- Submissions

Full Text
Trends in Textile Engineering & Fashion Technology
A Mini-Review of Using Additive Manufacturing in the Fashion & Textile Industry?
Behnam Akhoundi* and Ahmad Mashayekhi
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sirjan University of Technology, Sirjan, Kerman Province, Iran
*Corresponding author:Behnam Akhoundi, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sirjan University of Technology, Sirjan, Kerman Province, Iran
Submission: December 14, 2022; Published: January 13, 2023

ISSN 2578-0271 Volume 7 Issue5
Abstract
In additive manufacturing (AM) techniques, 3D objects are built layer by layer. After the introduction of AM techniques, they found extensive applications in various industries such as medicine, dentistry, architecture, aerospace, textile, fashion, and so forth. This study presents a brief overview of the AM techniques used in the textile and fashion industries, the materials used, the companies that use this technology, and the printed products in this area.
Keywords:Additive manufacturing; 3D Printing; Textile industry; Fashion industry; Accessories
Introduction
Figure 1:relationship between the textile and fashion industry and AM processes.
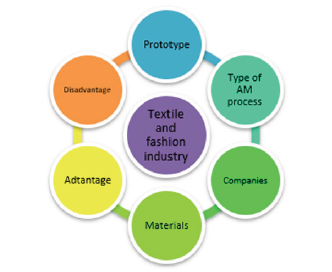
By introducing additive manufacturing (AM) techniques in recent decades, researchers and craftsmen investigated the use of these techniques in various industries such as healthcare, dentistry, architectural, aerospace, textile, fashion and so forth [1,2]. In all of these techniques, initially, a 3D model must be created in computer-aided design (CAD) software or must be scanned from existing 3D objects by 3D scanning devices. Once the 3D model is prepared, by taking into account the type of technique to be used and setting the related parameters, the model is sliced in computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and finally, the production sequence (G-codes/M-codes) is determined. As the state-of-the-art textile and fashion industries are also based on CAD/CAM, the use of AM techniques in these industries can be highly beneficial [3,4]. The use of AM techniques in the fashion industry was introduced in the fall of 2013 at the New York Fashion Week [5]. In this paper, the AM techniques used in these industries are reviewed, and the advantages and limitations of each of these techniques are studied. Also, the materials used and the printed products are reviewed. Figure 1 shows the relationship between the textile and fashion industry and AM processes.
Fashion industry and rapid prototype
Since these industries are based on CAD/CAM, rapid prototyping can solve many design-related problems [6]. Therefore, one of the most critical applications of AM methods is producing prototypes in these industries. Prototyping can improve product design by providing customers with uniqueness and personalization. It also enables the production of lighter and more flexible products and the comparison between the prototype and the initial modeling [3,5].
AM process used in the fashion & textile industry
By using AM processes, it is possible to print complex geometries. Among the AM methods in the fashion & textile industry, can be mentioned to fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), 3D printing (3DP-binder jetting), selective laser sintering (SLS), inkjet 3D printing, direct ink writing (DIW), and electrohydrodynamic direct writing (EHDP) [5,7].
Companies that use AM processes in the fashion & textile industry
The most important companies include Iris van Herpen, Lady Gaga, Dr. Richard Hoptroff, Francis Bitonti, Timberland, Nike, etc. The most important products that are 3D printed in this industry are long dress detailed components, dresses, garment components, jewelry, watches, metal accessories, corsets, masks, helmets, bathing suits, shoes, high heel shoes, lumbar support garments, etc. An image of printed products in the fashion & textile industry is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2:Some 3D printed products of the textile and fashion industry.

Materials used in AM in the fashion & textile industry
A wide range of materials is used in different AM methods. The most important materials used in the fashion & textile industry are thermoplastic polymers. If the goal is to produce a flexible product, thermoplastics such as thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) [6], and rubber materials are desirable. Nylon, polyamide, and polystyrene are generally used to produce non-flexible products.
Limitations of the use of AM methods in the fashion & textile industry
The main limitations of using AM methods in the fashion & textile industry are: the low speed of the process, the low surface quality in terms of thickness due to the step effect, the limited materials required in the fashion & textile industry, and the maximum dimensions that can be printed by a 3D printer [8].
Conclusion
In this mini-review paper, a brief overview is presented of the use of AM techniques in the textile and fashion industries. In addition to the AM techniques used in these industries, the companies active in this area are introduced, and the materials used and some printed products are explained. Ultimately, the advantages and limitations of AM techniques in these industries are examined. The significant point is that the textile and fashion industries are based on CAD/ CAM, and due to its position and the continuous progress of CAD/ CAM, it can make enormous strides in these industries. Also, the principal advantage of using AM in these industries is the capability to manufacture complex designs and produce unique, personalized, and private products.
References
- Akhoundi B, Hajami F (2022) Extruded polymer instability study of the polylactic acid in fused filament fabrication process: Printing speed effects on tensile strength. Polymer Engineering & Science 62(12): 4145-4155.
- Akhoundi B, Nabipour M, Hajami F, Band SS, Mosavi A (2020) Calculating filament feed in the fused deposition modeling process to correctly print continuous fiber composites in curved paths. Materials 13(20): 4480.
- Jin B, Cedrola E (2016) Palgrave studies in practice: Global fashion brand management. Springer.
- Millatunnisa S (2022) The 4.0 industry technology in fashion industries. 4th International Conference on Innovation in Engineering and Vocational Education (ICIEVE 2021): Atlantis Press; pp. 336-340.
- Vanderploeg A, Lee SE, Mamp M (2017) The application of 3D printing technology in the fashion industry. International Journal of Fashion Design, Technology and Education 10(2): 170-179.
- Xiao YQ, Kan CW (2022) Review on development and application of 3D-printing technology in textile and fashion design. Coatings 12(2): 267.
- Khajavi SH (2021) Additive manufacturing in the clothing industry: Towards sustainable new business models. Applied Sciences 11(19): 8994.
- Yap Y, Yeong W (2014) Additive manufacture of fashion and jewellery products: a mini review: This paper provides an insight into the future of 3D printing industries for fashion and jewellery products. Virtual and Physical Prototyping 9(3): 195-201.
© 2023 Behnam Akhoundi. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






