- Submissions

Full Text
Surgical Medicine Open Access Journal
Applying Artificial Intelligence and Fuzzy Logic to Predict Diagnosis and Treatment Planning in Medicine
Mazyar Ghadiri Nejad1* and Amirsalar Khandan2
1Industrial Engineering Department, Girne American University, Via Mersin 10, Kyrenia 99428, TRNC, Turkey
2Department of Endodontics, Dental Research Center, Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
*Corresponding author: Mazyar Ghadiri Nejad, Industrial Engineering Department, Girne American University, Via Mersin 10, Kyrenia 99428, TRNC, Turkey
Submission: November 11, 2022Published: November 30, 2022

ISSN 2578-0379 Volume5 Issue1
Introduction
The term “Artificial Intelligence” was first coined in 1956 within a scientific community, in Germany. Since then, it has been used within the dental and medical realm particularly in recent years [1]. In comparison
with the human workforce, artificial intelligence can perform tasks more accurately,
more expediently, and with less energy consumption [2]. Depending on practice organization,
artificial intelligence may be used to accomplish different tasks as follows:
A. Set up patient appointments
B. Classify and stratify patient medical history
C. Provide initial consultation
D. Assist in clinical diagnosis and treatment planning
E. Assist in the radiographic analysis
F. Assist in surgical procedures and postoperative care
G. Increase the speed of workflow in dental laboratories
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine
One of the most significant benefits of using artificial intelligence is providing a diagnosis. Since artificial intelligence is a highly focused computer vision system, its performance is not affected by the assumptions, bias, or fatigue that affect even the most skilled human radiologists [3]. Such a tool can positively influence treatment planning, patient confidence, insurance claim confirmation, and other aspects of medical care. Artificial intelligence can also increase predictability and can be used in preventative medicine and dentistry. Using this technique, various treatment options may be recommended for individuals with the same diagnosis, based on their specific genetic makeup, muscle composition, bacterial flora, bone density, dental/facial morphology, physiology etc. According to recent predictions, the application of artificial intelligence in the field of healthcare will grow up drastically in the next five years and will accelerate the interpretation of CT scans, X-rays, and MRI images with the help of specialized healthcare providers [4].
Further, the interpretation of the obtained images to formalize a diagnosis requires a certain level of education, knowledge, special expertise, and of course high accuracy. Studies have shown that the probability of errors in the diagnosis of diseases by doctors is more than 20% [5,6]. The use of artificial intelligence in this field not only has the potential to mitigate the above-mentioned issues, but also has higher level of precision and efficiency, and is less influenced by environmental conditions, in comparison to specialist doctors. In addition, artificial intelligence may be used to help educate students in the fields of medicine and dentistry. Today, even some developed countries use e-learning clinics or simulation laboratories to educate students. The advantages of these advancements include faster and more integrated learning, interaction with patients, as well as time and cost savings.
Fuzzy Logic Modeling in Medicine
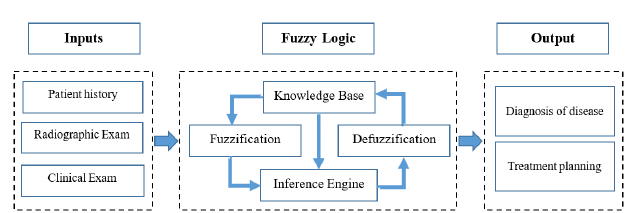
Lotfi Asgar Zadeh, an Iranian scientist, and professor at Berkeley University in the United States proposed fuzzy theory in 1965 [7]. Since its introduction, this theory has been dramatically expanded and used in various applications. Fuzzy theory is a notion for working in conditions of uncertainty. This theory is able to mathematically formulate a number of concepts, variables, and systems that are inaccurate and ambiguous, as is often the case in the real world, and provide the basis for reasoning, inference, control, and decision-making [8]. (Figure 1) Illustrates the architecture of the fuzzy model for the diagnosis and treatment planning of a patient.
Figure 1: Fuzzy logic architecture for diagnosis and treatment planning.
References
- Howard J (2019) Artificial intelligence: Implications for the future of work. American Journal of Industrial Medicine 62(11): 917-926.
- Mintz Y, Brodie R (2019) Introduction to artificial intelligence in medicine. Minimally Invasive Therapy & Allied Technologies 28(2): 73-81.
- Yeung S, Downing NL, Fei-Fei L, Milstein A (2018) Bedside computer vision-moving artificial intelligence from driver assistance to patient safety. N Engl J Med 378(14): 1271-1273.
- Suero-Abreu GA, Hamid A, Akbilgic O, Brown SA (2022) Trends in cardiology and oncology artificial intelligence publications. American Heart Journal Plus: Cardiology Research and Practice 17: 100162.
- Balogh EP, Miller BT, Ball JR (2015) In Improving diagnosis in health care. National Academies Press, USA, pp: 1-444.
- Carver N, Gupta V, Hipskind JE (2022) Medical error. Stat Pearls Publishing, USA.
- Ghadirinejad N, Nejad MG, Alsaadi N (2021) A fuzzy logic model and a neuro-fuzzy system development on supercritical CO2 regeneration of Ni/Al2O3 Journal of CO2 Utilization 54: 101706.
- Golabi M, Nejad MG (2022) Intelligent and fuzzy UAV transportation applications in aviation 4.0. In Intelligent and Fuzzy Techniques in Aviation 4.0 374: 431-458.
© 2022 Mazyar Ghadiri Nejad. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






