- Submissions

Full Text
Strategies in Accounting and Management
A Note on Disruptive Innovation Model of PDD Case
Wan Liu1 and Steven Si2*
1Zhejiang University, China
2Bloomsburg University of Pennsylvania, USA
*Corresponding author: Steven Si, Bloomsburg University of Pennsylvania, USA
Submission: February 09, 2021Published: March 04, 2021

ISSN:2770-6648Volume2 Issue3
Case Report
Pinduoduo e-commerce platform (NASDAQ: PDD) is a typical latecomer related with
disruptive innovation. When Pinduoduo entered China’s e-commerce field in 2015, it
already had various e-commerce platforms such as Taobao and others, among which Taobao
and Jingdong had a market share of more than 90%. Pinduoduo was facing the market
competition situation of oligopoly. Second, Pinduoduo is an undisputed disruptor of the
market. Pinduoduo adopts distributed AI technology that is different from other e-commerce
companies. It starts from the low-end market with the Pinduoduo mode and develops a lowend
market of e-commerce with more than 300 million users in just three years by relying
on low-cost commodities [1-3]. At present, the market coverage of Pinduoduo has gradually
expanded from the early low-end consumer groups to the middle and high-end consumer
groups, with the characteristics of disruptive innovation from the non-mainstream market
to the mainstream market; Thirdly, the company of Pinduoduo is registered and operated in
mainland China, which is convenient for researchers to observe. More importantly, Pinduoduo
successfully launched in the US in July 2018, making its public data more accessible to
researchers. Finally, in the e-commerce industry, Taobao (for the first time) took 5 years to go
public and Jingdong took 10 years. However, only three years, Pinduoduo successfully landed
on NASDAQ in the United States with 344 million active buyers and became the third largest
e-commerce company in China after Alibaba and Jingdong. Pinduoduo is a successful business
case in the digital age, so how to use business theory to analyze this case? We believe that
disruptive models of innovation are good.
In this short note, we select the disruptive perspectives-based business models to analyze
the case of PDD. Three business models Clayton Christensen proposed: solution shops, valueadded
process and facilitation network that can be used to explore and analyze the case of
PDD, see the PDD disruptive innovation model below:
In the PDD disruptive innovation model above, the solution shops refers to a team of
experts hired by the organization to diagnose and resolve decidedly unstructured problems
through the destruction process. For Pinduoduo, its rapid development is inseparable from
Huang Zheng (Founder and CEO) and the team of technical experts who support it. Prior to the
establishment of Pinduoduo, Huang Zheng was a successful serial entrepreneur and worked
with Pinduoduo’ s senior management team for over 10 years. At the same time, Pinduoduo
has a young and creative entrepreneurial team. The average age of the workers is 26. Seventy
percent of its members graduated from prestigious universities, and most have an educational
background in computer science and big data mining. At the same time, the company also
has a large number of employees who have been employed by global well-known companies
such as Google, Baidu, Alibaba and Tencent, and they have rich experience in e-commerce and
social networking industry. Therefore, PDD has the technical advantage of a team of experts
to help PDD consult and provide a differentiated and disruptive path for achieving success
through disruptive innovation (Figure 1).
The value-added processes (VAP) measures an enterprise’s ability to add value to customers
and suppliers, thereby generating revenue streams. PDD’s first value-added stream is its
customers. Pinduoduo translates as “buy together”, alluding to the platform’s unique discount points for group buying. Users use WeChat scans to persuade their
friends to join them in the purchase. This model, while lowering
prices for consumers, creates a large number of orders, enhancing
economies of scale and increasing profits for retailers. Users become
unofficial recruiters on the platform, which makes Pinduoduo’ s
cost per user acquisition lower than its rivals. The second valueadded
stream is PDD vendors. The “social + e-commerce” mode
maximizes unnecessary and abnormal operating costs with the
internal subversive innovation logic of “providing lower prices and
better products”, which not only increases consumers’ satisfied
shopping experience, but also increases the income of small and
medium-sized enterprises (farmers). Based on this new model,
Pinduoduo supports merchants by providing consumer insight,
research and development advice and preferences to help them
customize products for their target customers [3-6].
Figure 1:
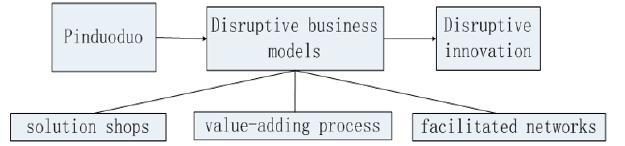
The facilitated networks highlight the importance of social networks for disruptive innovation. Pinduoduo is more than just a digital shopping platform, it’s actually a social e-commerce app that uses a “group buying” model and uses social sharing on Chinese social networks. By successfully integrating social features into its business model, Pinduoduo is revolutionizing the traditional solo online shopping experience, which it calls a “team buying” model. App users can unlock heavily discounted products by inviting friends and family to form shopping groups. Pinduoduo also offers other incentives, such as red envelopes, coupons, lucky draws and free products for inviting contacts. Pinduoduo’ s business model is also aimed at the low-end market, which is a huge user group. With low price and team purchase as the main features, the user focus and retention are achieved with the help of WeChat interaction. In general, this note uses Christensen’s three business model theories to analyze the case of PDD that helps us better understand the entrepreneurial process, which leads to the disruptive innovation in the e-commerce industry. We found that by creating a solution store (supporting teams of experts), a value-added process (discounted pricing), and enhancing the convenience network (social commerce), the model of disruptive innovation, PDD model has been impacted among second - and third-tier urban and rural customers, thus disrupting the status quo of e-commerce.
References
- Schumpeter J, Backhaus U (2003) The theory of economic development. In: Joseph AS (edn.), Springer, Boston, MA, USA, pp. 61-116.
- Christensen C, Raynor M (2013) The innovator's solution: Creating and sustaining successful growth. Harvard Business Review Press, Brighton, Massachusetts.
- Si S, Chen H, Liu W, Yan Y (2020) Disruptive innovation, business model and sharing economy: The bike-sharing cases in China. Management Decision.
- Si S, Chen H (2020) A literature review of disruptive innovation: What it is, how it works and where it goes. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management 56: 101568.
- Christensen CM, Grossman JH, Hwang J (2010) The innovator’s prescription. A disruptive solution for health care.
- Snihur Y, Thomas LD, Burgelman RA (2018) An ecosystem‐level process model of business model disruption: The disruptor's gambit. Journal of Management Studies 55(7): 1278-1316.
© 2021 Steven Si. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






