
Submission: August 21, 2017; Published: January 29, 2018

ISSN: 2637-7659 Volume1 Issue2
Abstract
Quercetin a flavonoid to be a member of a group of flavonols is universally consumed in the human diet and responsibly to give the color to various fruits and vegetables [1]. Mainly occur in the form of glycosides, but their other derivative have been identified [2-5]. This paper presents some recent advances regarding quercetin structure, derivatives, sources and their medicinal benefits with their effective dosage [6-8].
Keywords: Quercetin; Derivatives; Plant sources; Medicinal benefits
Abbreviations: Fe-NTA: Ferric Nitrilo Triacetate; MIC: Minimum Inhibitory Concentration, NF- KB; Nuclear Factor Kappa B, MBC: Minimum Bactericidal Concentration, INOS: Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase
Introduction
It is a 3, 5, 7, 3, 4-pentahydroxyflavon having the five hydroxyl groups placed at five different positions. [9] The chemical structure and different derivatives of quercetin presents in different food sources such as, Mango, plums, cranberry, blueberry, chokeberry, Buckwheat, honey, beans, lettuce, chicory, onion in different amount. Quercetin 3-O-galactoside, Quercetin 3-O-glucoside, Quercetin 3-O-glucuronide, Quercetin 7-O-glucoside, Quercetin 3-O-diglucoside and Quercetin 3-methyl ether are some derivatives that have been discovered in different plants [10-12] (Table 1 & Figure 1).
Table 1: Some important derivatives of quercetin and their food sources.
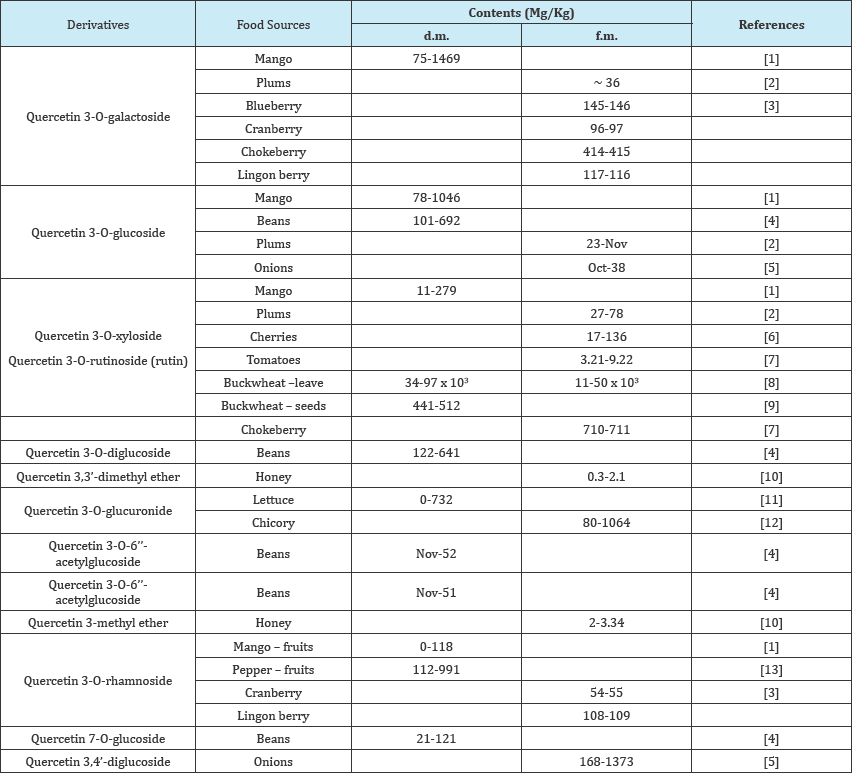
Figure 1: Chemical structure of quercetin.

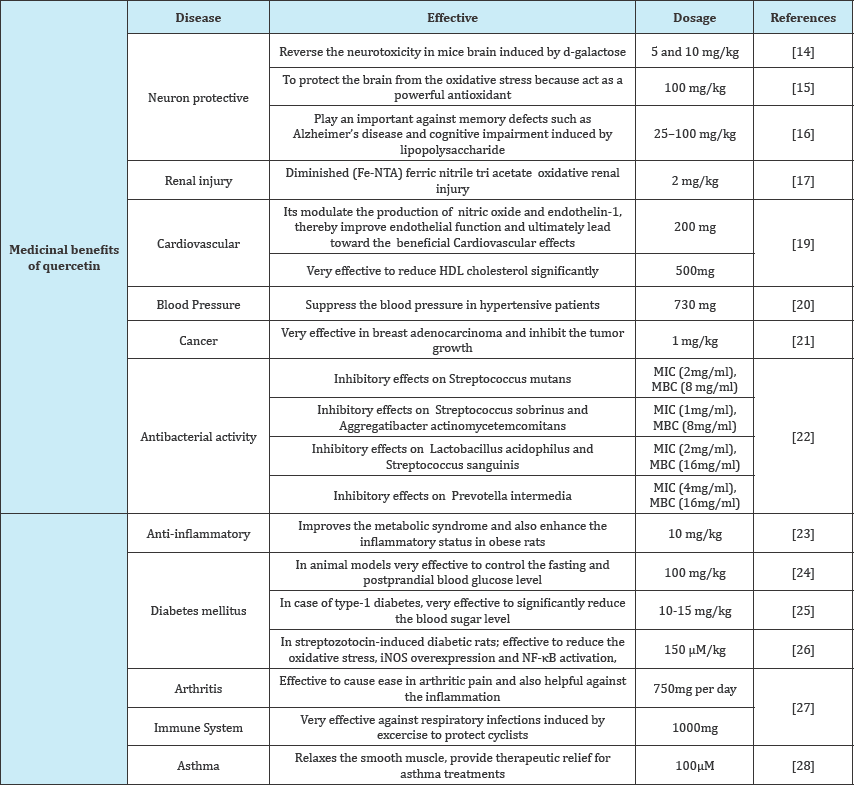
Quercetin is one of the most abundant food based flavonoids present in various edible vegetables, fruit and wine [13]. Quercetin contents present in different plants sources are categorized in different categories such as, vegetable, fruit, plant, herb, shrub, beverage and others [14-16]. The most prominent sources of quercetin is canned capers 180.76mg/100g (Table 2). It has different medicinal benefits against brain disorder, renal injury, cardiovascular diseases, blood pressure, cancer, bacterial activity, inflammation, diabetes mellitus, arthritis and asthma [17-19]. Medicinal benefits of quercetin with effective dose concentrations presented in Table 3 [20-22].
Table 2: Various food sources and quercetin contents (mg/100g).
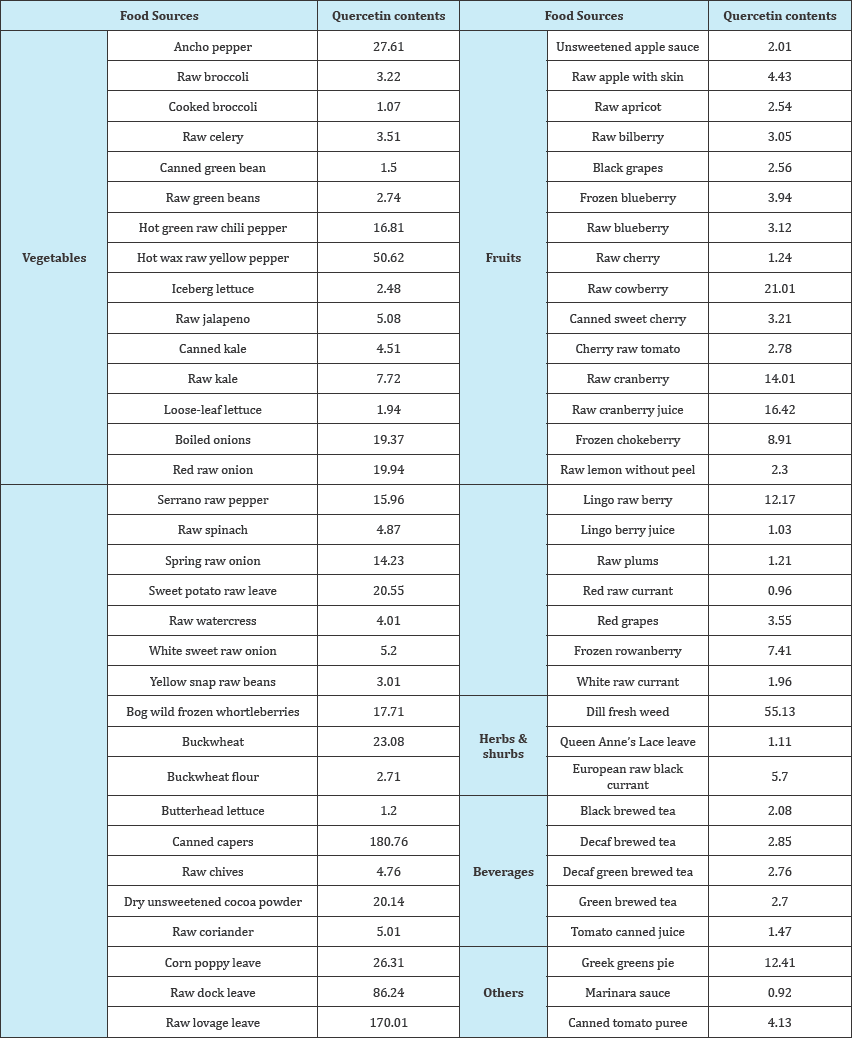
Table 3: Medicinal benefits of quercetin with effective dose concentrations.
Conclusion
Quercetin generally exist in the edible plants and mostly used to manufacturing of traditional medicine to relieve some type of diseases [23-25]. In some recent studies quercetin exerts its biological properties in vivo. Overall, the best source of quercetin is canned carpers with 180.76mg/100g and followed by raw lovage leave with 170.01mg/100g [26-28].
References
- Berardini N, Fezer R, Conrad J, Beifuss U, Carle R, et al. (2005) Screening of mango (Mangiferaindica L.) cultivars for their contents of flavonol O- and xanthone C-glycosides, anthocyanin's and pectin. J Agric Food Chem 53(5): 1563-1570.
- Kim DO, Chun OK, Kim YJ, Moon HY, Lee CY (2003) Quantification of polyphenolics and their antioxidant capacity in fresh plums. J Agric Food Chem 51(22): 6509-6515.
- Zeng W, Wang SY (2003) Oxygen radical absorbing capacity of phenolics in blueberries, cranberries, chokenberries and lingonberries. J Agric Food Chem 51(2): 502-509.
- Chang Q, Wong YS (2004) Identification of flavonoids in Hakmeitau beans (Vignasinensis) by high performance liquid chromatog-raphy- electrospray mass spectrometry (LC-ESI/MS). J Agric Food Chem 52(22): 6694-6699.
- Nemeth K, Piskuia MK (2007) Food content, processing, absorption and metabolism of onion flavonoids. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 47(4): 397-409.
- Goncalves K, Landbo AK, Knudsen D, Silva AP, Moutinho PJ, et al. (2004) Effect of ripeness and posthar-vest storage on the phenolic profiles of cherries (Prunusavium L.). J Agric Food Chem 52(3): 523-530.
- Slimestad R, Torskangerpoll K, Nateland HS, Johannessen T, Giske NH (2005) Flavonoids from black chokeberries, Aroniamelano-carpa. J Food Comp Anal 18: 61-68.
- Kalinova J, Triska J, Vrchotova N (2006) Distribution of vitamin E, squalene, epicatechin and rutin in common buckwheat plants (FagopyrumesculentumMoech). J Agric Food Chem 54(15): 5330-5335.
- Oomah BD, Mazza G (1996) Flavonoids and antioxidative activities in buckwheat. J Agric Food Chem 44(7): 1746-1750.
- Yao L, Datta N, Tomas BFA, Ferreres F, Martos I, et al. (2003) Flavonoids, phenolic acids and abscisic acid in Australian and New ZelandLeptospermum honeys. Food Chem 81: 159-168.
- Nicolle C, Carnat A, Fraisse D, Lamaison JL, Rock E, et al. (2004) Characterisation and variation of antioxidant micronutrients in lettuce (Lactucasativafolium). Science of Food and Agriculture 84(15): 20612069.
- Innocenti M, Gallori S, Giaccherini C, Ieri F, Vincieri FF, et al. (2005) Evaluation of the phenolic content in the aerial parts of different varieties of Cichoriumintybus L. J Agric Food Chem 53(16): 6497-6502.
- Materska M, Perucka I, Stochmal A, Piacente S, Oleszek W (2003) Quantitative and qualitative determination of flavonoids and phenolic acid derivatives from pericarp of hot pepper fruit cv. Bronowicka Ostra. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences 12(suppl 2): 72-76.
- Lu J, Zhenga YL, Luoc L, Wu DM, Suna D, et al. (2006) Quercetin reverses d-galactose induced neurotoxicity in mouse brain. Behav Brain Res 171(2): 251-260.
- Naidu PS, Kulkarni SK (2004) Quercetin, a bioflavonoid, reverses haloperidol-induced catalepsy. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 26(5): 323-326.
- Patil CS, Singh VP, Satyanarayan PSV, Jain NK, Singh A, et al. (2003) Protective Effect of Flavonoids against Aging- and Lipopolysaccharide- Induced Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Pharmacology 69(2): 59-67.
- Singh D, Chander V, Chopra K (2004) Quercetin, a Bioflavonoid, Attenuates Ferric Nitrilotriacetate-Induced Oxidative Renal Injury in Rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 27(2): 145-156.
- Loke WM, Hodgson JM, Proudfoot JM, McKinley JA, Puddey IB, et al. (2008) Pure dietary flavonoids quercetin and (-)-epicatechin augment nitric oxide products and reduce endothelin-1 acutely in healthy men. Am J Clin Nutr 88(4): 1018-1025.
- Zahedi M, Ghiasvand R, Feizi A, Asgari G, Darvish L (2013) Does Quercetin Improve Cardiovascular Risk factors and Inflammatory Biomarkers in Women with Type 2 Diabetes: A Double-blind Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int J Prev Med 4(7): 777-785.
- Edwards RL, Lyon T, Litwin SE, Rabovsky A, Symons JD, et al. (2007) Quercetin reduces blood pressure in hypertensive subjects. J Nutr 137(11): 2405-2411.
- Srivastava S, Ranganatha R, Somasagara, Hegde M, Nishana M, et al. (2016) Quercetin, a Natural Flavonoid Interacts with DNA, Arrests Cell Cycle and Causes Tumor Regression by Activating Mitochondrial Pathway of Apoptosis.
- Shu Y, Liu Y, LiL F, Lou B, Zhou X, et al. (2011) Antibacterial activity of quercetin on oral infectious pathogens. 5(30): 5358-5361.
- Rivera L, Moron R, Sanchez M, Zarzuelo A, Galisteo M (2008) Quercetin ameliorates metabolic syndrome and improves the inflammatory status in obese Zucker rats. Obesity 16(9): 2081-2087.
- Kim JH, Kang MJ, Choi HN, Jeong SM, Lee YM, et al. (2011) Quercetin attenuates fasting and postprandial hyperglycemia in animal models of diabetes mellitus. Nutr Res Pract 5(2): 107-111.
- Torres PM, Ortiz AR, Villalobos MR, Singh N, Medina FJL, et al. (2010) A comparative study of flavonoid analogues on streptozotocin- nicotinamide induced diabetic rats: quercetin as a potential antidiabetic agent acting via 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibition. Eur. J Med Chem 45(6): 2606-2612.
- Dias AS, Porawski M, Alonso M, Marroni N, Pilar S, et al. (2005) Quercetin decreases oxidative stress, NF-kB activation, and iNOS overexpression in liver of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Nutr 135(10): 2299-2304.
- Harrison A, Ross Cooper R (2008) Quercetin: health benefits with relevance to TNF-a-linked inflammatory diseases. J Pre-clinical & clinical Res 2(2): 97-101.
- Townsend EA, Emala CW (2013) Quercetin acutely relaxes airway smooth muscle and potentiates p-agonist-induced relaxation via dual phosphodiesterase inhibition of PLCp and PDE4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 305(5): 396-403.
© 2018 Muhammad FM, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






