- Submissions

Full Text
Research & Investigations in Sports Medicine
Women in Sports: Some Physiological Issues and Gender Differences - A Brief Overview
Abhijit Das*
Department of Anthropology, West Bengal State University, India
*Corresponding author: Abhijit Das, Associate Professor, Department of Anthropology, West Bengal State University, Barasat, West Bengal, India
Submission: December 16, 2021;Published: January 19, 2022

ISSN: 2577-1914 Volume8 Issue1
Abstract
Access to participation, training, and competition in sports has historically been denied to women. But clearly, this view has changed dramatically in recent years. The significant number of women in competition, coaching, administrative, officiating, ang training positions, is a matter of serious concern. The present article briefly highlights some important as well as pertinent physiological issues under the purview of gender along with some suggestive measures in favor of the worldwide movement of sports for all.
Keywords: Sports; Gender; Physiological parameters; Health; Medical issues; Equity measures
Preamble
Sports in the 21st Century is not a male dominating recreational domain in the form of primary, secondary as well tertiary involvements. Participation in sports and health related exercise or physical subcultures has sufficient instances of women’s participation specially in urban city contexts. It has many psychological (mental Health) and physical benefits and should be encouraged in girls and women of all age groups. However, the dramatic increase in participation of women in main stream sports and physical culture has enhanced our awareness of some of the medical and orthopedic issues as well as problems that may result. Today, women are participating in sports at all levels in significant or record members. This role changes have significantly improved both the athletic opportunities and the competitive sports for today’s young female sports persons and athletes. The historical genesis of gender issues in sports participation reflects that the Victorian era had significant impact on women’s participation in health and exercise.
Table 1: shows the physiological parameters important to exercise (adult females as compared to adult males) [1].
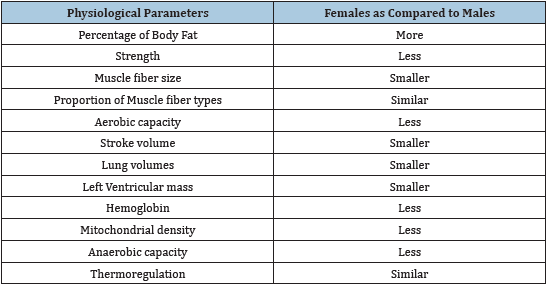
The understanding or study anatomical and physiological similarities and differences between male and female sports persons is valuable for enhancing primarily athletic performances and wellbeing (Table 1). It is extremely important to remember that there is great variability among individuals, regardless of their gender athletic abilities. Moreover, as the scientific body of knowledge as well as research on female athletics continuous to grow, they will be able to reach new heights and face a variety of challenges in all athletic areas and finally become empowered in the spheres of sports too.
In this section we shall face on to the variegated parameters of the adult female athlete in brief as considered among the sports scientists and sports medicines specialists. It is an important factor to mention that prepubescent boys have slightly higher anaerobic capacities than girls. Some studies comparing the cardiovascular responses to exercise of twenty-four boys and girls of age group (7-9 years) found few differences between gender, whereas, a study of 12 years old boys and girls found that peak oxygen uptake during exercise was significantly higher in boys. Percentage body fat, height, and weight are similar in boys and girls before puberty. Similarly muscular strength is similar in boys and girls until puberty. Regarding the rates of sport injury, it is found that the increase in non-contact anterior cruciate ligament injuries in women has come under much review and injury risk factors in complex, especially as they relate to gender. Wereis increasing evidence of Musculo skeletal disease which may be more common in women. The intrinsic and extrinsic factors, common Musculo skeletal problems stress fractures, foot pain for wearing sports shoe, shoulder pain, arthritic disorder under as common Musculo skeletal problems in the female athlete are quite significant too. Regarding medical concerns of the female athletes, that will be addressed include the problems of the triad, iron deficiency anemia and pelvic floor dysfunction [2,3].
Therefore, presently there are numerous scholarly studies on the participation and physiologic as well as medical domains of gender in sports. The observations unique anatomy (specially somatotypes) and physiology of women athletes have been reviewed and the intrinsic and extrinsic variables that may cause to sports injury in the female athlete have also been studied so far. The problems of disordered eating, amenorrhea, and premature osteoporosis are significant medical concerns along with marital fat increase that should be recognized studied and treated early. It is worth mentioning that special attention should be given to the calcium and iron deficiencies / needs of the female athletes as well as importance of maintaining positive energy balance. Thus, to provide the most effective health care for our growing population of female athletes, more research involving longitudinal, prospective, and applied studies are needed in the prevention and treatment of the medico orthopedic problem specific to the female athletes. In this task the sports scientists as well as physical educators should raise their hands jointly with sports medicine scholars.
References
- Garrett WE, Donald KT, Squire DL, Kitkowski MD (2001) Principles and practice of primary care sports medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkims, Philadelphia, USA.
- Daryl S, Hans van der Mars (1994) Introduction to physical education, fitness, and sport. (8th edn), Mayfield Publishing Company, London, UK.
- Dominic M (2008) The sage dictionary of sports studies. Sage Publications, London, UK.
© 2022 Abhijit Das. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






