- Submissions

Full Text
Research & Investigations in Sports Medicine
The Effect of Regular Physical Activity in Water with and without Ginger Supplementation on Adiponectin Levels in Women with Breast Cancer
Javad Alizadeh1, Mohammadbagher Forghani Ozrudi1*, Samaneh Forghani Ozrudi2 and Atena Rohi3
1Young Researchers and Elite Club, Babol Branch, Islamic Azad University, Iran
2Department of Food industry, Caspian Higher Education Institute, Iran
3Department of Physical Education, Tehran university, Tehran, Iran
*Corresponding author: Mohammadbagher Forghani Ozrudi, Young Researchers and Elite Club, Babol Branch, Islamic Azad University, Babol, Iran
Submission: March 10, 2021;Published: June 30, 2021

ISSN: 2577-1914 Volume7 Issue4
Abstract
The aim of this study was to determine the effect of regular physical activity in water with and without ginger supplementation on adiponectin levels in women with breast cancer. The population of the study, 98 women with a mean age of breast cancer patients (48±8.5), weight (76±9)kg and fat mass (8.41±4) formed that voluntarily participated in this study that 40 people of them were selected as sample. subjects were randomly divided into four groups (Group 1: placebo, Group 2: Selected exercises in water placebo, Group 3 and Group 4 supplementation Ginger: Ginger supplements selected exercises in water) were divided into groups of ginger supplements and exercise The Water Department ginger supplements daily for 6 weeks orally 4 capsules (750mg) were used. Programs supplement group ginger exercise and water exercise group placebo juice containing a combination of increased intensity and distance training, with 50% to 75% heart rate reserve for 60 to 75 minutes in a pool with a width of 15 meters and a depth of 4m, 4 times a week 6 weeks was performed. Fasting blood samples were collected at pre-test and post-test. The result of the study All findings using the statistical software in SPSS23 and evaluated p<0.05. Ginger supplements or exercise in water increase adiponectin was compared to baseline. However, the exercise group in water exercise with ginger showed a much better effect on the inflammatory marker adiponectin and blood, than the exercise group in water with placebo or the ginger group alone. The findings show that a protective effect of non-pharmacological strategies such as exercise in water and plant anti-inflammatory agents such as ginger has been detected in inflammatory and metabolic responses in obese women with breast cancer.
Keywords: Exercises in the water; Inflammatory system; Women; Breast cancer; Overweight
Introduction
Studies show that breast cancer is the most common cancer among women and second cancer death after lung cancer worldwide, especially in developed [1,2]. Statistics of breast cancer in Western countries, according to some reports, this rate was not less than 120 per hundred thousand people, which is even higher than in some Western countries [3]. Breast cancer prognosis and choice of treatment depends on several factors. The most important factor in smoking, obesity, age at menarche, oral contraceptive pill, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, involvement of axillary lymph nodes, the presence of estrogen and progesterone receptors, P53, protein, cathepsin D and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 [4-6]. It is a multifactorial disease and breast cancers are hormonal status, reproductive history, previous breast disease, anthropometric measures, demographic and family history of breast or ovarian cancer risk associated [7-10].
World Health Organization recently declared that 25 percent of breast cancer in the world has announced the result of overweight and sedentary lifestyle [11]. It is clear that obesity is a risk factor for developing breast cancer in postmenopausal women [12,13]. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated to increase the incidence of breast cancer and adipose tissue is associated with a higher incidence of mortality [14]. However,
although the effect of physical activity on reducing body fat in
different people, but the influence of activity on the environment,
especially water with additives such as anti- inflammatory ginger
floating in obese women with breast cancer studied and carry out
research in this area can Antioxidant some confusion about the role
of physical activity as well as anti-inflammatory response. The year
so far, the scientists were able to discover the effects of biological
control agents and to treat the Maed et al., Adiponectin hormone
called adiponectin, the family discovered that the biological effects
controls [14].
Adiponectin deficiency can be an early sign of heart risk-Vascular
risk factors contribute to atherosclerosis and atherosclerotic
plaque progression may be accelerated. On the other hand, in
women after menopause, the main source of fat tissue Armataz (the
enzyme that converts androgens to estrogens) and increasing the
size and number of fat cells in obese patients may contribute to the
strengthening of Aromatase androgens. Furthermore, the increase
in adipose tissue by increasing blood fats and reducing harmful
levels of adiponectin and insulin levels and insulin-like growth
factor type (IGF-1) which is involved in breast tumor progression
and is related to Mutagenic activity [15].
The role of physical activity in preventing disease and improving
health and wellbeing of people who are not covered. Seems to have
a positive effect on physical activity and mental health of cancer
patients [16]. However, the reported levels of physical activity after
a breast cancer diagnosis significantly reduces [17,18], and even
after the treatment is done only slightly [19]. Physical activity is
associated with quality of life [20,21], and Patients who reported
their activities during the treatment period and then permanently
reduce, the lowest quality of life [17]. Physically disabled patients
as compared to patients with more severe fatigue in physically
active lifestyle experience [14]. This in turn is ruining their
quality of life [22]. Numerous studies have been conducted on
the effects of aerobic exercise on adiponectin [23-26]. Ferguson
et al., reported that a single session of aerobic activity had no
effect on adiponectin and leptin, but increased insulin resistance
[27]. On the other hand, despite their effectiveness in controlling
stress and inflammation caused by certain medications, as well as
reports of numerous adverse side effects and is presented. Ginger
plants including medicinal plants, particularly in Iran, which
has been introduced in Iranian traditional medicine as an antiinflammatory
herb [28]. Despite multiple reports of the antitumor
effects of this plant, known mechanisms of these effects, reducing
inflammation occurs [2-7]. Several studies have also shown that
the modulation of immune responses capable of exacerbating
inflammatory cell extract [3]. In line with the anti-inflammatory
effects of plant drought, the analgesic effect induced by acetic acid
plant is shown [29]. Will be more marked effects like reduced fat
or sugar and anticancer activities of this plant, particularly through
the mechanisms modulating the inflammatory processes [4]. In
line with several reports have shown anti-inflammatory effects of
this plant the active compounds in plants like ginger, Shogol and
curcumin inhibits the ability to produce well Prostaglandin’s, even
vs nitrite and NO are involved in inflammation [7,10]. In addition
to producing enzymes specifically mediate the inflammatory
ingredients in this material are inhibited Ginger [8].
In the meantime, however, still a number of medications
and treatments prescribed for the control of cancer cells and
their role of these approaches are often, but experts believe that
the use of drugs and procedures such as chemotherapy often
associated with side effects such as pain and fatigue. Hence, the
use of non-pharmacological strategies such as anti-inflammatory
and antioxidant supplements to reduce adverse effects in cancer
has spread in recent decades. Although several researchers
have endorsed the role and effectiveness of ginger in decreasing
inflammation, the effect of nonpharmacological approaches to
obesity on markers such as Adiponectin in obese women with breast
cancer, especially in Iran, have not been seriously investigated and
hence necessitates further research in this area. Hence, the aim of
the present study the effects of exercise in water for 6 weeks with
or without supplementation of ginger on inflammatory markers in
overweight women with breast cancer.
Material and Methods
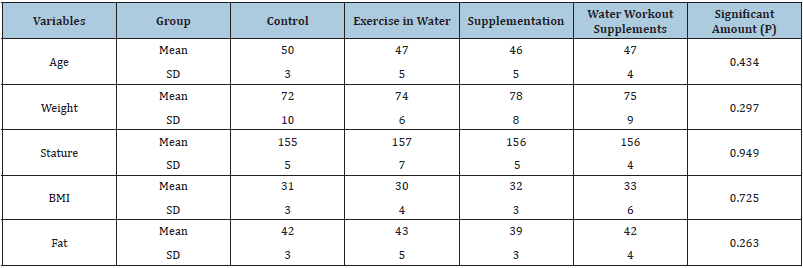
Quasi-experimental research methodology, and applications that were studied in four groups of human subjects in two phases: pre-test and post-test changes in blood lipids and inflammatory markers. After describing the design goals of 40 women with breast cancer, city of Babol during the years 2010 to 2012 confirm that the disease has been diagnosed with physician supervision and sampling randomly divided into experimental and control groups of ten and a double-blind, respectively. Table 1 shows the characteristics of the study subjects.
Table 1: Mean and standard deviation of the physiological characteristics of the study subjects.
Research protocol is used in the pre-test-post-test. For sampling and radiation oncology centers and pathology labs Rohani hospital and Pathology Laboratory was presented. Independent variables include water exercise, herbal supplement ginger, biochemical variables and dependent variables, including adiponectin were included. The questionnaire also included a three-day food records and physical activity levels. Research training protocol for 6 weeks and 4 weeks, each session was 60 minutes in the pool to a depth of 4 meters. Ginger herbal supplementation protocol as 7 days per week for 6 weeks to 3mg Herbal Supplement was conducted in two groups. Blood between 7am to 9am and then fasted for 12-hour contralateral hand vein surgery in the sitting position of 10ml was obtained. For the separation of blood plasma in tubes containing sodium heparin and EDTA tubes for serum separation were cast. Blood at 10000g at 4 °C was centrifuged for 10min. Serum and plasma was isolated at 80-Level C was maintained. All quantitative variables were normalized using Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) normality of distribution was studied. To compare each of the variables in the study before and after 6 weeks of exercise in water or supplementation of ginger Paired t-test between control and treatment groups were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance. In the present study, data were analyzed using SPSS23 software (p<0.05).
Results
The results of this study indicate that 6 weeks of aerobic exercise in water or ginger supplements increased 21% in the training group, increase of 7% in the ginger group and a significant increase in the amount of 45% of the combined group, while that is still below the levels in the control group and even shows a decrease of 7% compared to the pre-test and post-test (Table 2).
The results can be seen in Table 3, the mean and standard deviation only the amount of Adiponectin in the aerobic exercise group compared to the pre-test and post-test water -1.79±1.5 was found that the value of t equal to -3.70 is significant at the alpha level of 5%. Nevertheless, it is quite close to the significance level.
The results can be seen in Table 4, the mean and standard deviation values of adiponectin ginger supplementation group in pre-test and post-test compared to the amount equal to t=1.08 is not significant at the alpha level of 5%. The value obtained for the index of insulin t=0.67 and p=0.516 shall Ginger indicating no significant difference in serum insulin in women with breast cancer compared with the period before supplementation of ginger.
The results can be seen in Table 5 the mean and standard deviation of the difference is significant parameter examined in the study group workout supplements in water and ginger in comparing pre-test and post-test.
Table 2: Mean & standard deviation of index terms (mg/ ml) in pre & post-workout supplements.
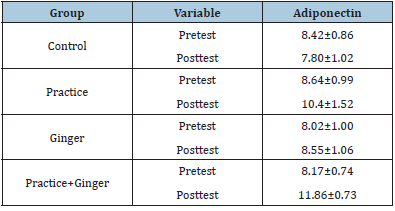
Table 3: Paired t-test indicators in the study after 6 weeks of training in water.

Table 4: Paired t-test indicators in the study after 6 weeks of supplementation ginger.

Table 5: Indicators related t-test after 6 weeks of training in the water and ginger supplements.

Conclusion
The present study investigated the effect of 6 weeks of regular
exercise in water and ginger supplementation on Adiponectin
in patients with breast cancer. The field was full of water and
ginger in a regular exercise has been significantly increases the
levels of Adiponectin in the two groups (exercise and practice supplement); and in particular, the combined approach, while the
control group Adiponectin amounts of ginger supplementation has
remained low. In addition, the study showed a significant difference
between the groups was significantly increased compared with
pretest levels Adiponectin that is the reduction in the group’s
control-Practice, Controls-Combined, Practice-Combined, Gingerpractice,
& practice-mixed. The results of this study are consistent
with findings Garekani et al., Some studies also confirmed the
findings of the study reported a significant increase in adiponectin
concentrations after resistance exercise with moderate to severe
[30]. Therefore, examined the effects of 6 months of resistance
exercise intensity-different low and moderate intensity of 50% and
above 80% RM 65% of the elderly adiponectin and finally reported
that adiponectin significantly increased after exercise intensity is
moderate to severe However, the low intensity remains unchanged
[31].
Brooks et al., study on the present study are consistent with
diabetes. The team of 16-week exercise program of strength on the
parameters before Anti-inflammatory Adult Spanish hybridization
with type 2 diabetes were investigated and found that exercise
reduces serum cytokine inflammatory C reactive protein and causes
increased cytokine anti-inflammatory adiponectin in patients [5].
However, the result of the present study is consistent with results
of other studies [32,33].
Ahmadizad et al., reported that 12 weeks of strength training
(including 11 stations in motion the circular regions of 3 days per
week for 12 weeks, each session is about 60 minutes 60-50% of
subjects) and training endurance (running for 80-75% maximum
heart rate, maximum 3 days per week for 12 weeks) caused
significant changes in plasma adiponectin levels as an indicator
of the subjects is not an anti-inflammatory. They stated that lowintensity
exercise may be due to change in adiponectin. The results
of this study showed that the effect of aerobic training on plasma
adiponectin increases, and the absolute values of the patients was
approximately twice the accumulation [34].
In line with the results of Atashak et al. [35] long-term effects
of resistance exercise on plasma adiponectin levels and lipid
profile in obese men looked at the results of this study indicated:
Adiponectin levels after 10 weeks of progressive resistance
training in the training group compared with the control group was
significantly higher [35]. Olson et al. [36] study found resistance
training significantly increased the concentration of adiponectin
and C-reactive protein levels in overweight women are the basis
[36]. However, the result of the present study is consistent with
results of other studies [31]. In addition, the group recently found
that despite the fact that (16 weeks of resistance training 2 times
a week), with dietary restriction improves Cardiac-Vascular risk
factors obesity is a disease in men, but decreased adiponectin levels
[13]. One likely reason for this discrepancy may be the result of the
age of the subjects mentioned. The reported BMI, sex, and weight
ranges, as well as previous studies [33]. It seems that one of the
main factors affecting the intensity resistance training may be the
case, so that it aligns with the results of this study, high-intensity
exercise has caused an increase in adiponectin [7].
Low intensity but caused no change in adiponectin levels.10
weeks of progressive resistance training in favorable lipid profile
in obese men, there is a way that the average total cholesterol
levels, exercise has been reduced. Also, resistance training causes
a decrease in other lipid markers were found, although the changes
are not significant [11]. Garekani et al. [30] found that adiponectin
was significantly characterized by central obesity and insulin
stimulation of glucose uptake due to their correlation. The effects
of exercise on serum HMW adiponectin, there are few studies. For
example, it has been shown that HMW adiponectin concentration
and its ratio to total adiponectin in middle-aged men after 12 weeks
of aerobic training and resistance to insulin increases. It was while
the effectiveness of a program of aerobic exercise in 3 different
effect on adiponectin and its isomers [30].
The research reports indicate that there is a positive relationship
between exercise and lipid metabolism and consequently increase
adiponectin gene expression [11,19]. In this regard, Kraemer &
Castracane stated amount of adiponectin response exercise can
be effective, such as the duration and intensity of exercise are
important factors in determining the response of adiponectin [9].
Must be acknowledged that the issue of the effect of exercise on
adiponectin in its infancy and there are also many unknown issues
about the role of adipose tissue and its relationship with other
tissues. The effect of exercise intensity and type of fuel in the tissues
[20,21] and the effect of adiponectin in plasma free fatty acids. one
can infer that changes in adiponectin levels after exercise can is
related to the intensity and duration of exercise. Although such
an approach yet identified any long-term exercise or withdrawal
of excess fat under skin surgical adiponectin will increase, it
today believes the spent intensity exercise some Connoisseurs the
adiponectin there is a relationship Stimulation. also, Kraemer and
Castracane, in a review paper to examine the effect of exercise on
adiponectin levels, and the stated amount of exercise can be effective
adiponectin response, so that a long-term activity with the volume
(intensity, duration and frequency) above can affect on adiponectin
concentrations and in the meantime, there are important factors
as the duration and intensity of exercise training on how to
respond to adiponectin [9]. Various researches have been applied
in different types of physical activity intensity and duration of the
individual [37]. The investigation shows the shortest duration of
exercise along with a diet that could affect the level of adiponectin
is two weeks [9]. However, as mentioned earlier, the duration and
intensity of exercise that can cause weight loss or body fat loss will
play an important role in adiponectin levels.
According to the results of the present study, ginger
supplementation and regular physical activity increases adiponectin
are markers. It measures the changes in insulin and insulin
resistance has developed. It seems that physical activity or taking
ginger supplements and especially the combination of the two can
be considered as a strategy to reduce or improve inflammation in
patients with breast cancer as the primary treatment for drug and
supplement used to improve the quality of life.
References
- Khanjani N, Noori A, Rostami F (2012) The knowledge and practice of breast cancer screening among women in Kerman, Iran. Al Ameen Journal of Medical Sciences 5(2): 177-182.
- Mousavi SM, Montazeri A, Mohagheghi MA, Jarrahi AM, Harirchi I, et al. (2007) Breast cancer in Iran: An epidemiological review. Breast J 13(4): 383-391.
- Kumar V, Abul A, Aster J (2020) Robins pathologic basis of disease. (10th edn), McGraw-Hill, Philadelphia, USA.
- Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA, Caggiano V (2007) Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)‐negative, Progesterone Receptor (PR)‐negative, and HER2‐negative invasive breast cancer, the so‐called triple‐negative phenotype: A population‐based study from the california cancer registry. Cancer 109(9): 1721-1728.
- Brooks N, Layne JE, Gordon PL, Roubenoff R, Nelson ME, et al. (2007) Strength training improves muscle quality and insulin sensitivity in Hispanic older adults with type 2 diabetes. Int J Med Sci 4(1): 19-27.
- Schwartz S (2019) Principles of surgery. (11th edn), Philadelphia: McGraw-Hill, USA.
- Beckmann MW, Bani MR, Fasching PA, Strick R, Lux MP (2007) Risk and risk assessment for breast cancer: Molecular and clinical aspects. Maturitas 57(1): 56-60.
- Egan KM, Stampfer MJ, Rosner BA, Trichopoulos D, Newcomb PA, et al. (1998) Risk factors for breast cancer in women with a breast cancer family history. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 7(5): 359-364.
- Kraemer RR, Castracane VD (2007) Exercise and humoral mediators of peripheral energy balance: Ghrelin and adiponectin. Exp Biol Med 232(2): 184-194.
- Szabo CI, King MC (1995) Inherited breast and ovarian cancer. Human Molecular Genetics 4(suppl_1): 1811-1817.
- Irwin ML, Yasui Y, Ulrich CM, Bowen D, Rudolph RE, et al. (2003) Effect of exercise on total and intra-abdominal body fat in postmenopausal women: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 289(3): 323-330.
- Lorincz AM, Sukumar S (2006) Molecular links between obesity and breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 13(2): 279-292.
- Wolk A, Gridley G, Svensson M, Nyrén O, McLaughlin JK, et al. (2001) A prospective study of obesity and cancer risk (Sweden). Cancer Causes Control 12(1): 13-21.
- Chlebowski RT, Aiello E, McTiernan A (2002) Weight loss in breast cancer patient management. Journal of Clinical Oncology 20(4): 1128-1143.
- Weltman A, Prizlaff CJ, Wideman R, Considine V, Fryburg DA, et al. (2000) Intensity of acute exercise does not affect serum leptin concentrations in young men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32(9): 1556-1561.
- Schmitz KH, Holtzman J, Courneya KS, Mâsse LC, Duval S, et al. (2005) Controlled physical activity trials in cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14(7): 1588-1595.
- Belfiore A, Frasca F (2008) IGF and insulin receptor signaling in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 13(4): 381-406.
- McNeely ML, Campbell KL, Rowe BH, Klassen TP, Mackey JR, et al. (2006) Effects of exercise on breast cancer patients and survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ 175(1): 34-41.
- Irwin ML, McTiernan A, Bernstein L, Gilliland FD, Baumgartner R, et al. (2004) Physical activity levels among breast cancer survivors. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36(9): 1484-1491.
- Shaibi GQ, Cruz ML, Ball GD, Weigensberg MJ, Salem GJ, et al. (2006) Effects of resistance training on insulin sensitivity in overweight Latino adolescent males. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38(7): 1208-1215.
- Zhaosheng T, Li Y, Chengying G, Yun L, Lian Z (2005) Effect of exercise on the expression of adiponectin mRNA and GLUT4 mRNA in type 2 diabetic rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 25(2): 191-193.
- Parsa P, Parsa B (2009) Effects of reproductive factors on risk of breast cancer: A literature review. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 10(4): 545-550.
- Chang HY, Sheu MJ, Yang CH, Lu TC, Chang YS, et al. (2011) Analgesic effects and the mechanisms of anti-inflammation of hispolon in mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011: 478246.
- Grzanna R, Phan P, Polotsky A, Lindmark L, Frondoza CG (2004) Ginger extract inhibits β-amyloid peptide-induced cytokine and chemokine expression in cultured thp-1 monocytes. J Altern Complement Med 10(6): 1009-1013.
- Lantz RC, Chen GJ, Sarihan M, Solyom AM, Jolad SD, et al. (2007) The effect of extracts from ginger rhizome on inflammatory mediator production. Phytomedicine 14(2-3): 123-128.
- Tripathi S, Bruch D, Kittur DS (2008) Ginger extract inhibits LPS induced macrophage activation and function. BMC Complement Altern Med 8(1): 1-7.
- Ferguson MA, White LJ, McCoy S, Kim HW, Petty T, et al. (2004) Plasma adiponectin response to acute exercise in healthy subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 91(2): 324-329.
- Stewart TH, Heppner GH (1997) Immunological enhancement of breast cancer. Parasitology 115(7): 141-153.
- Chae BJ, Bae JS, Lee A, Park WC, Seo YJ, et al. (2009) P53 as a specific prognostic factor in triple-negative breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 39(4): 217-224.
- Garekani ET, Mohebbi H, Kraemer RR, Fathi R (2011) Exercise training intensity/volume affects plasma and tissue adiponectin concentrations in the male rat. Peptides 32(5): 1008-1012.
- Jürimäe J, Purge P, Jürimäe T (2005) Adiponectin is altered after maximal exercise in highly trained male rowers. Eur J Appl Physiol 93(4): 502-505.
- Jamurtas AZ, Theocharis V, Koukoulis G, Stakias N, Fatouros IG, et al. (2006) The effects of acute exercise on serum adiponectin and resistin levels and their relation to insulin sensitivity in overweight males. Eur J Appl Physiol 97(1): 122-126.
- Bruun JM, Lihn AS, Verdich C, Pedersen SB, Toubro S, et al. (2003) Regulation of adiponectin by adipose tissue-derived cytokines: in vivo and in vitro investigations in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285(3): 527-533.
- Ahmadizad S, Haghighi AH, Hamedinia MR (2007) Effects of resistance versus endurance training on serum adiponectin and insulin resistance index. Eur J Endocrinol 157(5): 625-632.
- Atashak S, Jafari A, Azerbaijani A (2011) Long-term effects of resistance exercise on plasma adiponectin levels and lipid profiles in obese men. Razi Journal of Medical Sciences 18(86): 1-11.
- Olson TP, Dengel DR, Leon AS, Schmitz KH (2007) Changes in inflammatory biomarkers following one-year of moderate resistance training in overweight women. Int J Obes 31(6): 996-1003.
- Ryan AS, Nicklas BJ, Berman DM, Elahi D (2003) Adiponectin levels do not change with moderate dietary induced weight loss and exercise in obese postmenopausal women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27(9): 1066-1071.
© 2021 Mohammadbagher Forghani Ozrudi. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






