- Submissions

Full Text
Research & Investigations in Sports Medicine
The Effect of 8-Week Endurance Training with Sage Supplementation on Anabolic and Catabolic Hormone Responses in Overweight Male Students
Forghani Ozrudi M1*, Ozrudi SF2 and Atena Rohi3
1Young Researchers and Elite Club, Islamic Azad University, Iran
2Department of Food industry, Caspian Higher Education Institute, Iran
3Department of Physical Education, Tehran university, Iran
*Corresponding author: Mohammadbagher Forghani Ozrudi, Young Researchers and Elite Club, Babol Branch, Islamic Azad University, Babol, Iran
Submission: March 10, 2021;Published: July 19, 2021

ISSN: 2577-1914 Volume7 Issue5
Abstract
The aim of this study was the effect of 8-week endurance training with sage supplementation on anabolic and catabolic hormone responses in overweight male students. 16 of the male students at the Damavand Islamic Azad University as subjects in this study were selected and randomly divided into four groups: a control group, Salvia officinalis groups, training group and training and Salvia officinalis group. The experimental group consisted of 8 weeks of endurance training three times a week. The dependent variable of this study is included TSH, T3, T4, testosterone and cortisol. Blood samples from after 12 hours fast and before and after 8 weeks (48 hours after the last training session) were collected. The results showed that endurance training not significant difference in TSH and T3. But T4 mean in pre and posttest has shown that difference means are meaningful increase in extract and train and extract groups. Of course, testosterone mean in pre and posttest has meaningful increase in training and training and extract group. also, Comparison of testosterone means between groups showed that Endurance training group compared to the Salvia officinalis group and training and salvia officinalis groups were significantly different. but cortisol means in pretest and posttest has shown that difference means are meaningful decrease in training and extract group. These results suggest that intensity and duration of the exercise training are important and an increase in accessible energy would result in a change in thyroid hormones levels.
Keywords: Endurance training; Salvia officinalis; Obese; Students’ men
Introduction
Exercises that involve the release of anabolic and catabolic hormone such as testosterone
and cortisol will result in little to no accumulation of muscle mass but will burn lots of calories
in the process of enhancing cardiovascular fitness. Since the benefits of exercise are virtually
all hormonally mediated, it follows logically that manipulating levels of key hormones in
the body can produce exaggerated responses to exercise. An example is the use of synthetic
testosterone hormone in athletes [1]. Therefore, this study was conducted to assess the effects
of progressive endurance training with salvia officinalis extract on TSH, T3, T4, testosterone
and cortisol in obese men students. Excessive adiposity increases oxidative stress, and
thus may play a critical role in the pathogenesis and development of obesity-associated
comorbidities, in particular atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, and arterial hypertension.
Improved body composition, through exercise training and diet, may therefore significantly
contribute to a reduction in oxidative stress. Further, some foods high in antioxidants (e.g.,
salvia officinalis) provide additional defense against oxidation [2,3]. Salvia officinalis is a plant
that belongs to the Zingiberaceae family. It is indigenous to Southeast Asia, and for centuries
has been an important ingredient in Chinese, Ayurvedic, and Unani-tibb herbal medicines for
the treatment of different diseases. It has been widely speculated that salvia officinalis might
be beneficial to human health because it exerts antioxidant activity. The main components
of salvia officinalis are 6-salvia officinalis ol, 6-shogaol, 8-salvia officinalis ol, and 10-salvia officinalis ol and these constituents have previously been shown to
exhibit strong antioxidant activity in vitro. Salvia officinalis extract
has been shown to reduce oxidative stress and increase plasma
nonenzymatic antioxidant capacity in rodents Also known as
ground nut, it grows primarily in wooded areas of the northeastern
Unites States and Canada. Panax zingiberensis, commonly called
salvia officinalis ginseng, is an endangered species in China [4,5].
Through exercise training and diet, may therefore significantly
contribute to a reduction in oxidative stress. Further, some foods
high in antioxidants (e.g., salvia officinalis) provide additional
defense against oxidation [6].
We have recently shown that salvia officinalis supplementation,
alone or in combination with endurance training, can reduce
chronic low-grade inflammation, although the mechanism for this
effect is not known. We speculate that the antioxidant properties of
salvia officinalis may produce at least some of this beneficial effect.
Supplementation with salvia officinalis combined with strength
training reduces the damage wreaked by aggressive molecules in
obese people, but the combination doesn’t work better than either
supplementation or training alone [5,7]. The researchers also
looked at the effect of the supplementation and the weight training
on the subjects’ body composition and discovered that strength
training with or without salvia officinalis led to an increase in lean
body mass. The combination group seemed to do better than the
strength-training group [8].
Increased activity of the pituitary-thyroid axis, as well as the
adrenal cortex, plays a major role in adaptations to exercise training.
Moreover, it has been Demonstrated that changes in their secretory
activity in response to training are not only closely correlated with
muscular work intensity, but also influenced by Food consumption.
However, few studies have been published on hormonal regulation
during endurance training. In this paper. We report on the changes
in concentration of thyroid Stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroxine
(T4), triiodothyronine (T3), testosterone and cortisol in plasma
after of endurance training and consumption salvia officinalis
extract [9]. Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) are iodinecontaining
hormones secreted from the thyroid gland into blood
circulation. Most of the circulating T3 and T4 are bound to serum
proteins and only a fraction of them circulates freely. The secretion
of T3 and T4 is stimulated by the pituitary hormone TSH (thyroid
stimulating hormone) by a feedback mechanism [10].
Thyroid hormones have various effects on the reproductive
system of the human men. Change in thyroid function, especially
hypothyroidism, could be cause lead to impaired male fertility [11].
Hypothyroidism are often accompanied by increased serum free
testosterone. These results protect the functional role of moderate
exercise in this high-risk population. The results indicated that
moderate- intensity exercise without significant weight loss
improved several components of the lipoprotein profiles of men
[6]. The ratio of testosterone/cortisol is considered to be a suitable
biomarker for monitoring the relative anabolic/catabolic state [12].
This ratio might even be used to modify the amount of resistance
or endurance training that is performed [11]. It was reported that
there was a noticeable increase in the levels of testosterone without
a big difference in cortisol levels after maximum endurance training
[13]; and this variation in adrenal hormones may be related to
subjects having differences in their response to exercise [14].
While, cortisol has a catabolic effect, testosterone is responsible for
the stimulation of the anabolic process of skeletal muscle growth
which increases linearly in response to exercise [13,14].
also reported significantly increased serum and testicular
testosterone levels as well as increase in weight of the testis and
testicular cholesterol level in healthy rats. but one preliminary
study by showed high statistically significant increase of serum
hormones (p<0.01) in infertile men [12]. After 30-week treatment
serum testosterone has increased by 17,7%, serum luteinizing
hormone by 43,2% and serum follicle-stimulating hormone
by 17,6%; dosage of salvia officinalis used was not disclosed
[14]. The researchers wanted to determine the effect of salvia
officinalis on luteinizing hormone, testosterone levels, and certain
semen parameters of infertile men. The researchers found that
testosterone concentration levels increased significantly among
infertile men who were given a salvia officinalis supplement. The
total increase was determined to be 17.7% [12,15]. The most
important glucocorticoid in humans is cortisol which is essential for
life. Cortisol is secreted in response to various stressful situations.
Cortisol mobilizes glucose amino acids and obesity acids, increases
vascular tone and inhibits allergic and immune reactions [8,11].
Material and Methods
Participants
This study is semi-experimental. statistic society of this study was male students at the Damavand Islamic Azad University. 16 obese males [88±4.7kg body weight, aged 21±2 years] volunteered for participation after receiving a detailed explanation of the study. All the participants had to meet the following criteria prior to enrollment in the study: no regular participation in physical activity, no current chronic health problems, nonsmokers, no cardiovascular, metabolic, or respiratory disease; and no consumption of any dietary antioxidant supplements or drugs within the past 6 months.
Research Design
Subjects were randomly assigned to 4 groups, control group, Salvia officinalis groups, training group, training and Salvia officinalis group. Then salvia officinalis extract dried in exposure to air without any exposition to sunlight, on a clean textile. For better drying the plants were high and down until they lost their water. Dried mistletoe (leaf and stem) homogenized to affine powder. Distilled water (100ml-70-80) was poured in Erlenmeyer flask containing 30g powdered material and placed in Ben Murray for 24 hours in 60). Then removed from the heat source and then was filtered. Each subject consumed 10mg/kg/day of extract for six weeks of intervention [16,17].
All anthropometric measurements were performed by the same specialist person on the day the blood samples were taken. Height and weight were measured while the participants wore only underwear, and BMI [body weight (kg)/height (m2)] was calculated. Body obese percent (BF%) was estimated from skinfold measurements taken on the right side of the body at the triceps, abdominal, and suprailiac sites after 10 hours of fasting, and calculated using the formula of Brozek [18]. All subjects in training group, training and Salvia officinalis group performed 40 min of endurance training 3d/wk at 60-75% Maximum Heart Rate Reserve (MHRR). The rest period, as running slow and ranges %35- 45 heart rate reserve and were running about two minutes.
Data Analysis
All tests were carried out early in the afternoon, after the subjects had fasted for the previous 8h. Successive tests were separated by a day’s rest. Measurements were made toward the end of the training season. Heart rate was continuously recorded during exercise by Polar Vantage XL telemetric heart rate monitors. Blood samples (10ml) were obtained from an antecubital vein after resting in a supine position for 15min before, and immediately (less than 30 sec) after each training event. Plasma TSH, T4, T3, testosterone and cortisol were measured by Quality Immunoassay Kits from company Diagnostics Biochem Canada Inc (DBC).
Procedure
To demonstrate the effectiveness of the independent variable and the comparison between groups, t-test and ANOVA were used. To determine differences between the groups, the Scheffe test was used that showed significant changes in any of the variables. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS23 Software.
Result
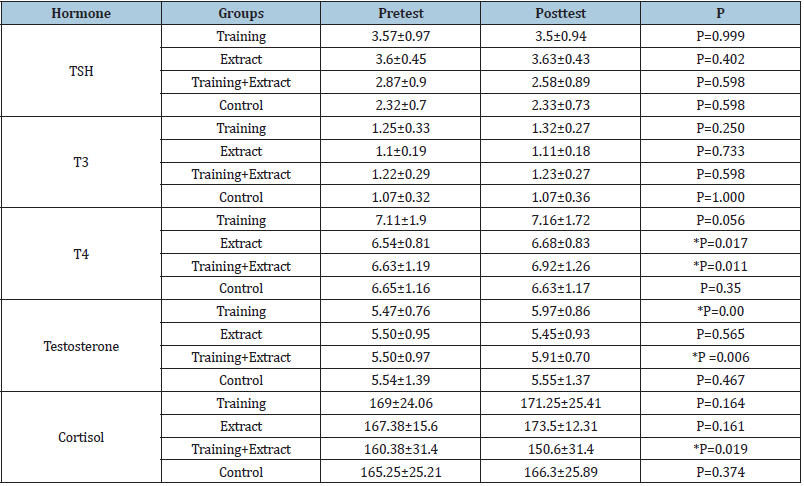
Results of research has shown that 8 weeks of endurance training program causes decrease in weight body and Obese mass (p≤0.05). The effects of endurance training and salvia officinalis extract on TSH, T3, T4, testosterone and cortisol shown for the groups in Table 1. Results of research has shown that endurance training program not significant difference in TSH means in any of the four groups. also, Comparison of TSH means between groups showed that there was no significant difference between the groups (p = 0.672). By considering of T3 means difference in pre and posttest was not meaningful in four groups. Also, Comparison of T3 means between groups showed that there was no significant difference between the groups (p=0.096). Comparison of T4 mean in pretest and posttest has shown that difference means are meaningful increase in extract and train and extract groups (p=0.017, p=0.011). Also, Comparison of T4 means between groups showed that there was no significant difference between the groups (P=0.994). Comparison of testosterone mean in pretest and posttest has shown that difference means are meaningful increase in training and training and extract group (p=0.00, p=0.006). Also, Comparison of testosterone means between groups showed that there was significant difference between the groups (P=0.001). The results of post hoc Bonferroni test showed that endurance group compared to Salvia officinalis extracts group and endurance and Salvia officinalis extract group was significantly in testosterone hormone in obese men.
Comparison of cortisol mean in pretest and posttest has shown that difference means are meaningful decrease in training and extract group (p=0.019). Also, Comparison of cortisol means between groups showed that there was significant difference between the groups (P=0.001). The results of post hoc Bonferroni test showed that group of endurance training and Salvia officinalis extracts compared to Salvia officinalis extracts group and endurance group was significantly in cortisol hormone (Table 1).
Table 1: The results of Paired t-test and changes in hormonal.
Discussion
In conclusion, the results of this study indicated that endurance
training not significant difference in TSH means in any of the four
groups also T3 in pre and posttest was not meaningful in four
groups. but T4 mean in pre, and posttest has shown that difference
means are meaningful increase in extract and train and extract
groups. Of course, testosterone mean in pre, and posttest has shown
that meaningful increase in training and training and extract group.
but cortisol mean in pretest and posttest has shown that difference
means are meaningful decrease in training and extract group. The
investigation revealed that examined the thyroid hormone levels
of professional cyclists during a 3-week stage competition, they
concluded that serum T4, FT4 and FT3 levels showed a significant
increase by the last week of competition while concentrations of
TSH and T3 remained unchanged [3,19].
Exercise training and consumption of foods rich in antioxidants
may increase physiological antioxidant defenses and thus minimizes
oxidative stress. This study investigated the effects of A potential
mechanism for the endurance training-induced reduction of oxidant
stress could include contraction-induced antioxidant enzyme
upregulation [3,15,20]. Other research showed that there were no
statistically significant differences among three measurements in
the serum levels of TSH and thyroid hormones [3,6]. This current
study shows that as compared to the thyroid hormone values
during low intensity exercise (45% max. heart rate), there is an
increase in TSH values at moderate intensity (70% max. heart
rate) and high intensity exercise levels (90% max. heart rate) [3].
Throughout the world of testosterone boosting supplements, there
are numerous ingredients that are commonly used to help the body
increase its production of testosterone naturally or to increase the
production of Luteinizing Hormone (LH). The goal is to produce
freer testosterone, as opposed to bound testosterone. This will help
the individual gain more energy, build muscle mass, and have an
increased libido. Salvia officinalis is one of those ingredients that
has the potential to promote an increase in testosterone production
in the body [1,6].
More noteworthy is that serum luteinizing hormone
concentration levels significantly increased for infertile men after
treatment with salvia officinalis. The numbers that were found in
this research study are as follows: (6.475±0.92mlU/ml) as compared
with before treatment (3.676±0.789mlU/ml). Serum LH level was
increased after treatment by 43.2%. The researchers found that
treating with salvia officinalis significantly increases luteinizing
hormone and testosterone levels [2,8,14]. The researchers in
this study determined that there wasn’t a significant impact on
luteinizing hormone for these test subject rats. They did find that
a significant increase in salvia officinalis intake on a daily basis
increased total testosterone levels as well as sperm viability and
motility [16,17,21]. The endocrine system, by Balanced of anabolic
and catabolic processes, plays a major role in the physiological
adaptation to exercise training. Hormonal assays particularly
anabolic (testosterone) and catabolic (cortisol) hormones have
been suggested as being valuable indicators of the exercise intensity
and workload. The ratio between anabolic and catabolic hormones
has been used to determine the readiness status of individuals.
Whereas, the free testosterone to cortisol ratio is used as an
adaptation exercise index for males [11,12,20]. Exercise training
produces changes in the concentration of several biologically active
molecules including cortisol and testosterone, which play pivotal
roles as catabolic and anabolic agents in gluconeogenesis via the
proteolytic pathway. The storage of glycogen and muscular protein
synthesis is stimulated by testosterone [8,12].
Conclusion
In summary, the intensity and duration of the exercise training are important and an increase in accessible energy would result in a change in thyroid hormones levels. Therefore, we can conclude that exercise can change hormonal concentration of T4. Of course, Thyroid function depends to a certain degree on the exercise intensity and perhaps to other factors such as specific characteristics of the athletes. But no significant changes in TSH and T3. But Individuals who consume salvia officinalis may very well help to boost serum testosterone levels in the body.
References
- Ha Ja (2010) Hormonal response to exercise. World of sports science Rev pp: 434-435.
- Ahn YM, Kim SK, Lee SH, Ahn SY, Kang SW, et al. (2010) Renoprotective effect of tanshinone IIA, an active component of salvia miltiorrhiza, on rats with chronic kidney disease. Phytother Res 24(12): 886-1892.
- Ciloglu F, Peker I, Pehlivan A, Karacabey K, İlhan N, et al. (2005) Exercise intensity and its effects on thyroid hormones. Neuroendocrinology letters 26(6): 830-834.
- Atashak S, Peeri M, Azarbayjani MA, Stannard SR, Haghighi MM (2011) Obesity-related cardiovascular risk factors after long-term resistance training and ginger supplementation. J Sports Sci Med 10(4): 685-691.
- Oboh G, Henle T (2009) Antioxidant and inhibitory effects of aqueous extracts of salvia officinalis leaves on pro-oxidant-induced lipid peroxidation in brain and liver in vitro. J Med Food 12(1): 77-84.
- Tremblay MS, Copeland JL, Van Helder W (2005) Influence of exercise duration on post-exercise steroid hormone responses in trained males. Eur J Appl Physiol 94(5-6): 505-513.
- Kota N, Krishna P, Polasa K (2008) Alterations in antioxidant status of rats following intake of ginger through diet. Food chemistry 106(3): 991-996.
- Smilios I, Pilianidis T, Karamouzis M, Tokmakidis SP (2003) Hormonal responses after various resistance exercise protocols. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(4): 644-654.
- Mohamed GA, Ibrahim SR, Elkhayat ES, El Dine RS (2014) Natural anti-obesity agents. Bulletin of Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University 52(2): 269-284.
- Altaye KZ, Mondal S, Legesse K, Abdulkedir M (2019) Effects of aerobic exercise on thyroid hormonal change responses among adolescents with intellectual disabilities. BMJ open sport & exercise medicine 5(1): 000524.
- Silva TS, Longui CA, Faria CD, Rocha MN, Melo MR, et al. (2008) Impact of prolonged physical training on the pituitary glucocorticoid sensitivity determined by very low dose intravenous dexamethasone suppression test. Horm Metab Res 40(10): 718-721.
- Grandys M, Majerczak J, Duda K, Bukowska ZJ, Kulpa J, et al. (2009) Endurance training of moderate intensity increases testosterone concentration in young, healthy men. Int J Sports Med 30(07): 489-495.
- Ahmadi R, Balali S, Tavakoli P, Mafi M, Haji GR (2013) The effect of hydroalcoholic leaf extract of Salvia officinalis on serum levels of FSH, LH, testosterone and testicular tissue in rats. KAUMS Journal (FEYZ) 17(3): 225-231.
- Kraemer WJ, Ratamess NA (2005) Hormonal responses and adaptations to resistance exercise and training. Sports Med 35(4): 339-361.
- Khaki A, Khaki AA, Hajhosseini L, Golzar FS, Ainehchi N (2014) The anti-oxidant effects of ginger and cinnamon on spermatogenesis dys-function of diabetes rats. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 11(4): 1-8.
- Kianbakht S, Abasi B, Perham M, Hashem Dabaghian F (2011) Antihyperlipidemic effects of salvia officinalis l. leaf extract in patients with hyperlipidemia: A randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled clinical trial. Phytother Res 25(12): 1849-1853.
- Zancan KC, Marques MOM, Petenate AJ (2002) Extraction of salvia officinalis (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) oleoresin with CO2 and co-solvents: A study of the antioxidant action of the extracts. J Supercrit Fluids 24: 57-76.
- Brozek J, Henschel A (1961) Techniques for measuring body composition. National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC, USA, pp. 223-244.
- Van Geffen C, Bavegems V, Duchateau L, De Roover K, Daminet S (2006) Serum thyroid hormone concentrations and thyroglobulin autoantibodies in trained and non-trained healthy whippets. Vet J 172(1): 135-140.
- Kar A, Panda S, Bharti S (2002) Relative efficacy of three medicinal plant extracts in the alteration of thyroid hormone concentrations in male mice. J Ethnopharmacol 81(2): 281-285.
- Ali BH, Blunden G, Tanira MO, Nemmar A (2008) Some phytochemical, pharmacological and toxicological properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe): A review of recent research. Food Chem Toxicol 46(2): 409-420.
© 2021 Mohammadbagher Forghani Ozrudi. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






