- Submissions

Full Text
Research & Investigations in Sports Medicine
Determining the Effective Factors in the Appropriate Organization of Student Sports Events
Mohammadbagher Forghani Ozrudi*
Department of Physical Education, Master of bachelor, Iran
*Corresponding author:Mohammadbagher Forghani Ozrudi, Department of Physical Education, Master of bachelor, Iran
Submission: December 09, 2023;Published: December 21, 2023

ISSN: 2577-1914 Volume10 Issue1
Abstract
Introduction:Student sports are the foundation of professional and championship sports and should have a special place in the development of sports events. The aim of this research was to determine the effective factors in the appropriate organization of student sports events. Methods:This research method was qualitative and it is based on the foundation data approach with Glaser approach and field way. Information gathering is done 17 experts who are familiar with sports events, events, security school sports and sports management experts, interviews without structure in a purposed way and simultaneously analyzed with a collection of open, axial and selective codes. Also, stability way of interview retest was used for stability measurement and that was 0.85. Factors ranking were analyzed with Shannon entropy test and SPSS24 software. Results:The results showed that factors such as health management, human resource management, financial resource management, organizational and managerial developments, event contribution in achieving the organization goals, the consequences of the event, and safety and security management are effective factors in safety and security of sport events in Student competitions. Entropy analysis showed that safety and security management, financial resource management, human resource management, have the highest score and the lowest score in impression degree on security and safety management of student sports events. Conclusion:According to this result, it is suggested that the various categories extracted from this research be considered in the safety management of student sports events to prevent accidents. Also, special attention should be paid to many factors to prevent problems and accidents, promote safety culture, planning and management.
Keywords:Sport event; Security; Safety; Student sports; Appropriate organization
Introduction
The most fundamental factor in the economic, social and political growth and development of each country is education and this provides more possibility of quality and inclusive education [1]. Therefore, educative and effective sport has a special place in the formal education system and is considered by the country macro policies [2]. Supporting the development of educational, training, cultural, artistic and sports spaces and equipment are the duties of the National Organization of Child Education [3], with the practical strategies of the Ministry of Education. The development of physical education and sports is a basis for providing and training the healthy manpower and it is the part of national development programs [4] and it is regarded in the document macro-policies and perspective of the Islamic Republic of Iran in 2025 and in country five-years development plans. Also, the fundamental transformation document in education and also in the national curriculum, the physical education with religious, intellectual and social emotional education is considered in the canal documents of the Ministry of education, it emphasized the importance of school sports development [5]. On the other hand, sport is a socio-cultural phenomenon that has a dynamic relationship with a set of social institutions and should be considered as part of the human structural needs [6].
This social phenomenon includes dynamic power that can enhance the factors in social and cultural structures with each interaction and make them new one [7]; but they are affected by dangerous factors and create problems for society [8]. The geographical, racial, ethnic, political and ideological borders are the same for all athletes, because of increasing sport development and student sports is one of them [9]. Educational sport is an essential part of the formal school curriculum, which, is a rule in the sports pyramid, to target the student community, and it is one of the effective movements in developing health and promoting an active lifestyle and respect to different ethnicities and languages with considering student society [10]. This effective approach considered for increasing the ‘physical activity, development of students emotional, moral and educational abilities with sports activities and events in a supportive environment with safe and comfortable infrastructure and facilities. There is no doubt in studies about student’s sport and school sport potential for solving the various problem of students educational psychological and social issues in political, media and scientific environments [11]. Sport extension in different society, especially in student community is one of the practical strategies for the development of public sports that guarantee the physical, mental, emotional health and reduce students’ social tensions and on the other hand it is the development of championship sports in student sports and national teams and it is in each country [12]. Therefore, the purpose of the student sports development program is to increase participation in sports, identifying and developing sports talents, and promoting a culture of healthy and active lifestyle and strengthen social cohesion among students and in society consequently [13,14].
Today, attention in safety management process is in planning and organizing activities with a focus or risk management such as sports competitions [15]; Attention to equipment and facilities, safety, budget, staff, time and place of a sporting event are very important in achieving success [16]. Safe attitude is an individual concept and is rooted in the reflection of feelings and beliefs that a person has about different ways of safety and it is an important factor in preventing events as a security attitude [17]. Safety awareness also shows people’s perception of danger in the workplace and activities [18]. Many different groups in sport spaces, parents’ concerns for children distance, public transportation dangers, health, efficiency of facilities and human resources trust, such as coach and referee and executive factors that shows the importance of management security, is the reason of this issue [19,20]. The best way to prevent events in sports is reducing dangerous condition and also safety in sport places [4]. Safety principles mean reducing the risks in sport places. All possible dangers in a process should be identified and controlled with accurate and correct evaluation to prevent the events [21,22]. Basically, in sports, there are events and problems due to disobeying the safety principles. Athletes’ safety is one of the most important factors in development and growth of sports activities [23]. Also, Sports facilities play an important role in safety management of competitions and athletes’ success. Students are seen as sports pieces and future champions in education of the developed countries of the world [24]. Most sports places are available to schools and by allocating appropriate budgets for achieving this goal and they prepare their future champions for winning medals in the Olympics and world areas [25].
Event safety management is so important due to events and athletes physical, mental and psychological injuries in sport spaces [26]. These events can be due to the inadequate quality of sports facilities and places, lack of proper physical fitness in players, lack of coach’s knowledge about various injuries, poor performance of sports skills, etc. [27]. These horrible events cause athletes injuries and finally cause damage and other costs and legal problems, negative psychological atmosphere on sports, reducing the motivation of beginners, reducing the ability of professional athletes and stopping sports activities, loss of manpower, injury and family suffering, productivity reduction and heavy costs [28] and either they effect the healthy economic costs, very serious psychological costs on athletes and family special society [29]. One of the solutions that proposed by the Ministry of Education in 2019, was promoting the level of sport knowledge and they are in basis of sports events and happenings and damages of school and it is stopped due to the occurrence of pandemic disease Covid-19 [30], which due to the occurrence of pandemic disease Covid-19 stopped. Regarding safety in sports event management, Habibnia Remi et al. [31] said about the events and barriers such as lack of informing and correct planning from ministry to offices, non-observance of safety tips and suitable places for Olympiad, and ignorance of goals and celebrants non-cooperation in Olympics of in school plans [31]; Kargaz et al. [7] divided the factors that affect the safety and security of sport events into five areas: substructions , technology, media and advertisement, human resources, and cultural activities [7]. considered these twelve major effects as safety factors in sport. including professional and committed management, organizational safety culture, professional competence, safety rules and regulations, legal and ethical requirements, health principles, positive approach to the environment, physical and psychological characteristics and personal equipment, space human engineering (ergonomics), standard places and equipment, medical procedures and the use of modern technologies [4]. A study by Veitch et al. [32] in Australia found that 94% of parents said safety is the most important reason to choose a game for their children’s play [32]. Examining the risks of sports activities, Yevstafyev and Yevstafyev [33] with evaluating the dangers of sport activities, stated that all aspects of risk probability, importance of risk level and technical characteristics of risk are considered, so it is necessary to analyze many inherent risk factors in sports places [33].
Ghahramani & Fazli [34] stated that some safety experts believe that all accidents occur due to the weak and negative attitude of individuals [34]. Efforts to safety in sports is one of the key factors and attention to the safety principles and prevention of accidents caused by sports activities should have priority in all societies, especially in developing countries. Therefore, care and attention to athletes has an extremely important role in human capital and in preventing the loss of material resources [33]. Planners and practitioners of sport activities should consider athletes’ safety due to the above considerations. Also, they should present appropriate and effective models of all components related to safety in education aspect [29]. All research about sports safety, surveyed hardware factors such as sports field, space and place, platforms and how to access them and ignored other factors that have more role in this field. Among the organizations and executive parts of the country, the Deputy of Physical Education and Health Education, as the agent of student sports, has an important role in student event safety. Presently, students participate in festivals, competitions, and sports Olympic in school, regional stage (between schools), provincial stage and national competitions [35]. In these competitions, the participants are at least 10% students of country including more girls and outridden areas, in different sport fields as Champion School and Champion Center. Also, in recent years, sport honors of country are 67 Asian and world championships of national student teams that are taken by students in Asian football, futsal, basketball, Asian wrestling, Asian judo, Asian taekwondo, athletics and wrestling etc., it is obtained. This study identifies the factors that affect the safety and security of sport events in student competitions despite the improvement of quantitative indicators in student sports during the country’s development programs and special attention to student sports in the document of education fundamental transformation and also the structural improvement of physical education in ministry of education and implementation of various programs, activities and projects in deputy of physical education and health and on the other hand, the importance of safe and un risky sports events and also the lack of a holistic systematic plan in safety of student sports events with lack of research resources in this field.
Fgure 1A:Preoperative sagittal MRI.

Fgure 1B:Post-operative sagittal MRI.

Methodology
This research method is based on the database strategy and on the Glaser approach in fielded way. This method is used when the research literature on the subject does not have the necessary richness. Also, the aim is to present a new theory that has not been proposed in the research communities. The main method of data collection in this method is the use of interviews. By analyzing and coding the text of the interviews, a paradigm model is presented. In the grounded theory method, a theory is developed using a set of data. So that this theory explains a process, action or interaction on a broad level. Therefore, this study is practical in nature and its research method was qualitative. The interviewees in this study are experts of sports events safety in school sports, school sports coaches and sports management specialists in Ministry of Education, the Ministry of Sports, universities and the Student Sports Federation. The sampling in this study was non-random and in purposeful method. Sampling was continued until theoretical saturation and finally the opinions of 17 experts were collected during unstructured interviews until the theoretical saturation was reached in the present study. In the purposive sampling of data collected by the database theorist to describe processes, it includes various forms of qualitative data, and for interviewing with observation, database theory supports a unique approach that distinguishes it from other quantitative and qualitative approaches to data collection. On the other hand, unlike the sampling done in quantitative methods, theoretical sampling cannot be planned before starting the study and database theory. Rather, special sampling decisions are formed during the research process itself.
In the first part of the data collection process, the data were used with library methods, and in the second part, qualitative interviews with elites, experts and experts, in this project. According to theoretical foundations of qualitative research, the analysis and coding were performed with interviews at the same time. Then, summarization, presentation and conclusions of data were done respectively. And identify the final list of factors that affect the safety management of student sports events. The data and codes production process of interviews was done in three stages, open, axial and selective coding. Researchers analyzed data with open and axial coding for developing the theoretical components of safety management of student sports events. Open and axial coding process is continued to clarification or effected factors., and the main and sub-categories and their relationship were integrated during the selective codification and finally affective factors to security management and safety of sport events in students’ competitions were identified. Also, credibility, transferability and dependability are used for credit and validity. In this project, for stability measurement, the re-test reliability method was used, that refers to the degree of compatibility of data classification over time. During this project and coding of interviews, some interviews were re-coded as samples in one week. The interviews of this project were 0.85 refer to first extracted codes from those interviews and re-test reliability codes. Factor rankings were analyzed using Shannon entropy test and MAXQDA & SPSS24 software.
Result
There are 13 male (76.47%) and 4 female (23.53%) in this research. That 94.11% had a master’s degree (6 people) and PHD (10 people) and physical education and they had valuable history in planning and executive management in macro level of country student’s sport. The age average of participants was 44.76±5.11 years and the work history average history of the participants was 26.12±4.07 years. In Table 1, the advent process of physical fitness, psycho-mental, safety of places and sports facilities, personal and social health and management and planning were specified according to interviews texts, codes, concepts and categories. Different categories and concepts were produced based on the qualitative findings of the interviews in this project. Some categories are for safe performance and some of them are for safe condition in sport safety at events prevention. There are 299 open codes from interviews and 75 open codes from texts and projects. After the open codification process, these codes were incorporated in concept format by data analyzing and putting the open codes together several times in different forms but in same process and meaning and open codes were classified into 21 concepts. In step 281, initial code has 10 main categories include management and planning (with 5 sub-categories), health principles (with 3 subcategories), management of places and equipment (with 5 subcategories), emergency services (with 4 sub categories), Expertise and competence (with 4 sub-categories), human resource management (with 3 sub-categories), mental and psychological needs (with 4 sub-categories), physical and mental condition (with 2 sub-categories), usage of new achievements (with 3 subcategories), Ministerial instructions (with 2 sub-categories) were extracted implicitly (Table 2).
Table 1:Details of open codes and related categories of research concepts.
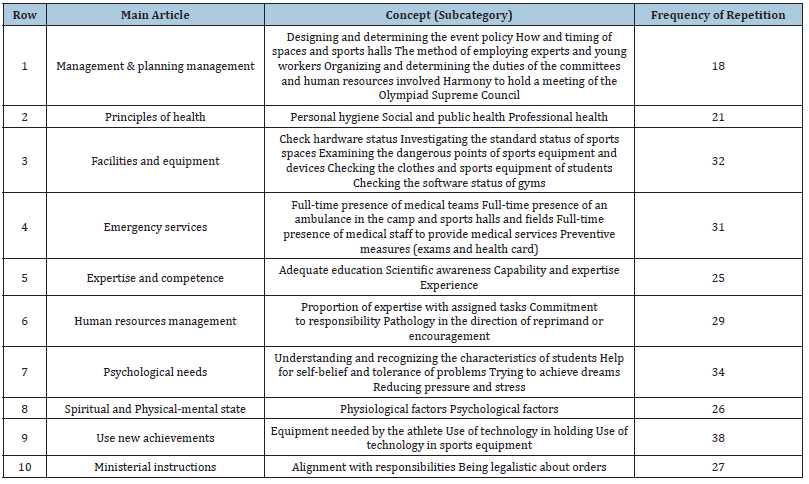
Table 2:Presentation of selective (theoretical) coding of interviewees.
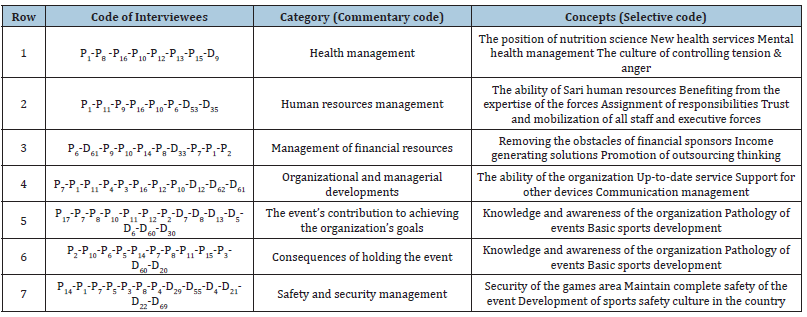
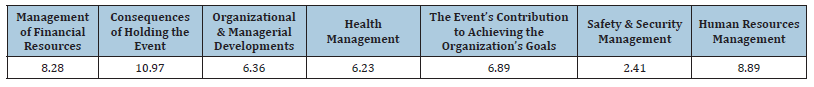
After that, the relationships between research main categories were explained by researcher notes and theoretical codification (which explains the relationships between codes) and finally, after selective (theoretical) codification, 7 main categories including health management (4 concepts), Human resource management (4 concepts), financial resource management (3 concepts), organizational and managerial developments (4 concepts), event contribution in organization goals (3 concepts), events consequences (3 concepts), safety and security management (3 concept) were approved by experts. Finally, in Table 3, concepts and categories from data and indicators weighting process by Shannon entropy method are presented based on codes. Results show index weight, according to the steps mentioned in Tables 3&4. Table 4 shows that in general, the variables of safety and security management is in priority, financial resource management is in second priority, human resource management is in third priority and event consequences is in last priority of affecting to security and safety management in student sports events from different respondents.
Table 3:Weighting of indicators using the Shannon entropy method.
X1=Health management, X2=Human resources management, X3=Financial resources management, X4=Organizational &
managerial developments, X5=The contribution of the event to achieving the organization’s goals, X6= The consequences
of holding the event, X7=Safety & security management
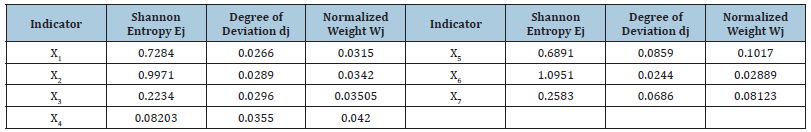
Table 4:Dimensions weight.
Discussion and Conclusion
This study s goal was to identify and prioritize the effective components of safety and security management in sport events (Case study: Student competitions). According to that physical education and sports are essential parts of formal school curriculum; Student sport requires an effective approach to increase students’ physical activity through sports programs, activities and events in a supportive place with safe and comfortable substructure and facilities. Therefore, sport development includes structures, systems, equal opportunities, and processes that enable individuals to participate in sport and improve their performance to desired level [13]. The goal of student sports development program is to increase participation in sports, identify and develop sports talents, promote the culture of healthy and active lifestyle, and strengthen social cohesion among students and consequently in society [14]. This project is for institutionalize safety management in student sports events and student sports Olympiads before, during and after competitions and sports place and sites such as stadium, gym, swimming pool, outdoor sports field, health paths, transportation, security issues, personal and environmental health, management and planning of competitions, etc., to prevent incidents in student sports. And it can determine safety in sport places and students sports Olympiad. According to explanation of finding about safety management and identification of its categories, ten main categories including safety and security management, management and planning, health principles, facilities and equipment management, emergency services, expertise and competence, human resource management, spiritual and Mental needs, physical and mental condition, using new achievements, ministerial instructions were identified.
Each of these categories also includes several dimensions and concepts that are considered as basis categories of safe condition based on criteria such as high repetition, centrality, communication with other categories, ability to effect other categories and make changes in them “safety process management” as safety central category in student sports events, safety culture of competence and expertise, ministry directives and instructions, professional obligations and responsibilities as basis categories of safety activities and security management, sports places and facilities standardization, health and cleanliness management, Physical and mental fitness status and sports equipment, student sports development attitude, medical and emergency services, proper management of human resource utilization, management and planning. Factor physical priority results show that in general, safety and security management is in the priority, financial resource management is in the second priority, human resource management is in the third priority and event consequences is in the last priority to affect security and safety management of student sports events from different respondents’ point of view. This project finding is consistent with the results of Hosseinpour et al. [4], Mirzaei Kalar et al. [5], Vahdani et al. [36], Faber et al. [37]. Paying attention to essential and requirable infrastructures for the success and development of sports activities is very important and necessary [37].
Student sport, which covers a large population of the community, needs attention more than any other athlete. The growth and development of student sports will ensure the development and success for national teams and youth national teams in the coming years. Safety literature has focused on sport places and equipment security. To safety for preventing the events, more attention has been paid to upgrading the places and standard equipment that lack of technology and standard in sport places and equipment cause incident in sport. In this regard, Hosseinpour et al. [4] identified twelve major categories including professional and committed management, organizational safety culture, professional competence and comfit, safety rules and regulations, legal and ethical requirements of health principles, positive approach to environment, Physical and psychological characteristics and personal equipment, human engineering (ergonomics) of space, standard places and equipment, medical procedures and application of modern technologies [4]. For the student successful event that can help to student sport development, other effective factors such as developing strategies and programs are very important. The goal of strategy explication is to provide a vision for development. Strategy identifies specific priorities, programs and special support for us. Due to the student presence in the educational places for several years in three grades of elementary, junior high and high school, student sport needs to develop a strategy and implement it. The success of student-athletes can help base national teams to discover top talent and promote the success way for athletes. Athletes’ abiliment blossoming and the regular holding of student competitions and exercises require long-term and codified planning to succeed in student sports. And this case is one of the concepts about safety in this project. Faber et al. [37] examined the factors and barriers to develop strategies for increasing school sports and identified the key factors for motivation of physical education teachers, managers planning and structures and organizations support [37]. Mirzaei Kalar et al. [5] said that strategies factors, processes and paths have a direct and meaningful effect on student sports development and the factor of stakeholders also influences development outcomes [5]. Vahdani et al. [36] stated that improving space quality and sports equipment (safety, standardization, etc.) as two main and key strategic goals of the Physical Education Office, play the most important roles in development of physical education curriculum and public sports and extracurricular sport activities [36].
Another important and effective issue regarding sport event health is its “security management”. Kargaz et al. [7] considered the process of event security management in several steps of management, planning, policies and disciplinary plans, etc. Security management was evaluated as one of the main categories of this research in creating safety conditions [7]. Sport can be an opportunity for transforming organized social competition into a non-violent struggle; and also, sometimes it is in violence and conflicts. Safety and security in sports places and facilities are one of the most important factors that can have a great impact on attracting more people to sports and, conversely, lack of them can cause many people digress to sport [38]. The security process is one of the most important and essential issues in planning and organizing the organizers activities in sports competitions; The reason is attention and presence of many different groups in sports places, such as football stadiums, which needs more security arrangements. Security arrangements and processes in sport and social places have a special place in event organizers planning and major and international competitions, and sport senior executives seek solutions to deal with and prevent unforeseen events in stadiums and sports places [39]. For example, Mohammadnejad [40] stated that facilities and equipment improving for football fans, optimal and standard construction stadium will lead to controlling the sport violence and aggression in Iranian football [40]. On the other hand, providing security and hosting student games can always bring peace for parents and the educational system in the country. It will also help maintain the country’s stability and enhance the country’s position and capabilities in holding international events on the other hand, providing security in the village or hosting student games can always bring peace to parents and the entire educational system of the country. It will also help maintain the country’s stability and enhance the country’s position and capabilities in holding international events. Attention to prevention management and safety culture has a mutual relationship with safety management, and in this project, effective categories for creating safe conditions and success in sports places and important categories in providing safe practices in sports and activities are stated.
According to Henrich theory, the main causes of incidents are related to people’s unsafe performance and unsafe conditions in the sports places. Given that most causes of incidents are unsafe behaviours and, consciously or unconsciously, these result from negligence, or lack of necessary training, it seems that unsafe behaviours and activities can be minimized by using an identified category. Using technical and specialized training and how to use places and equipment, institutionalizing safety culture and applying safety instructions can have some kind of maximum efficiency. In sports facilities utilization, ergonomic engineering, health and environmental status, and also using modern technologies, medical services, and personal equipment should be considered to provide safe conditions for student sports events. Among the limitations of this research was the lack of updating of human resources information on holding student competitions at the country level due to the occurrence of corona restrictions and the lack of holding competitions in recent years. According to the results of the research, it is suggested that to improve the safety of student sports events in each national and provincial competition period, the pathology of student sports events should be addressed to locally prepare and standardize the checklists for holding sports competitions before and during the event. and preparing the relevant reports after the event to hold these competitions with maximum safety in the future. On the other hand, strategies for empowering human resources in holding student sports events in all cases (health management, human resources management, financial resources management, organizational and managerial developments, the contribution of the event to achieving the organization’s goals, the consequences of holding the event and safety and security management) to be planned and implemented in the form of specialized training courses during the academic year from the level of the ministry to the headquarters of the provinces. Also, the solutions presented in different departments should be introduced to the participants of such competitions in specialized national seminars (face-to-face or online) in the form of experience-oriented in holding student sports competitions.
Acknowledgment
We are grateful to all participants who helped us with this research. The article is an extract from a research project (code: 14603/m) Mazandaran University of Science and Technology.
- Bastanipour MM, Nozari H, Shirzadi R (2021) A comparative study of the development-oriented approach of the upstream documents of the education system of Iran and Turkey. Educational and Scholastic Studies 9(4): 311-333.
- Rasekh N, Sajjadi S, Razavi S, Dousti M (2018) Analysis of the educational sport structure in Iran. Research on Educational Sport 6(14): 17-44.
- Supreme Council of the Cultural Revolution (2021) Statute of the national organization of child education.
- Hosseinpour E, Bagheri G, Alidost Ghahfarokhi E, Amiry M, Jalali Farahani M (2018) Designing safety model in sports (using grounded theory). Iranian Journal of Occupational Health 15(4): 34-49.
- Mirzaei Kalar A, Hemmatinejad MA, Ramezani Nejad R, Moradi Lenbar M (2016) Development of student sports in the documents of the deputy minister of physical education. Second National Conference on Applied Sports and Health Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
- Forghani Ozrudi MB, Nikkhoo Amiri M (2018) Investigating the relationship between holding in-school sports Olympiads and reducing delinquency in students. Roshd Physical Education Training 19(1): 23-25.
- Kargaz G, Ghafouri F, Mohammadi Moghaddam Y, Moradi Siasar G (2018) Presenting a model of factors affecting security of Iranian sport events. Journal of Social Order 8(4): 157-190.
- Saeidi Majd N, Abdolmaleki H, Khodatari A (2020) Identifying and prioritizing factors affecting the security of sport facilities based on fuzzy Delphi and MADM. Sports Marketing Studies 1(3): 50-26.
- Dastigerdi M, Dabir A, Shariati Feizabadi M (2020) The structural equation modelling of disorders concepts in Iranian stadiums. Karafan Quarterly Scientific Journal 16(2): 189-206.
- Choi SM, Sum KWR, Leung FLE, Ha SCA, Sit C, et al. (2021) Predictors of physical activity levels in university physical education implementing sport education. Journal of Sports Science & Medicine 20(3): 516-524.
- Siedentop D, Hastie P, Van der Mars H (2019) Complete guide to sport education. Human Kinetics, (3rd edn), p. 328.
- Bailey R (2018) Sport, physical education and educational worth. Educational Review 70(1): 51-66.
- Raw K, Sherry E, Rowe K, Turner S (2021) Safety and relational continuity in sport for development with marginalized young people. Journal of Sport Management 36(4): 369-382.
- Sherry E, Schulenkorf N, Chalip L (2015) Managing sport for social change: The state of play. Taylor & Francis 18(1): 1-5.
- Porsanger L, Sandseter EBH (2021) Risk and safety management in physical education: Teachers’ perceptions. Education Sciences 11(7): 321.
- Khodayari M (2019) Factors affecting the proper holding of a sporting event. Journal of Physical Education Development 20(3): 33-35.
- Rudgarnejad F (2019) The effect of job stress on safety behavior with the role of emotional intelligence modulator in the terminal of operators of the general administration of ports and maritime of guilan province. Teaching on Marine Sciences 6(3): 119-134.
- Khakpour AR, Samiei Zafarghandi A (2015) Model for safety performance evaluation based on organizational factors affecting safety industries using Fuzzy Inference System. Irtiqa Imini Pishgiri Masdumiyat 3(1): 25-34.
- Abernethy L, MacAuley D (2003) Impact of school sports injury. British journal of sports medicine 37(4): 354-355.
- Janbozorgi E, Eliasi M, Hosseinian S (2010) Preventative role of policing in preventing football spectators’ from displaying destructive behavior. Police Management Studies Quarterly 5(2): 251-271.
- Kim IG, Kwon HW, Choi JH (2016) Safety management network of sports facilities abroad and system status. Journal of digital Convergence 14(6): 547-562.
- Lee YJ, Kim Y, Yu H (2018) Improving local safety management in Korea: A case study on local safety index and leisure sports safety management. Information & Security: An International Journal 40: 92-99.
- Ford MT, Tetrick LE (2008) Safety motivation and human resource management in North America. The International Journal of Human Resource Management 19(8): 1472-1485.
- Porsanger L, Magnussen LI (2021) Risk and safety management in physical education: A study of teachers' practice perspectives. Frontiers in Sports and Active Living 3: 76.
- Alizadeh V, Shahlaei J, Alizadeh L (2017) An Investigation into safety conditions of outdoor sport spaces in public middle schools of Ardabil. Applied Research in Sport Management 5(3): 47-54.
- Eskandari M, Agha Davoodi MA, Davarpour M, Rakhsati M, Zande Kar M (2017) Principles and intermediate of grade 3 coaching, sports climbing. Sports Climbing Working Group Publishing, Tehran, Iran.
- Porsanger L (2021) Risk and safety management in physical education: Teachers’ knowledge. Physical Education and Sport Pedagogy 28(1): 16-28.
- Gang W (2021) Research on the development of safety education content in the field of physical education based on big data analysis. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 1744(3): 032243.
- Mahdinia M, Arsanqjang S, Sadeghi A, Malakouti J, Karimi A (2016) Development and validation of a questionnaire for safety behavior assessment. Iran Occup Health 13(2): 92-102.
- Soroush Fard Z (2019) Sports injury prevention scan to increase awareness of physical education teachers and students and their parents. Journal of Physical Education Development 20(1): 26-31.
- Habibnia Rami S, Dousti M, Darvishi A (2016) Identification of problems and benefits of indoor school Olympiad project: a case study of Mazandaran province. New Trends in Sport Management 4(13): 49-59.
- Veitch J, Bagley S, Ball K, Salmon J (2006) Where do children usually play? A qualitative study of parents’ perceptions of influences on children's active free play. Health & place 12(4): 383-393.
- Yevstafyev EN, Yevstafyev NV (2014) Risk assessment in concessions: A case study of municipal sports facilities. Procedia Economics and Finance 16: 73-76.
- Ghahramani A, Fazli B (2017) An investigation of safety attitude in a number of manufacturing companies in Urmia. Journal of Health & Safety at Work 6(4): 41-50.
- Moghali HR (2018) The importance of intra-school sports Olympiad on the prosperity of elementary students in Gerash-Fars. The third national congress of sports science and health achievements, Rasht, Iran.
- Vahdani M, Hamidi M, Khabiri M, Alidoust Ghahfarrokhi E (2017) Codification a strategy map of physical education and sports activities in ministry of education of Iran. Research on Educational Sport 5(12): 17-36.
- Faber L, Hodges Kulinna P, Darst P (2007) Strategies for physical activity promotion beyond the physical education classroom. Journal of Physical Education, Recreation & Dance 78(9): 27-31.
- Gosai J, Jowett S, Nascimento Júnior JRAD (2021) When leadership, relationships and psychological safety promote flourishing in sport and life. Sports Coaching Review 12(2): 1-21.
- Shoaei M, Azadfada S, Rezaian GBA (2020) Identification of key components and drivers of security events in the Islamic republic of Iran. Police Knowledge Journal 22: 233-257.
- Mohammadnejad A, Hoseini S, Mohammadi N, Moradi Sayasar G (2022) Designing a model for sustainable security in major sports events in Iran. Sport Management Studies 13(70): 186-218.
© 2023 Mohammadbagher Forghani Ozrudi*. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






