- Submissions

Full Text
Significances of Bioengineering & Biosciences
A Simulation Model to Study the Effect of Smart Drugs on the Blood Transfusion Vessels
Hamidreza Shirzadfar*, Mehrsadat Hosseini Nezhad and Hamideh Salimiyan
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Iran
*Corresponding author: Hamidreza Shirzadfar, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Isfahan, Iran
Submission: February 18, 2019 Published: March 14, 2019

ISSN 2637-8078Volume3 Issue1
Abstract
Normal cells of body are growing, reproducing and eventually will die in reaction to motivation that internally and externally evoke them. when one normal cell is mutated, changed and turned into cancer cell. Mutation or the change happens in DNA or genetic substance. When DNA of a cell is changed, that cell will be different from its adjacent cells and it, any more won’t do the functions of normal body cells. When the ‘‘mutant cell’’ is divided, it will be turned into two new ‘‘mutant’ ’cells and this procedure is continued as the same way to turn into that vulnerable cell or mass of cells which is called tumor. One of the treatments of cancer is chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is one of the prevalent methods of curing diseases that by using chemical drugs and chemical substances. lots of chemical drugs that are used for chemotherapy, affect the cell division of cancer cells, particularly those cancers that have very fast cell division. We used Taxol or Paclitaxel for Simulation in this article. which leads to induction of polymerization of microtubules. Paclitaxel is used for treatment of breast and ovary carcinoma, lung cancer and Kaposi sarcoma caused by AIDS.
Keywords:Simulation; Cancer; Smart Drugs; Chemotherapy; Paclitaxel
Introduction
Figure 1:Difference in cell division of normal cells and cancer cell [4].
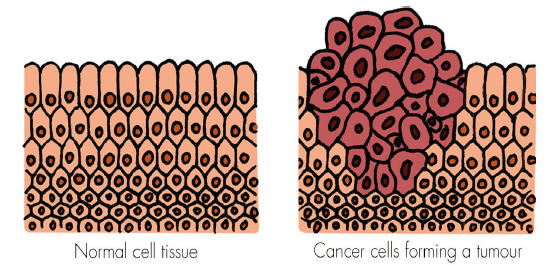
Normal cells of body are growing, reproducing and eventually will die in reaction to motivation that internally and externally evoke them. If this procedure is happened in its balanced and correct way, the body will be healthy and keep its normal function. But the problem begins when one normal cell is mutated, changed and turned into cancer cell. One normal cell may change to cancer cell without any clear reason, but in most cases, this converting is happened because of frequent exposure to carcinogenic substance such as alcohol and tobacco [1]. Formation and function of carcinomatous cells and normal cells are different. Mutation or the change happens in DNA or genetic substance. DNA is responsible to control the formation and function of the cell. When DNA of a cell is changed, that cell will be different from its adjacent cells and it, any more won’t do the functions of normal body cells. This mutant cell will be separated from adjacent cells and won’t know when its growth should end and die [2,3]. In other words, the mutant cell doesn’t follow the instructions or internal signals which other cells are under their control and instead of coordination with other cells, it acts arbitrarily. When the ‘‘mutant cell’’ is divided, it will be turned into two new ‘‘mutant ‘cells and this procedure is continued as the same way to turn into that vulnerable cell or mass of cells which is called tumor (Figure 1). Sometimes, these tumors are benign, and they don’t develop. But if the cells of tumor are developed and divided and destroy their adjacent cells and invade other parts of body, too, they will be considered as malignant tumor. The biggest threat of malignant tumor is their ability in invading healthy tissues and spreading in whole body and this is a metastasis of cancer. If the tumors grow and become bigger, they will block nutrition’s and oxygen to healthy cells and by cancer developing, the healthy cells will die, and patient’s health and performance will be faded away. If this procedure wasn’t stopped, the cancer would lead to the patient’s death [4].
One of the cancer treatments is chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is one of the prevalent methods of curing diseases that by using chemical drugs and chemical substances eradicates the cells especially the cells of microorganisms and cancer cells [5]. The meaning of chemotherapy is not only related to the drugs which are used to cure cancerous glands but also include antibiotics. Generally, lots of chemical drugs that are used for chemotherapy, affect the cell division of cancer cells, particularly those cancers that have very fast cell division. These drugs that cause a damage to a cell, are called Cytotoxic. Some of these drugs make the cell have radical changes and stop its growth that is known as planning for cell death. Scientists have been studying unique characteristics of dangerous and resistant cancer cells in order to target them specifically. It is because during the procedure of chemotherapy besides the cancer cells, other cells such as cells related to growth of hair and internal cells of intestine which have very fast growth speed are invaded and their growth stream will be stopped that leads to disorder in patient’s affairs [6-8]. Although some of the more appropriate drugs have been produced that enable physicians to treat the cancer well. The drugs of chemotherapy can be injected into the body by injections that the drug of chemotherapy is injected in arm, thigh, hip muscle or just below the skin in adipose tissue of arm, leg or abdomen: inside the arteries (IA) that the drug is directly injected into arteries which are nutrients of tumor; intraperitoneally (IP) that the drug of chemotherapy is directly injected into peritonea cavity which involves the intestines, stomach, liver and gonads; intravenously (IV) that the drug directly is injected into vein; locally that in this method, the drug of chemotherapy is like cream (ointment) which the patient put this cream on desired area of skin and orally that the drug of chemotherapy which is in the form of tablet, capsule or is liquid is injected into the body. In simulation, we use intravenous injection of drug (IV), so we should know that in this method the drug of chemotherapy usually is injected into the body through a narrow needle which is inserted in vein of hand or lower part of arm. At the start of each treatment, the nurse inserts this needle into the patient’s hand and extracts it at the end of treatment. If anyone during intravenous chemotherapy suffered pain and irritation (synesthesia), he/she must inform his/ her doctor or nurse. Intravenous chemotherapy is usually carried out through catheter or port and sometimes it is carried out with the help of one pump.
Materials and Methods
Taxol or Paclitaxel is one anticancer drug which leads to induction of polymerization of microtubules.
Figure 2:chemical structure of Paclitaxel.
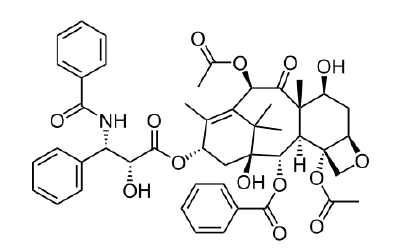
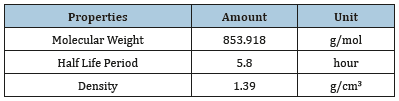
Paclitaxel is used for treatment of breast and ovary carcinoma, lung cancer and Kaposi sarcoma caused by AIDS that its chemical formula is C47H51NO14 (Figure 2). This drug is a Ditripeny compound which is often extracted from yew plant. Nowadays this substance is used effectively all around the world as the most important natural anticancer compound with different mechanism in compare to other similar drugs. This drug looks white and there is not any tablet form, this is a harmful chemical substance which can cause phlebitis (swelling and inflammation of a vein). Sometimes the patient suffers pain, redness or swelling in the area of receiving the drug. Whereas severe allergic reactions took place in some of the sufferers, the patients were asked to take some medicines to prevent these reactions and the physician (doctor) prescribed the particular diet. Paclitaxel is recommended in different times and doses and different plans. The given dose and plan depend on many factors such as height, weight, general health or other health problems and the type of cancer and treatment condition. Metabolism of the drug is hepatic, and its half-life period is 5.3 to 17.4hour. A large quantity of Paclitaxel and its metabolites are repulsed through bile. This drug should be prescribed very cautiously in case of weakness of marrow’s activity or cardiac disorders. Anemia, allergic reactions, reduction of white blood cells or neutropenia and reduction of hematoblast are common complications of Paclitaxel. Due to possibility of occurrence of allergic reactions, the undertreatment patients must be under control at least in the first thirty minutes of infusion of the drug. This drug must be diluted before intravenous injection. The dose of this drug must be decreased 20% in case of the presence of environmental neuropathy or severe neutropenia [9-13], some of its properties are given in (Table 1).
Table 1:The specification and properties of selected drug.
The drug in constant volume is transferred from inside a vein with fixed speed. Part of vessel wall which includes permeable membrane, undertakes the concentrated drug solution release. To express this procedure, it is assumed that there is a constant flux during the contact of the vessel wall and the drug. The final concentration of the drug can be formulated by replacement of droplet velocity. The principles and the way of doing the operation is given in (Figure 3). The desired droplet is inserted in proximity of tip of the geometry. Horizontal lines passing the vessel are applied for the model in operation stage of meshing. First, the droplet is constant at the tip of the environment, but by Appling the constant velocity, it is accelerated before reaching to permeable membrane. Permeable membrane of the vessel is not observable as a single part of the geometry and in marginal conditions is expressed in functional terms.
Figure 3:Overview of marginal conditions and the way of doing the procedure of drug release simulation.
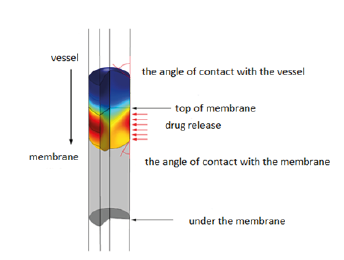
Figure 4:Overview of the variation related to the velocity of passing the drug from the vessel.

Figure 5:Overview of the variations of the received number of moles of the drug over the time.
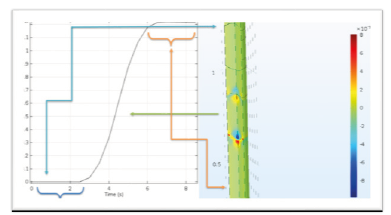
Figure 6:Variations of the drug concentration
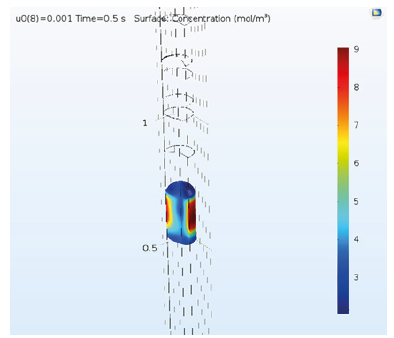
Figure 7:Variations of the drug concentration.
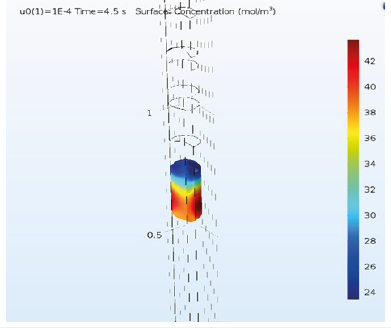
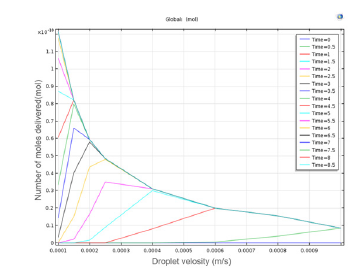
Figure 8:Overview of the variations of delivering drug final amount against droplet velocity.
Result
The drug droplet velocity is invariable before reaching the membrane and as it gets to the membrane, it is accelerated and then after passing the membrane it moves with constant velocity (Figure 4). In first 3 seconds, the drug droplet does not reach to the desired membrane and the membrane doesn’t receive any drug. But after a while, a large amount of that is received and after about six seconds the membrane receives total dose of the drug (Figure 5). By increasing the velocity, the drug is concentrated toward the walls and its lowest concentration is in the center (Figure 6). Regarding that the drug is received in six -second period and the total time of delivery is eight seconds, we choose the time between them to observe the concentration and formation of the drug on that point (Figure 7). By decreasing the passing velocity, the drug concentration is released uniformly. Level of the treatment of the drug should be enough in patients that meets the patient’s needs until the next consumption time of the drug. But unfortunately, it can be observed that irregular decrease or increase of the drug level in the body, can affect its effectiveness. In fact, after sudden infusion of some toxins into the body, it can cause the toxicity in the injection area. Because of this, some technologies were introduced aiming to control and target the drug release toward one special tissue or area. Using these systems makes limitations that may include presence of new toxicities due to applying the new substances in the body along with drugs, delay in drug release and need to new tests to study the drug carrier. The passing droplet velocity has a negative relation with the number of receiving mole. It means if the passing velocity is slower, the greater number of moles will be received (Figure 8).
The aim of drug infusion is increase of the drug bioavailability and we attempt to increase the getting drug to special areas and special times. The drugs are usually introduced into the body digestively (enter through mouth and absorb toward blood along the gastrointestinal tract (digestive tract)) and non-digestively (injection, eye drops…). Therefore, the time of drug infusion must be considered to increase the effectiveness of the drug because the half-life period of the cancer drugs is low so the useful life of the drug should be considered during the infusion.
Therefore, we can say that time and velocity are two parameters which should be considered simultaneously. Because, although by decreasing the velocity of drug injection, its absorption is increased, the time of giving the drug is increased, too that this leads to ineffectiveness of the drug. Also, sometimes may be injected into the patient’s body several times in one day and each time it takes a lot of time, and this is not very pleasant for the patient. Finally, the drug after its delivery is repulsed through kidney or liver, of course small amount of it, is repulsed through saliva or sweat (Figure 8).
Conclusion
The drug release is called the sets of functions, formulations, techniques and systems which are used for transferring of one combined drug into the body to secure the effect of treatment. This may scientifically depend on inside the body or may act by facilitating in systematic pharmaceutics field. Anyway, the amount and the time of drug release and the quality of the release are generally important. The drug release is usually expressed by chemical formula of the drug, but it may include medical drugs or combined drugs. The drug release is a concept that is defined depend on the intensity and dose rate and the way of penetration. In delivering the cancer drug, two parameters; time and velocity, are very important and these two parameters are interdependent. By increasing the velocity, the drug concentration is concentrated in vessel walls, but by decreasing the velocity, we have the steady concentration, also by decreasing the velocity, the number of receiving moles of drug is increased, too. On the other hand, because of interdependence of velocity and time, the time of delivering the drug is increased by decreasing the velocity and with this action, the useful life time of the drug is decreased. Therefore, a specialist very cautiously and considering patient’s needed volume and velocity should injects the drug.
References
- Sudhakar A (2009) History of cancer, ancient and modern treatment methods. J Cancer Sci Ther 1(2): 1-4.
- Halazonetis TD, Vassilis GG, Bartek J (2008) An oncogene-induced DNA damage model for cancer development. science 319(5868): 1352-1355.
- Wiseman H, Halliwell B (1996) Damage to DNA by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: role in inflammatory disease and progression to cancer. Biochem J 313(1): 17-29.
- www.haleo.co.uk
- Devita VT, Chu E (2008) A history of cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res 68(21): 8643-8653.
- Shirzadfar H, Hosseini NM, Salimiyan H, (2018) The medication side effects in the treatment of cancer: a review. Austin Journal of Biosensors & Bioelectronics 4(1): 1-4.
- Nygren P (2001) What is cancer chemotherapy? Acta Oncologica 40 (2- 3): 166-174.
- Asghar TK, Hamidreza S, Elham TK, (2017) Dendrimers and dendrimersgrafted superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, functionalization, and biological applications in drug delivery systems. Nano and Microscale Drug Delivery Systems 75-94.
- Henningsson A, Mats K, Lucia V, Luca G, et al. (2001) Mechanism-based pharmacokinetic model for paclitaxel. J Clin Oncol 19(20): 4065-4073.
- Peltier S, Jean MC, Frédéric L, William C, Jean PB (2006) Enhanced oral paclitaxel bioavailability after administration of paclitaxel-loaded lipid Nano capsules. Pharm Res 23(6): 1243-1250.
- Sandler A, Robert G, Perry MC, Brahmer J, et al. (2006) Paclitaxelcarboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 355 (24): 2542-2550.
- Johnson DH, Novotny WF, Herbst RS, Nemunaitis JJ, et al. (2004) Randomized phase II trial comparing bevacizumab plus carboplatin and paclitaxel with carboplatin and paclitaxel alone in previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 22 (11): 2184-2191.
- Mok TS, YiLong Wu, Thongprasert S, Patrapim S et al. (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361 (10): 947-957.
© 2019 Hamidreza Shirzadfar. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






