- Submissions

Full Text
Research in Pediatrics & Neonatology
Deep Breathing Exercise in Reducing Blood Pressure Among Hypertensive People at Selected Rural Areas of Northern Gujarat
Siva Subramanian N1 and Mahalakshmi B2*
1Department of Mental Health Nursing, Nootan College of Nursing, Sankalchand Patel University, India
2Department of Pediatric Nursing, Nootan College of Nursing, Sankalchand Patel University, India
*Corresponding author: Mahalakshmi B, Department of Mental Health Nursing, Nootan College of Nursing, Sankalchand Patel University, India
Submission: June 18, 2022; Published: August 10, 2022

ISSN: 2577-9200 Volume6 Issue4
Abstract
In developed countries, hypertension is the fourth leading cause of mortality, whereas in poor countries, it is the seventh [1]. Some other treatments are required to manage hypertension. Hypertension is a major public health concern in India and around the world, owing to its high prevalence and associated risk of cardiovascular and kidney disease [2]. Hypertension makes individuals multiple times more inclined to stroke and multiple times bound to have coronary failures. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of deep breathing exercise on blood pressure among patients with hypertension. A Pre-Experimental one Group Pre- test Post- test design was adopted. A sample of 30 Hypertensive patients was selected using convenient sampling technique at Kansarakui visnagar.
Data on demographic variables were assessed. Deep breathing exercise was demonstrated to the participants and their level of blood pressure was measured by sphygmomanometer before and after the intervention. The result displays that in pre-test out of 30 samples, (28%) had pre-hypertension, (20%) had Stage I hypertension, (8%) had Stage II hypertension and (4%) have Normal Blood Pressure. Whereas after intervention, Post-test results shows that out of 50 samples (16%) have Normal Blood Pressure, (20%) had Pre-hypertension and (4%) had Stage I Hypertension among clients with Hypertension. The pre-test mean score among patients with Hypertension was 1.50 with standard deviation 11.352 and post-test mean score among patient with Hypertension was1107 with standard deviation9.090. The calculated paired ‘t’ test value is t=7.971 was found to be statistically significant at p value.
Keywords: Hypertension; Breathing exercise; Hypertensive patients
Introduction
High blood pressure is a major public health issue in India, and its prevalence is on the rise in both urban and rural areas [1]. In fact, hypertension is India’s most common chronic condition. Pharmacological, non-pharmacological, and alternative therapy can all be used to treat hypertension [3]. Deep breathing exercise is one of the exercise and relaxation techniques that helps to keep blood pressure in a healthy range [4]. The study’s purpose is to see how efficient deep breathing exercise is at lowering blood pressure in hypertensive patients [5]. laughter breathing exercise is also taking key role in reducing stress and helps to recovery from hypertension [2,6].
Need of the Study
In South Asia, high Blood Pressure (BP) is the third most important risk factor for disease related burden (2010). In India, Hypertension (HTN) has a significant public health impact on cardiovascular health and healthcare systems. In India, HTN is directly responsible for 57% of all stroke deaths and 24% of all Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) deaths. In 2013, the global prevalence of high blood pressure in persons aged 25 and above was estimated to be over 40%. Cardiovascular disease killed 17.3% of persons, and noncommunicable disease kills 80% of people in poor and middle income nations [7].
Objectives
A. To assess the pre and post-test level of the blood pressure
among hypertensive clients in experimental group.
B. To compare the pre and post-test level of blood pressure
among hypertensive clients in experimental group.
C. To find out the effectiveness of deep breathing exercise on
post-test level of blood pressure among hypertensive clients in
experimental group.
D. To determine association between the pre-test blood
pressure level among clients with hypertension with their
selected demographic variable such as age, gender ,education
status, occupations, durations of hypertension ,family history
,food pattern
Hypothesest
H1: There will be significant difference in pre and post-test
level of blood pressure level among hypertensive client in
experimental and control group
H?2: There will be significant difference between post-test level of
blood pressure level among hypertensive client in experimental
and control group
H3: There will be significant Association between pre-test level
of blood pressure level among hypertensive client with selected
demographic variable like age, gender, education, status and
occupation, duration of hypertension, food pattern, and family
history..
Materials and Methods
A Quasi-Experimental One Group Pre-test Post- test research design was used to conduct the study at Kansarakui, visnagar among 30 Hypertensive samples using the convenience sampling technique. The criteria for sample selection were known Hypertension Patient and who is medically fit to do Breathing exercise. The exclusion criteria were smokers and Women under contraceptives. The data collection was done with prior permission from Medical Officer at Kansarakui, visnagar. The purpose of the study was explained to the patients and written informed consent was obtained. The demographic data was collected by using questionnaire and the pre-test level of Blood Pressure was measured by using Sphygmomanometer. After the pretest, the investigator demonstrated the deep breathing exercise to the patients and Repetitive trails were given to the patients for 10-20 minutes twice a day, for 5 consecutive days. On the 7th day, the post-test level of blood pressure was assessed by using sphygmomanometer and recordings are noted in the chart. The data was analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics. The sample characteristics and level of Blood pressure were described using frequency and percentage. Chi- square was used to associate the pre-test and post-test level of blood pressure with the selected demographic variables.
Results and Discussion
Table 1: Frequency and percentage distribution of the sample according to the demographic variables in control group and experimental group.
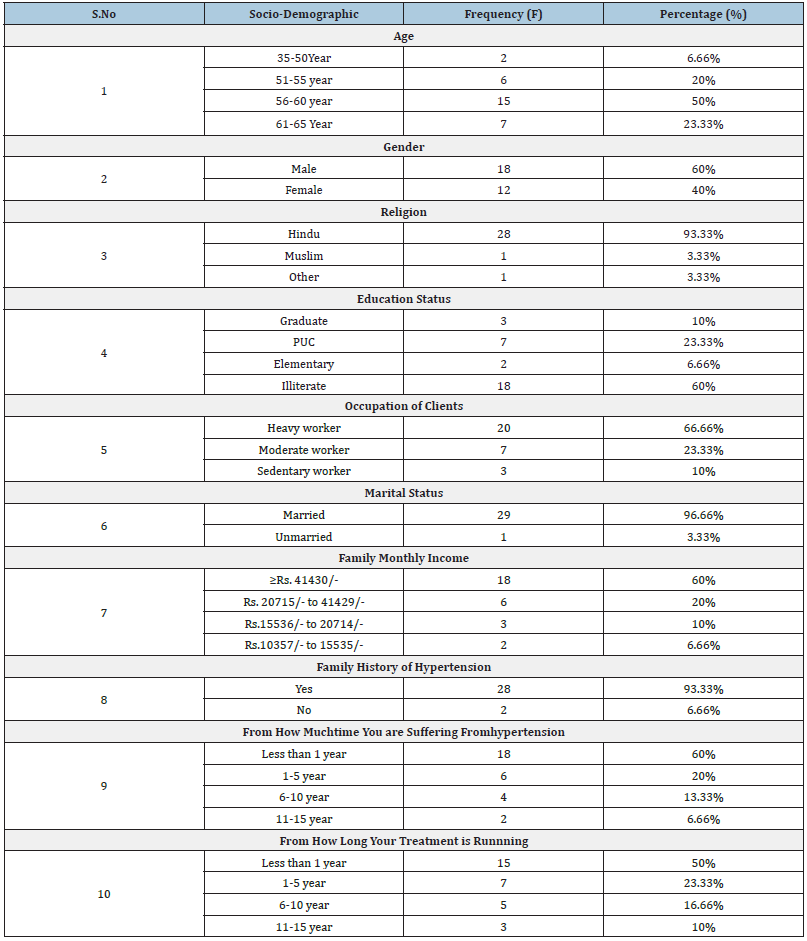
Table 1 show that the Frequency and percentage distribution of demographic variables of patients with hypertension showed that out of 30 sample in regards to the age 40% bellows to 50-60 years, 28% belongs to 40-50 years, 20%belongs to 60-70 years and 12% belongs to 30-40 years. with respect to religion, 98% were Hindu, 0% were Muslim and Christian. Educational status shows that 40% are instructed up to higher secondary. According to occupation 46% are Employee. As far as dietary pattern concerned as 80% are Non- vegetarian and 20% are vegetarian.
Figure 1:Determine the effectiveness of deep breathing exercise on level of blood pressure among patients with Hypertension.
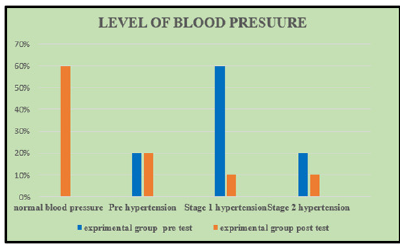
Figure 1 result shows that in the pre-test, out of 30 samples (20%) had pre-hypertension, (20%) had Stage I hypertension, (60%) had Stage II hypertension and (20%) have Normal Blood Pressure. Whereas in the Post- test after intervention, out of 30 samples (60%) have Normal Blood Pressure, (20%) had Prehypertension and (10%) had Stage I Hypertension , (10%) had Stage II hypertension among patients with Hypertension.
Table 2: Mean standarddeviationandpairedtestvalueonpreandpost-testbloodpressurelevelamongclients with hypertension in experimental group and control group.
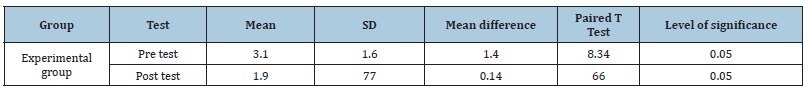
Mean and standard deviation of pre-test and post-test among patients with hypertension. Table 2 represent, the mean score on blood pressure level in experimental group was 3.0 in pre-test and 1.90in post-test. The paired t‘ value was 8.34 which is significant at p>0.05. It shows that yoga was effective in reducing the blood pressure level among clients with hypertension. Hence the research hypothesis (H1) is accepted. Association between the Post Test Level of Blood Pressure among Patients with Hypertensive Patients with Selected Demographic Variables The result discovered that there is no significant association between level of blood pressure with selected demographic variables such as Age, Religion, Educational status, occupation and dietary pattern of hypertensive patients.
Discussion
Our current study looked at the impact of a “deep breathing exercise” among hypertensive patients and show decreased blood pressure. The results of the current study show that doing deep breathing exercises twice a day for a week lowers systolic blood pressure significantly. Numerous studies on the benefits of breathing exercise on blood pressure reduction have been conducted, none of which have found a beneficial result. The researchers conducted a 3-month interventional trial with 60 samples of fast and slow breathing exercises, and the results show that both therapies reduced blood pressure longitudinally. In the experimental group, the mean pre-test blood pressure level was 2.0 and the post-test blood pressure level was 9.70. At p>0.05, the paired t value was 7.28, which is significant. It demonstrates that yoga is useful in lowering blood pressure in hypertensive patients. The mean blood pressure level in the control group was 5.96 in the pretest and 2.83 in the posttest. The pairing which is unimportant. There is no link between pre-test blood pressure levels and selected demographic characteristics such as occupation, gender, length of illness, family history, and food pattern among hypertensive patients.
Summary
Using a quantitative evaluative technique, In a selected community, a true experimental design was performed to test the effectiveness of yoga among hypertensive customers. As indicated by Newby, the conceptual framework was based on Ludwig Von Bertalanffy’s General System Theory (Modified) (1968). (1996). The study’s instrument was divided into two parts. The first half dealt with demographic factors, while the second dealt with yoga. The sample was collected using a simple random sampling procedure, and the data was acquired from the study participants in the experimental group. Descriptive and inferential statistics were used to collect and analyze the data. p > 0.05 was used to determine the threshold of significance. Put the hypothesis to the test.
Conclusion
Regular practice of deep breathing exercise is viable in lessening systolic and diastolic blood pressure by upgrading parasympathetic action and reducing sympathetic excitability thereby effectively reducing the blood pressure.
References
- Huang Y, Cai X, Li Y, Su L, Mai W, et al. (2014) Prehypertension and the risk of stroke a meta-analysis. Neurology 82(13): 1153-1161.
- Sivasubramanian N (2021) Impact of life changing therapies on stress, depression and quality of life of geriatric groups. International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews 8(2): 105-110.
- Mahtani KR, Beinortas T, Bauza K, Nunan D (2016) Device guided breathing for hypertension: A summary evidence review. Curr Hypertens Rep 18(4): 33.
- Cernes R, Zimlichman R (2017) Role of paced breathing for treatment of hypertension. Current Hyperten Rep 19(6): 45.
- Elakkuvana Bhaskara Raj (2011) Text book of community health nursing, (1st edn), Jaypee Brothers Medical Publications, New Delhi, pp. 123.
- Sivasubramannian N (2021) The music versus laughter on depletion of depression among old age. Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research 8(4): 356-361
- Vasuki G, Sweety LM (2017) The study of usefulness of deep breathing exercise on blood pressure in pre hypertensive and hypertensive patients. Indian Journal of Clinical Anatomy and Physiology 4(3): 400-403.
© 2022 Mahalakshmi B. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






