- Submissions

Full Text
Research & Investigations in Sports Medicine
Frequency of Common Clinical Condition among Client Presented at Habib Physiotherapy Complex
Mahboob ur Rahman1* and Aftab Ahmad2
1 Chairman, Mahboob Medical Institute, Pakistan
2 Assistant Professor, Mahboob Medical Institute, Pakistan
*Corresponding author: Mahboob ur Rahman, Chairman, Mahboob Medical Institute, Habib Physiotherapy Complex, Phase 5, Hayatabad, Peshawar, Pakistan
Submission: September 15, 2017; Published: March 28, 2018

ISSN: 2577-1914 Volume2 Issue3
Abstract
Background: Physiotherapy is multi-dimensional and can treat a vast variety of conditions, ranging from musculoskeletal aches, arthritis, joints problems, paraplegia, hemiplegic, sports injuries and frozen shoulder etc. Apart from culture competency and core medical knowledge a physiotherapist must be competent enough in all physiotherapist medical conditions where physical therapy plays a vital role. This study aims to identify the frequency of common clinical conditions among client presented at Habib Physiotherapy Complex (HPC), Hayatabad during 2010.
Methodology: This was a descriptive study; the data were retrieved from record register of HPC (Indoor and Outdoor patients) recording their presenting complaints and known diagnoses. Data was collected on a structure grid. Data was analyzed using SPSS version 15 and presented in term of frequency and percentages.
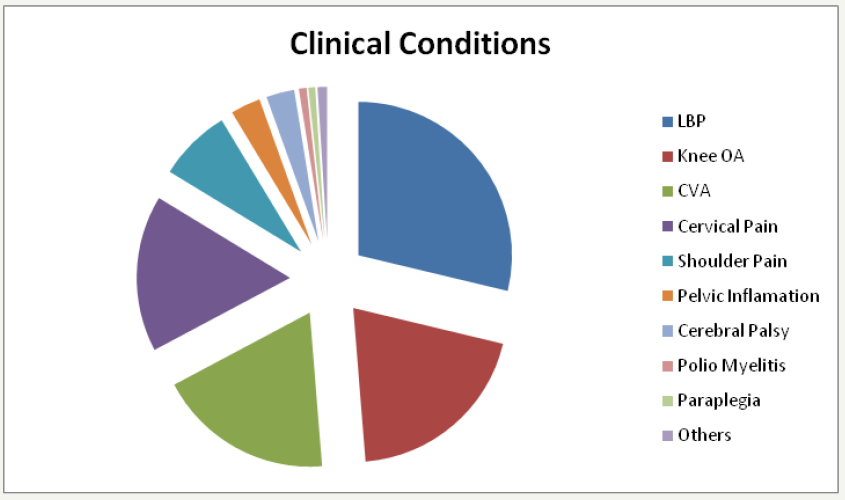
Result: The majority of clients (1280 (29%)) were suffering from low back pain. The second common condition 891(20%) was osteoarthritis of the knee joint and cerebrovascular accidents 824(18.4%), while cervical pain accounted for 734(16.4%). The rest of clinical conditions included; frozen shoulder, pelvic inflammation, cerebral palsy, polio effected and paraplegia.
Conclusion: The Study reveals the occurrence of Osteoarthritis (Low Back, Cervical Pain, and Knee Joints Pain) were the most common condition which deteriorated the performance of common individuals in our society
Keywords: Physiotherapy; Arthritis; Cerebral palsy; Stroke
Introduction
Physiotherapists developed strong reputation in rehabilitation therapy after the Great War in the early part of the 20th century [1,2]. The skills were shifted to the management of children and adults during the global poliomyelitis epidemic [2]. Physiotherapy plays a vital role in helping people to achieve the best physical function and healthy lifestyle. Physiotherapists treat people of all ages which undergo back pain, cystic fibrosis, knee pain, shoulder problems and many more. Physiotherapists are educated to evaluate, treat and prevent the physical limitations and dysfunction through exercises, mobilization and therapeutic techniques. Physiotherapists are involved in taking care of their patients to live an independent life [3,4]. Physiotherapists have provided care to those who have any disorder that needs treatment to improve their functional limitations. Physical therapy covers specialized skills and takes in development of new principles and applications to come across current and developing health needs [4,5]. Physiotherapist can evaluate and treat a wide range of medical conditions from sprained ankles to strokes, i.e. from musculoskeletal conditions to neurological conditions, improve balance, relieve pain and help in healing injuries, improve strength, and Spinal cord injury, improve cardiovascular performance, improve range of motion, back and neck pain, arthritis and osteoarthritis, improve mobility after joint replacements, sports injuries, developmental delay, stroke, parkinson’s disease, and fractures or sprains [5,6].
In a descriptive study among musculoskeletal disorders, low back pain is the most prevalent disorder with estimates ranging from 32% to 90%. Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders at other sites, including the neck (12% to 52%), shoulders (17% to 48%) and knees (7% to 68%), are to some extent lesser [7,8]. Among neurological conditions, stroke is a leading worldwide health threat. Yearly, about 25,000-30,000 individuals in the population were diagnosed with stroke in Sweden. It is the third recorded common source of death in Sweden. High BP, smoking, DM, heart diseases, vascular diseases and hypercholesterolemia are risk factors for stroke [9]. Cerebral palsy is a common and significant motor development disorder, with an incidence of 2-2.5 per 1000 live births [10]. Habib Physiotherapy Complex was the first ever rehabilitation complex in the locality and therefore the need for study was determined.
Methodology
A cross-sectional study was conducted on patient of Habib Physiotherapy Complex (HPC) Hayatabad Peshawar. The data were retrieved from record register of HPC (Indoor and Outdoor Patients) recording their presenting complaints and known diagnoses. Data was collected on a structure grid. Data was analyzed using SPSS version 15 and presented in term of frequency and percentages. Ethical approval was taken from the Institute.
Results
The total patients (4455) presented different physical conditions for analysis. The major portion of patients was from the age group 41-50 years comprising of 44 percent of total patients which came to the Habib Physiotherapy Complex in 2010. The patients were analyzed using descriptive statistics by gender. The female gender had greater representation compared to males as shown in the Table 1. The distribution of patients revealed that low back pain was the most frequent clinical condition followed by Osteoarthritis, CVA, cervical pain, shoulder pain (including frozen shoulder), pelvic inflammation, cerebral palsy, polio affected, paraplegia and others respectively detailed in Figure 1 and Table 2.
Table 1: Age distribution of patients at HPC.
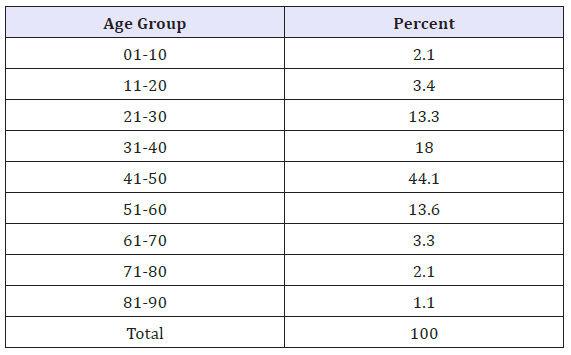
Table 2: Gender distribution of patients at HPC.
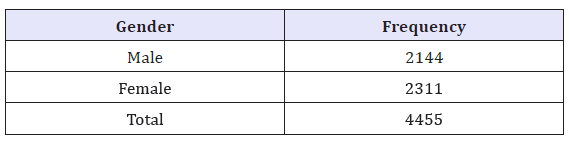
Figure 1:
Discussion
In this study the most frequent clinical condition was LBP which is similar to the study findings by Choobineh on 12 months prevalence of musculoskeletal condition [11]. This study finding is also supported by Sheikhzadeh’s study on work related musculoskeletal disorder [12]. Walker et al. [13] conducted a study in 2000 which showed that low back pain is the most common back pain with a point prevalence of 12-33% and the life time prevalence estimated to be 11 to 84% and the annul prevalence of LBP was 22- 65% respectively [13]. In this study the second most frequent clinical condition was knee OA which is higher than the finding by the Dutch Institute of Public Health i.e. knee osteoarthritis prevalence in the people at the age of 55 and above was 46.1%. It rises to 43.7% in the people over the age of eighty years [14]. The third frequent clinical condition was CVA which hospitalized in Habib Physiotherapy complex is the finding less than the study in United States by Hall et al. [15]. Cervical Pain reported by this study was almost 50 percent reported in Sweden (48-53%), and the United States (45.8%) [16,17].
Conclusion
The Study reveals the occurrence of Osteoarthritis (Low Back, Cervical Pain, and Knee Joints Pain) were the most common condition which deteriorated the performance of common individuals in our society.
References
- Critchley DJ, Ratcliffe J, Noonan S, Jones RH, Hurley MV (2007) Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of three types of physiotherapy used to reduce chronic low back pain disability: a pragmatic randomized trial with economic evaluation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32(14): 1474-1481
- English C, Hillier S, Kaur G, Hundertmark L (2014) People with stroke spend more time in active task practice, but similar time in walking practice, when physiotherapy rehabilitation is provided in circuit classes compared to individual therapy sessions: an observational study. J Physiother 60(1): 50-54.
- Islam MS, Habib MM, Hafez MA, Nahar N, Lindstrom-Hazel D, et al. (2015) Musculoskeletal complaints among physiotherapy and occupational therapy rehabilitation professionals in Bangladesh. Work 50(3): 379- 386.
- Giovanni A, Duflo S, Robert D (2013) Principal techniques of rehabilitation. Referral to physiotherapy and speech therapy. Rev Prat 54(1): 97-102.
- Walkeden S, Walker KM (2014) Perceptions of physiotherapists about their role in health promotion at an acute hospital: a qualitative study. Physiotherapy 101(2): 226-231.
- Sheppard L (1996) Analysis of the physiotherapy industry: challenges for marketing. Health Mark Q 14(2): 35-42.
- Buckle PW, Devereux JJ (2002) The nature of work-related neck and upper limb musculoskeletal disorders. Appl Ergon 33(3): 207-217.
- Munabi IG, Buwembo W, Kitara DL, Ochieng J, Mwaka ES (2014) Musculoskeletal disorder risk factors among nursing professionals in low resource settings: a cross-sectional study in Uganda. BMC Nurs 13(1): 7.
- Brogårdh C (2006) Constraint induced movement therapy influence of restraint and type of training on performance and on brain plasticity.
- Eunson P (2016) Aetiology and epidemiology of cerebral palsy. Paediatrics and Child Health 26(9): 367-372.
- Trinkoff AM, Lipscomb JA, Geiger‐Brown J, Brady B (2002) Musculoskeletal problems of the neck, shoulder, and back and functional consequences in nurses. Am J Ind Med 41(3): 170-178.
- Harcombe H, McBride D, Derrett S, Gray A (2010) Physical and psychosocial risk factors for musculoskeletal disorders in New Zealand nurses, postal workers and office workers. Inj Prev 16(2): 96-100.
- Litwic A, Edwards MH, Dennison EM, Cooper C (2013) Epidemiology and burden of osteoarthritis. Br Med Bull 105: 185-199.
- Walker BF (2000) The prevalence of low back pain: a systematic review of the literature from 1966 to 1998. J Spinal Disord 13(3): 205-217.
- Hall MJ, Levant S, De Frances CJ (2012) Hospitalization for stroke in U.S. hospitals, 1989-2009. NCHS data brief 95: 1-8.
- Botha W, Bridger R (1998) Anthropometric variability, equipment usability and musculoskeletal pain in a group of nurses in the Western Cape. Appl Ergon 29(6): 481-490.
- Chiou WK, Wong MK, Lee YH (1994) Epidemiology of low back pain in Chinese nurses. Int J Nurs Stud 31(4): 361-368.
© 2018 Mahboob ur Rahman. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






