- Submissions

Full Text
COJ Nursing & Healthcare
Evaluation of the Safety Profile of Diarrhea Stop Capsule: A Natural Herbal Product in Healthy Volunteers
Hussien O Kadi1*, Ismail Hamoud Ali Al-geobri2, Abdulmalek Abu-Donia3, Abdullalh Alharzi4 and Mohammed H Kadi5
1Yemen University, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Yemen
2Yemen University, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Yemen
3Sana’a University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics, Yemen
4Sana’a University, Faculty of Medicine, Central Laboratory for Medical Analysis, Yemen
5Yemen University, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Yemen
*Corresponding author: Hussien O Kadi, Sana’a University, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Yemen
Submission: May 09, 2025;Published: June 27, 2025

ISSN: 2577-2007Volume9 Issue 3
Abstract
Background: Diarrhea Stop Capsule is a natural herbal formulation developed to manage diarrhea symptoms effectively. Despite the historical use of its components, clinical evaluation of its safety is essential.
Methods: A single-arm, open-label clinical study was conducted on 30 healthy volunteers receiving different dosing regimens of Diarrhea Stop Capsule. Laboratory parameters and vital signs were measured before and after administration. Statistical analysis was performed to compare baseline and post-administration values, considering p-values>0.05 as non-significant.
Results: No statistically significant differences were observed in hematological, renal, hepatic, or vital sign parameters before- and after-administration. No serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusion: Diarrhea Stop Capsule demonstrated a favorable safety profile in healthy volunteers, which can be used in the treatment of diarrhea in recommended dose.
Keywords:Diarrhea; Stop; Capsule; Natural; Herbal
Introduction
Worldwide, one in ten deaths among children under five years of age (approximately 800,000) is due to diarrhea [1]. It is estimated that more than 2.8 billion adolescents, adults, and children over the age of five suffer from diarrhea each year [2]. Diarrhea is a common gastrointestinal disease that can lead to severe dehydration and other health complications. Herbal medicines have been utilized for centuries in the management of various diseases due to their natural origin, availability, and favorable safety profile [3]. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that about 80% of the world’s population relies on traditional medicine for primary healthcare needs [4].
Diarrhea remains a major health burden globally, being a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, particularly in developing countries [5]. Although synthetic antidiarrheal drugs are effective, concerns over their side effects and contraindications in certain populations, such as children and elderly patients, have driven interest toward herbal alternatives [6-9]. Several medicinal plants have traditionally been employed for the treatment of diarrhea, attributed to their antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and astringent properties [10]. Herbal formulations provide a multi-target approach, combining the effects of multiple active phytoconstituents, which may offer a broader therapeutic spectrum compared to single-agent pharmaceuticals [11]. Plants such as Vernonia amygdaloides, cinnamon bark, ginger, and ginseng exhibit remarkable anti-diarrhea properties through various mechanisms, including modulation of the gut microbiota, enhancement of the gut barrier function, and anti-inflammatory effects [12]. These plants are often multi-ingredient medicines, or phytoplankton. They contain multiple active ingredients that work synergistically to relieve symptoms. Numerous studies have confirmed the traditional use of medicinal plants for the treatment of diarrhea by investigating the bioactivity of these plant extracts [13]. Active extracts contain a variety of phytochemicals (e.g., alkaloids, tannins, flavonoids, and terpenes), of which tannins and flavonoids are thought to exert their antidiarrheal effects. They have antispasmodic effects, delay intestinal transit, inhibit intestinal motility, stimulate water absorption, or reduce electrolyte secretion [14]. Several clinical trials have investigated the safety and tolerability of traditional and herbal medicines for the treatment of diarrhea, generally showing minimal side effects [15]. Despite their long history of use, herbal products must undergo rigorous clinical and laboratory evaluations to ensure safety and efficacy [16,17]. The WHO and other regulatory agencies emphasize the need for clinical validation of herbal therapies under Good Clinical Practice (GCP) standards [18].
Diarrhea Stop Capsule is a natural herbal formulation containing a synergistic blend of medicinal herbs traditionally used to manage diarrhea. Although the individual herbs have documented safety records, the safety of the combined formulation must be clinically evaluated. Therefore, this study aims to assess the safety profile of Diarrhea Stop Capsule through clinical monitoring of laboratory parameters and adverse events in healthy volunteers. The hypothesis of new formulation of Diarrhea Stop capsule contain mixture of six natural herbs with different amounts for each one which was done by Prof. Dr. Hussien O. Kadi (Patent).
Materials & Methods
A single-arm, open-label clinical study was conducted at Yemen University 24/2/2025 to evaluate the safety use of Diarrhea Stop Capsule in healthy adult volunteers. Thirty healthy volunteers aged 18-50 years with a BMI of 18.5-25kg/m² were enrolled. Participants were allocated into three groups: Group 1 received a single capsule; Group 2 received four capsules as a high single dose; Group 3 received multiple daily doses (morning and evening) for three days. Baseline screening included full clinical history, physical examination, vital signs, and laboratory tests covering liver and kidney function, glucose, and serum electrolytes. Post-dosing assessments were conducted at multiple intervals, with follow-up testing on Day 6. Volunteer gave a written informed consent and the Ethics Committee of Yemen University; Faculty of medical Sciences approved the clinical protocol and have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was conducted following the ethical principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines.
All participants underwent a comprehensive before evaluation
including:
Complete Blood Count (CBC), Liver function tests (SGPT, SGOT),
Renal function tests (Urea, creatinine), Heart enzyme (CK) and Vital
signs (blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate and temperature).
After-administration assessments were performed according to the
study schedule. All adverse events were recorded.
Statistical analysis: Paired t-tests were conducted to compare
before and after-treatment values. A p-value greater than 0.05 was
considered statistically non-significant, indicating no clinically
relevant changes.
Results: Results of Clinical Evaluation of Safety Use of Diarrhea Stop Capsule in Healthy Human Volunteers
The study included 30 healthy human volunteers with a mean age of 28±5 years. No participant withdrew from the study. Comparative analysis between before and after-administration laboratory values revealed no statistically significant changes (p>0.05) across all evaluated parameters, including: Hematological parameters (WBC, RBC, hemoglobin, platelets and ESR), Liver enzymes (SGPT, SGOT), Renal function (Urea, creatinine), heart enzyme (CK) and Vital signs (blood pressure, pulse rate, respiratory rate, body temperature). A comparative statistical analysis was conducted on laboratory test results of a group of healthy volunteers before and after the administration of the Diarrhea Stop capsule. The tests included a comprehensive panel covering liver function, kidney function, cardiac enzyme, blood glucose, and various electrolytes, hematological parameters and vital signs.
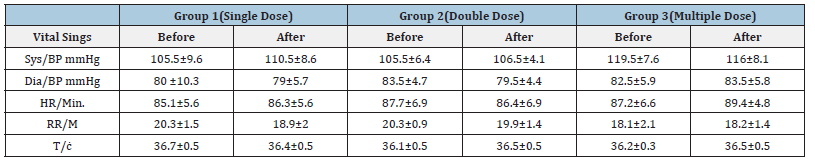
The Paired T-Test was employed to assess changes in values before- and after-administration of single, double and multiple doses of Diarrhea Stop capsule. The parameters showed no statistically significant difference (P-value > 0.05), suggesting a stable biochemical profile and no adverse impact from the Diarrhea Stop capsule as shown in Tables 1-6. Key biomarkers such as creatinine, potassium, sodium, phosphorus, calcium, and liver enzymes remained within the normal physiological range without significant alterations. Mild fluctuations were observed in a few parameters such as Magnesium (Mg) and Random Blood Sugar (RBS), but these changes were still within acceptable biological variation and likely attributed to individual differences rather than a pharmacological effect. The Diarrhea Stop capsule appears to be biochemically and clinically safe when used at the tested dose in healthy adult volunteers, with no detectable adverse laboratory effects. Also, no adverse reactions were recorded. Minor, self-limiting gastrointestinal discomfort (such as mild abdominal cramping) was reported in 2 participants (6.7%), but resolved spontaneously without intervention. No serious adverse events or clinically significant laboratory abnormalities were observed during the study.
Table 1: Effect of Diarrhea Stop capsule on liver functions test before and after single, double and multiple dose administration in healthy volunteers. Each group N=10 (M±SD).
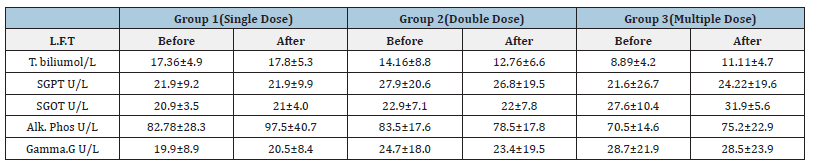
Table 2:Effect of Diarrhea Stop capsule on kidney function test before and after single, double and multiple dose administration in healthy volunteers. Each group N=10 (M±SD).
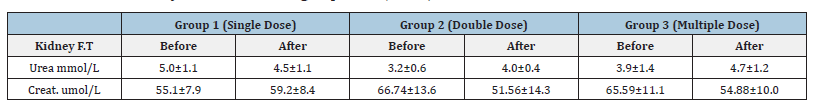
Table 3: Effect of Diarrhea Stop capsule on heart function before and after single, double and multiple dose administration in healthy volunteers. Each group N=10 (M±SD).
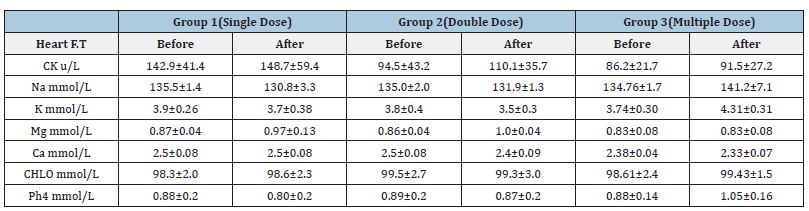
Table 4:Effect of Diarrhea Stop capsule on blood level before and after single, double and multiple dose administration in healthy volunteers. Each group N=10 (M±SD).
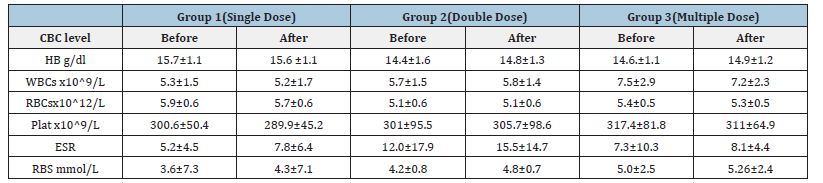
Table 5:Effect of Diarrhea Stop capsule on vital signs before and after 24 hours of single, double and multiple dose administration in healthy volunteers. Each group N=10 (M±SD).
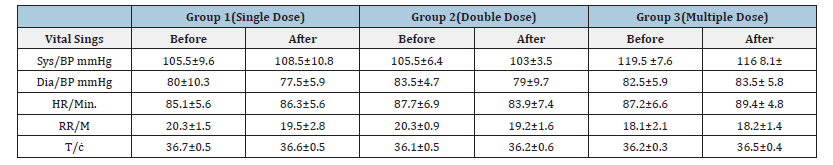
Table 6:Effect of Diarrhea Stop capsule on vital signs before and after 72 hours of single, double and multiple dose administration in healthy volunteers. Each group N=10 (M±SD).
Discussion
The findings of this study confirm the favorable safety profile of Diarrhea Stop Capsule when administered to healthy volunteers. The absence of statistically significant changes in hematological, hepatic, renal, and vital sign parameters suggests that the herbal formulation does not adversely impact major physiological functions [3,7,10]. Herbal medicines are often presumed safe due to their natural origin; however, numerous reports emphasize the necessity of formal clinical evaluations to identify potential adverse effects, particularly when combining multiple herbal constituents [10,11,13]. The current study adheres to these standards by systematically monitoring safety endpoints. Several of the individual herbs contained within the Diarrhea Stop Capsule, such as Psidium guajava (guava leaf) and Punica granatum (pomegranate peel), have been traditionally recognized for their antidiarrheal and antimicrobial properties [5,7,16]. Preclinical studies have shown that these botanicals can modulate gut motility, reduce intestinal secretions, and inhibit pathogenic bacterial growth [17,19].
Importantly, no clinically meaningful adverse events were observed in this study. The results support the safety and tolerability of Diarrhea Stop capsule in a healthy population. No clinically significant laboratory changes or adverse events were noted. These findings align with preclinical evidence indicating the benign nature of the herbal components. Minor gastrointestinal discomfort reported in a small number of participants is common with herbal products and is often attributed to adaptive gastrointestinal responses to plant secondary metabolites [20]. Compared to conventional antidiarrheal drugs, herbal formulations offer potential advantages, such as lower risks of severe side effects like constipation, dependence, or systemic toxicity [6,18,21]. However, it is crucial that these preparations meet standardized quality controls and undergo rigorous clinical testing to ensure consistency and safety [22,23].
Overall, the safety findings observed here are consistent with the global trend advocating for the integration of scientifically validated herbal products into modern healthcare systems [6,24,25]. Moreover, some herbal formulations possess immunomodulatory effects, enhancing the gut’s response to pathogens. Research indicates that natural extracts from turmeric contain curcumin, which exhibits powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties beneficial in managing inflammatory diarrhea [26]. In addition, the focus on herbal formulations is increasingly important in light of the rising tide of antibiotic resistance, which is a growing concern among healthcare professionals globally. Conventional antibiotics may be ineffective at treating certain diarrheal diseases, particularly those caused by resistant pathogens. The diverse phytochemicals in many herbal products may offer multi-targeted therapeutic pathways while minimizing the risk of resistance development [27]. Many studies reported that Pomegranate peel contains tannins and ellagitannins that have antimicrobial and astringent properties. Studies have shown its effectiveness in inhibiting diarrhea-causing pathogens and reducing intestinal fluid secretion [28]. Guava leaves are rich in flavonoids like quercetin, which demonstrate anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects. They reduce intestinal motility and fluid loss [29]. Chamomile possesses anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects due to compounds like apigenin and bisabolol. It soothes intestinal lining and reduces cramps [30]. Carob contains tannins and insoluble fiber that help absorb excess water and bind toxins in the gut, making it effective in treating acute diarrhea. Black tea is a rich source of catechins and tannins with astringent and antiinflammatory effects, commonly used in folk medicine for diarrhea [31]. Ginger has antimicrobial and gut-soothing properties. It alleviates nausea and intestinal inflammation, making it supportive in gastrointestinal disorders [32].
The present study suggests that Diarrhea stop capsule herbs exhibit multiple mechanisms contributing to their antidiarrheal effect via astringency and reduce intestinal secretion; inhibit motility and inflammation and antimicrobial activity. Combined in a multi-herb formulation, they act synergistically to manage diarrheal symptoms effectively.
Conclusion
The clinical evaluation of Diarrhea Stop Capsule in healthy volunteers demonstrated a favorable safety profile. No significant adverse effects, laboratory abnormalities, or vital sign deviations were observed following administration across different dosing regimens. These findings support the safety and tolerability of this natural herbal product when used in accordance with recommended doses.
References
- Rawat P, Singh PK, Kumar V (2017) Evidence based traditional anti-diarrheal medicinal plants and their phytocompounds. Biomed Pharmacother 96: 1453-1464.
- Effo KE, Adehouni YA, Tia GE, Irié-N’Guessan AG, Siransy NG (2023) Safety, tolerability and anti-diarrhoeal activity of “Diarra”, a preparation of medicinal plants used in Ivorian traditional medicine. Pharmacology & Pharmacy 14(10): 428-440.
- Barnes J, Anderson LA, Phillipson JD (2008) Herbal medicines. (3rd edn), Pharmaceutical Press, London, UK.
- World Health Organization (2013) WHO traditional medicine strategy 2014-2023, WHO Press, Geneva, Switzerland.
- Guerrant RL, Van Gilder T, Steiner TS, Thielman NM, Slutsker L, et al. (2001) Practice guidelines for the management of infectious diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis 32(3): 331-351.
- Chen YF, Jobanputra P, Barton P (2008) Systematic review: The effectiveness of loperamide in the treatment of acute diarrhea. BMC Infect Dis.
- Tilburt JC, Kaptchuk TJ (2008) Herbal medicine research and global health: An ethical analysis. Bull World Health Organ 86(8): 594-599.
- Izzo AA, Ernst E (2001) Interactions between herbal medicines and prescribed drugs. Drugs 69(13): 1777-1798.
- Palombo EA (2011) Traditional medicinal plant extracts and natural products with activity against oral bacteria: Potential application in the prevention and treatment of oral diseases. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011: 680354.
- Plaatjie TA, Onyiche TE, Ramatla T, Bezuidenhout JJ, Legoabe L, et al. (2024) A scoping review on efficacy and safety of medicinal plants used for the treatment of diarrhea in sub-Saharan Africa Moitshepi. Tropical Medicine and Health 52(1): 6.
- Rawat P, Singh PK, Kumar V (2017) Evidence based traditional anti-diarrheal medicinal plants and their phytocompounds. Review. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 96: 1453-1464.
- Chan K (2003) Some aspects of toxic contaminants in herbal medicines. Chemosphere 52(9): 1361-1371.
- Gahamanyi N, Munyaneza E, Dukuzimana E, Tuyiringire N, Pan CH, et al. (2021) Ethnobotany, ethnopharmacology, and phytochemistry of medicinal plants used for treating human diarrheal cases in Rwanda: A review. Antibiotics 10(10): 1231.
- Ekor M (2014) The growing use of herbal medicines: Issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front Pharmacol 4: 177.
- Bent S (2008) Herbal medicine in the United States: Review of efficacy, safety, and regulation: Grand rounds at University of California, San Francisco Medical Center. J Gen Intern Med 23(6): 854-859.
- Begum S, Hassan SI, Ali SN, Siddiqui BS (2002) Chemical constituents from the leaves of Psidium guajava. Nat Prod Res 18(2): 135-140.
- Gutierrez RM, Mitchell S, Solis RV (2008) Psidium guajava: A review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol 117(1): 1-27.
- Borrelli F, Capasso R, Pinto A, Izzo AA (2006) Inhibitory effect of pomegranate juice on intestinal motility and electrolyte loss in mice. Pharmacol Res.
- Caceres A, Giron LM, Alvarado SR, Torres MF (1990) Screening of antimicrobial activity of plants popularly used in Guatemala for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. J Ethnopharmacol 20(3): 223-237.
- World Health Organization (1991) WHO guidelines for the assessment of herbal medicines, WHO, Geneva, Switzerland.
- Lanza FL (1989) Gastrointestinal adverse effects of anti-inflammatory agents: New insights into prevention and treatment. Gastroenterology.
- Mukherjee PK, Venkatesh M, Kumar V (2010) An overview on the development in regulation and control of herbal drugs. Indian J Nat Prod Resour.
- Chan K (2003) Quality assurance of herbal medicines. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
- Rasheed HM, Al-Shawi SG (2005) Antidiarrheal activity of medicinal plants. J Ethnopharmacol.
- Sofowora A, Ogunbodede E, Onayade A (2013) The role and place of medicinal plants in the strategies for disease prevention. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 10(5): 210-229.
- Wang Y (2018) Curcumin and its effects on inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review. Phytotherapy Research 32(4): 620-629.
- Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2013) Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 25(1): 296-298.
- Begum S (2004) Antimicrobial activity of Punica granatum Fitoterapia.
- Koc F (2010) The effectiveness of carob bean (Ceratonia siliqua) for acute diarrhea in children. Pediatr Int.
- Lozoya X (2002) Intestinal anti-spasmodic effect of Psidium guajava leaf extract. J Ethnopharmacol.
- McKay DL, Blumberg JB (2006) A review of the bioactivity of chamomile tea. Phytother Res.
- Ali BH, Blunden G, Tanira MO, Nemmar A (2008) Some phytochemical, pharmacological, and toxicological properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe): A review of recent research. Food Chem Toxicol 46(2): 409-420.
© 2025 Hussien O Kadi. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






