- Submissions
Full Text
Research & Investigations in Sports Medicine
Effects of Anxiety on Athletic Performance
Muhammad Khushdil Khan, Alamgir Khan*, Sami Ullah Khan, Salahuddin Khan
Department of Sports Science and Physical Education, Gomal University, Pakistan
*Corresponding author: Alamgir Khan, Department of Sports Science & Physical Education Gomal University, Pakistan
Submission: September 21, 2017; Published: October 25, 2017

ISSN: 2577-1914 Volume1 Issue2
Abstract
The study was initiated to know the effect of anxiety on sports performance of players of Gomal university Deraismail khan K.P.K Pakistan. The main objective of this particular study was to know about effect of anxiety on players regarding physiological, psychological and behavioral perspective. The population of this research study was comprised of all players participating in different sports activities at Gomal University. A complete list of all registered players was taken from directorate of sports Gomal University. For data collection the researcher developed closed form of questionnaire and personally get back response from his responses from 120 players which were selected randomly as a target population. After collection of data it was tabulated and analyzed by using percentage and mean average as statistical tool by the researcher. After analysis of data the researcher arrived at conclusion that anxiety negatively affects the overall sports performance of a player. The data also revealed that awareness about anxiety and its negative effects and also reduction processes and practices such as medication, meditation, Psychotherapy are most important to overcome and face anxiety in sports participation.
Keywords: Anxiety; Sports; Players; Sports performance
Introduction
According to Kumar et al. [1] an individual feels mentally disturbed, he is said to be an anxious mood. As for as anxiety in the field of physical education and sports activities are concerned, it is said that anxiety is most common in competitive sports environment. According to Robinson et al. [2] anxiety and sports are deeply related with each other. He further stated that anxiety is not always bad but it can help the players in focusing and alerting in performing their actions. While participating in various sports activities, it is observed that the participants get anxious. In a research study, conducted by Kumar et al. [3] it is concluded that mostly young or inexperienced players become anxious and as a result they affect their performance. The author recommended that the player should not be too anxious neither his level of anxiety should be very low. In moderation, anxiety is not always bad. According to Robinson et al. [2] adequate level of anxiety can produce better result in sports. The author further illustrated that best result can only be obtained when the player participate with moderate level of anxiety.
The researcher himself is a player and is being participating in sports at different levels. During his sports career the researcher being a player faced plenty of difficulties like stress, arousal and anxiety with reference to sports environment. In the current research work, the researcher would like to emphasize on the effects of anxiety on sports performance. The researcher is of the opinion that the effects of anxiety would be studied from three perspectives like physiological, cognitive and behavioral.
Statement of the problem
Sports and anxiety are related to each other. Anxiety in sports has been one of the factors participating at various levels of sports. They should also know that how one can cope with such situations and avoid such kinds of situation to occur in sports activities. This study in hand is an attempt to evaluate the perception of players regarding effects of anxiety on sports performance. This study is conducted in Gomal University DeraIsmail Khan. The researchers address the perception of players in connection to the effects of anxiety upon their sports participation through questionnaire. All possible efforts are made to reach at certain findings and conclusions of the study.
Objectives of the study
This research was based on the following objectives
a) To find out the perception of players regarding effects of anxiety from physiological perspective.
b) To assess the perception of players regarding effects of anxiety from psychological perspective.
c) To evaluate the perception of players regarding effects of anxiety from behavioral perspective.
Significance of the study
This study is related to the effects of anxiety upon sports participation. Through this study the readers will be able to know the effects of anxiety from different perspectives. The findings of this study may be very helpful to assess the perception of players regarding effects of anxiety in connection to their sports participation. In this way they will be able to cope with such circumstances which lead to the occurrence of anxiety. Similarly, through this study the coach, managers and players will be able to educate the inexperience players with special reference to anxiety in sports. Moreover the recommendations of the study will be helpful to achieve better results in sports.
Hypotheses of the study
The following Null Hypothesis were tested
HO1 There is no significant effects of anxiety upon physiological performance as perceived by players.
HO2 There is no significant effects of anxiety upon psychological performance as perceived by players.
HO1 There is no significant effects of anxiety upon behavioral perspective as perceived by players.
Methodology of the study
The following procedural steps were taken to reach at certain findings of the study.
Population of the study: The population of this study comprised of all the players at different level of sports activities.
Sampling: A complete list of the players obtained from the Directorate of Sports Gomal University DeraIs
mail Khan. The researcher collected representative numbers of the sample from both (New Campus and City Campus) by applying convenient sample technique.
Instrument and mode data collection: The researcher prepared and used questionnaire consist of three options for the purpose of data collection regarding effects of anxiety on sports. The questionnaire was developed under the guidance of research supervisor and literature review also. The researcher personally distributed the developed questionnaire and collected back after getting it filled by the respondents.
Data analysis: The collected data was analyzed through appropriated statistical tools.
Anxiety and Sports
Anxiety is a natural human reaction that involves mind and body. It is an alarm system that is activated whenever a person perceives danger or threat. When the body and mind react to danger or threat, a person feels physical sensations of anxiety. Anxiety, as a negative emotional, affect perceptions in sport competitions, where a large majority of athletes consider anxiety to be debilitative towards performance, which may result in decreases in performance [4,5]. Many researches showed that winning in a competition depend on how an athlete can control their anxiety level [6]. Anxiety consists of two subcomponents: cognitive and somatic anxiety, which influence performance [7,8]. The cognitive is the mental component, which characterized by negative expectations about success or selfevaluation, negative self-talk, worries about performance, images of failure, inability to concentrate, and disrupted attention [6,7]. Contradictory, the somatic is the physiological element, which related to autonomic arousals, negative symptoms such as feelings of nervous, high blood pressure, dry throat, muscular tension, rapid heart rate, sweaty palms and butterflies in your stomach [7,8].
Anxiety is a construct that has consistently been studied in the field of sport psychology, and has become the most heavily researched psychological variable that influences athletic performance [9]. There is a closer relationship of sports and anxiety because we know that sports is competitive in nature while win and loss is the part of sports. Any sporting game or contest can give rise to anxiety when one’s perceived ability does not measure up to the demands of the task. A great deal of research has been devoted to the effect of anxiety on sports performance. Researchers have found that competitive state anxiety is higher for amateur athletes in individual sports compared with athletes in team sports [10].
Anxiety plays a paramount role in sport. It is the challenge to sports participation which produces anxiety. How and athlete handles the anxiety determines how successful he would be. The degree of anxiety also varies with a number of different conditions. Anxiety is likely to be greater in higher competitive sports than in relatively non-competitive sports, because in the competitive sports, participants are expected to win and great demands are made upon them to succeed. The individual and team sports persons may have to appearance of anxiety. Nobody is without anxiety in the field of games and sports. It is this important factor which affects the performance of sports persons in their understandings and challenges at sports. Hann [11] found “sports psychologist have long believed that high levels of anxiety during competition are harmful, worsening performance and even leading to dropout.” Anxiety may be reduced or it may be increased with circumstances. Athletes can manage anxiety using techniques such as relaxation, hypnotherapy, cognitive behavior therapy and positive thinking.
Effect of Anxiety on Sports Performance
Anxiety affects the overall performance through following ways:
Psychological effects
Concentration towards any external threat takes place in human body immediately and automatically. Ampofo-Boateng [12] noted that anxiety disrupted the attention and worries about the performance in competitive situation. The effect on a person’s thinking can range from mild worry to extreme terror. In other research study anxiety was considered one of the main important psychological factor influences on sports performance [13].
Effect on central nervous system (CNS)
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives, coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies. Anxiety effect directly on sympathetic nervous system and the link between body parts and CNS is affected and in this regard a person became unable to perform the mental function effectively and efficiently which effect directly sports performance of athletes. Researchers showed that anxiety effect on the mental level of an athlete and changes the performance in the shape of feelings of nervous, high blood pressure etc. which are direct related to central nerves system [7]. In other way Anxiety and stress stimulate the production of Catecholamine commonly known as epinephrine, nor epinephrine and dopamine. These chemicals have adverse effect on memory, both long term memory and short term memory of the person affected. Person becomes forgetful and irritable can experience lack of concentration, feeling of fear and decreased sleep or disturbed sleep pattern.
Following are some of the general mental effects of anxiety:
a. Difficulty concentrating, racing thoughts
b. Trouble learning new information
c. Forgetfulness, disorganization, confusion
d. Difficulty in making decisions
Physiological effects
Physiological effects refer to the changes which take place in the movements of different organ of the body. Anxiety affects directly or indirectly different functions of the body in various ways which include muscles shake, fast heartbeat, sweating fast breathing [14]. Some of the physiological effects of anxiety are discussed below.
Gastrointestinal effects
When a person is feeling anxious or having an anxiety attack they can experience some gastrointestinal upset which affects on the performance of athlete. He can have frequent urination or diarrhea, where needs to use the bathroom more than normal. If someone has stomach upset, it may be accompanied by dizziness [15].
Muscular effects
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) noted that anxiety can also have an effect on individual’s muscles. For example, the anxious player may have tremors, where he has a shaking movement that he cannot control. These tremors or twitches can occur when the individual is still, moving or holding an item. Another muscular effect of anxiety is muscle tension, where the individual has tight muscles that can sometimes feel painful [15].
Breathing effects and glandular effects
Rapid breathing is known as hyperventilating. Hyperventilation can be a normal response when you are anxious. A common symptom of anxiety, according to the NIH, is sweating; during a bout of anxiety, the sweat glands produce more sweat than normal. The player can also experience changes in breathing: she may have shortness of breath or rapid breathing. When the patient has shortness of breath, it can feel like she is choking and grasping for air [16].
Other effects on the body
Anxiety can also affect other parts of the body. For example, the heart can be affected, resulting in either a pounding heart or an irregular heartbeat. The player can also have headaches, insomnia and fatigue. Problems with the mouth and throat can happen, such as a dry mouth or difficulty swallowing.
Effect on cardiovascular system
Anxiety can lead to increased heart rate, palpitations, increased blood pressure. All these changes take place in the body by more production of stress hormones like adrenalin, noradrenalin and cortisol.
Effect of anxiety on skin and hair
Anxiety can affect the skin badly in terms of loss of glow, development of acne etc. Certain skin diseases like psoriasis and eczema are known to appear because of anxiety. Hair fall is also very common in constantly anxious people. Prolonged anxiety could trigger under-active thyroid or hypothyroid, which in turn, could lead to many loss of hair, loss of glow on skin, and other symptoms.
Behavioral effects
Anxiety effects also on the behavior of an individual because Anger, displeasure, problems in communication and unfriendliness are the common effects of anxiety.
Personality changes
The term personality is used to describe the consistent individual patterns of thoughts, emotion, and behavior that characterize each person across time and situations. Each individual’s personality is thought to be influenced by both an inherited “genetic” component (usually called temperament) and by their interactions with the environment. Some people experience personality changes in response to stress hormones, which are part of their internal environment. The following changes in personality are not uncommon to observe in people who are anxious:
a. displeasure
b. unfriendliness
c. Frustration
d. Anger
e. Aggressive feelings and behavior
f. Decreased interest in appearance
g. Decreased concern with punctuality
h. Obsessive/compulsive behavior (trying to cope with unwanted repeated thoughts or obsessions, by engaging in compulsive behavior rituals such as counting, checking, washing, etc.)
i. Reduced work efficiency or productivity
j. Lying or making excuses to cover up poor work
k. Excessive defensiveness or suspiciousness
l. Problems in communication
m. Social withdrawal and isolation
n. Impulsivity (expressed as impulse buying, gambling, sexual behavior, or similar)
Treatment of Anxiety
Anxiety disorders are real disorders that require treatment. Recovery is not simply a matter of will and self-discipline. Fortunately, much progress has been made in the last two decades in the treatment of people with mental illnesses. Although the exact treatment approach depends on the type of disorder, one or a combination of the following therapies might be used for most anxiety disorders:
Medication
Medicines used to reduce the symptoms of anxiety disorders include antidepressants and anxiety-reducing medications.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy (a type of counseling) addresses the emotional response to mental illness. It is a process in which trained mental health professionals help people by talking through strategies for understanding and dealing with their disorder.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy
People suffering from anxiety disorders often participate in this type of therapy in which the person learns to recognize and change thought patterns and behaviors that lead to troublesome feelings.
Presentation and Analysis of Data
H01
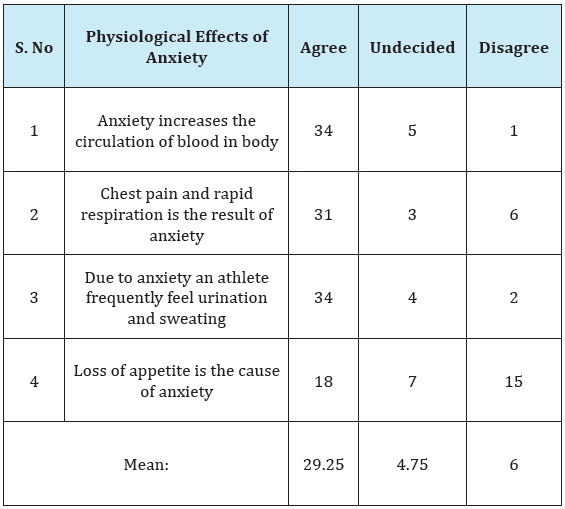
There is no significant effect of anxiety upon physiological performance as perceived by players. Table 1 shows that there is significant effect of anxiety upon physiological performance as perceived by players because the mean of Agree is 29.25 and undecided is 4.75 and mean of disagree is 06 (29.25>4.75 & 06) while null hypothesis stating that there is no significant effect of anxiety upon physiological performance of the player so hypothesis No.1 is rejected
H02
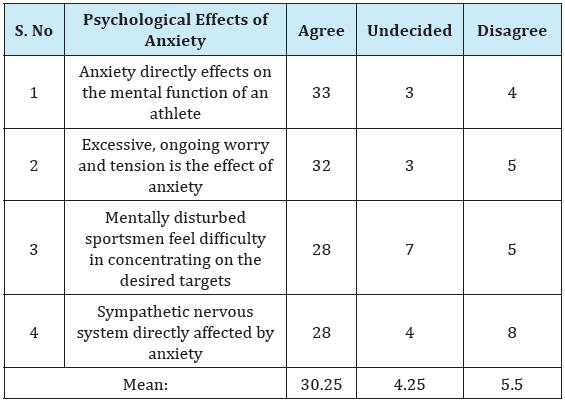
There is no significant effect of anxiety upon psychological performance as perceived by players. Table 2 shows that there is significant effect of anxiety upon psychological performance as perceived by players because the mean of Agree is 30.25 and undecided is 4.25 and mean of disagree is 5.50 (30.25>4.25 & 5.50) while null hypothesis stating that there is no significant effect of anxiety upon psychological performance as perceived by the players. So hypothesis No.2 is hereby rejected
H03
There are no significant effects of anxiety upon behavioral perspective as perceived by players. Table 3 shows that there is significant effect of anxiety behavioral performance as perceived by players because the mean of Agree is 29.16 and undecided is 5.16 and mean of disagree is 5.66 (29.16>5.16 & 5.66) while null hypothesis stating that there is no significant effect of anxiety upon behavioral performance as perceived by the players. So hypothesis No.3 is hereby rejected
H04
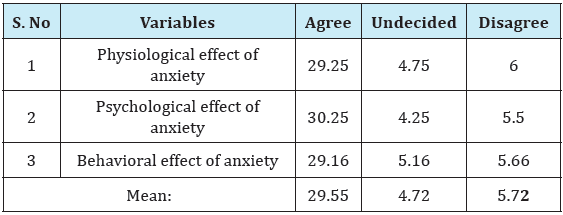
There is no significant effect of anxiety upon sports performance as perceived by the players. Table 4 shows that there is significant effect of anxiety upon sports performance as perceived by players because the mean of Agree is 29.55 and undecided is 4.72 and mean of disagree is 5.72 (29.55>4.72 & 5.72) while null hypothesis stating that there is no significant effect of anxiety upon Sports performance as perceived by the players. So hypothesis No 4 is hereby rejected
Findings
On the basis of data analysis the finding of the study are following
1. There is significant effect of anxiety upon physiological performance as perceived by the players because the mean of Agree is 29.25 and undecided is 4.75 and mean of disagree is 06 (29.25>4.75 & 06) while null hypothesis stating that there is no significant effect of anxiety upon physiological performance. So hypothesis No.1 is rejected (Table 1).
Table 1: Showing the effect of anxiety upon physiological performance.
2. There is significant effect of anxiety upon psychological performance as perceived by the players because the mean of Agree is 30.25 and undecided is 4.25 and mean of disagree is 5.50 (30.25>4.25 & 5.50) while null hypothesis stating that there is no significant effect of anxiety upon psychological performance. So hypothesis No.2 is rejected (Table 2).
Table 2: Mean showing the effect of anxiety upon psychological performance.
3. There is significant effect of anxiety upon behavioral performance as perceived by the players because the mean of Agree is 29.16 and undecided is 5.16 and mean of disagree is 5.66 (29.16>5.16 & 5.66) while null hypothesis stating that their no significant effect of anxiety upon behavioral performance. So hypothesis No.3 is rejected (Table 3 & 4).
Table 3: Mean showing the effect of anxiety upon behavioral performance.
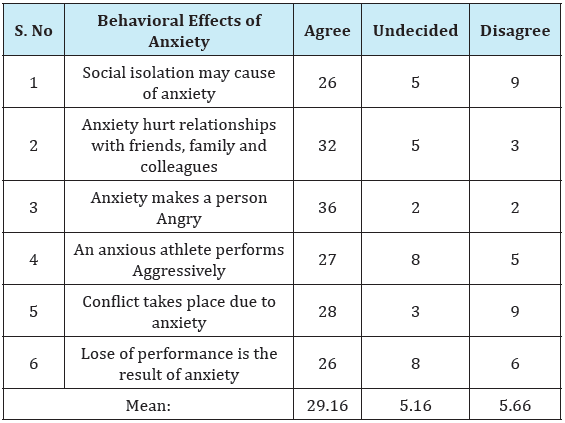
Table 4: Mean showing the effect of anxiety upon sports performance.
Conclusion
On the basis of findings the researcher arrived at conclusion that anxiety has a significant effect on the overall physiological, psychological and behavioral performance of a sportsman. It means that anxiety has significantly effects the overall performance of athlete.
Recommendation of the Study
On the basis of findings and conclusion the researcher recommended that
1. Different awareness program may be conducted about anxiety and its effects on performance
2. Athlete may be kept aware about different psychological factors effecting their performance
3. Athlete may be kept aware about different physiological factors effecting their performance
4. Athlete may be kept aware about different behavioral factors affecting their performance.
References
- Feldman G, Hayes A, Greeson J, Kumar S, Laurenceau JP (2007) Mindfulness and emotion regulation: The development and initial validation of the Cognitive and Affective Mindfulness Scale-Revised (CAMS-R). Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment 29: 177-190.
- Robinson E, Smith E (2015) Biblical Researches in Palestine and the adjacent regions (Vol 2). Cambridge University Press, New York, USA.
- Kumar MS, Woo J (2015) Public debt and growth. Economica 82(328): 705-739.
- Weinberg RS, Gould D (2011) Foundations of Sport and Exercise Psychology. (2nd edn), Champaign, Human Kinetics Illinois, USA.
- Raglin JS, Hanin YL (2000) Competitive anxiety. In: Yuri LH (Ed.), Emotions in Sport. Champaign, Human Kinetics, Illinois, USA.
- Humara M (2001) The relationship between anxiety and performance: A Cognitive behavioral perspective. The Online Journal of Sport Psychology.
- Jarvis M (2002) Sport Psychology. Routledge, New York, USA.
- Martens R, Vealey RS, Burton D (1990) Competitive Anxiety in Sport. Champaign, Human Kinetics, Illinois, USA.
- Cox RH (2007) Sport psychology: Concepts and applications. McGraw- Hill Companies Inc., New York, USA.
- Simon JA, Martens R (1977) S.C.A.T. as a predictor of A-states in varying competitive situations. In: Landers DM, Christina RW (Eds.), Psychology of Motor Behaviour and Sport (Vol 2) Human Kinetics, Champaign, Illinois, USA, pp. 146-156.
- Hann YL (2000) Emotions in sports. Champaign, Human Kinetics, Illinois, USA.
- Ampofo-Boateng K (2009) Understanding sport psychology. In: Shah Alam, Selangor (Eds.), UPENA, Malaysia.
- Raglin JS, Hanin YL (2000) Competitive anxiety. In: Yuri LH (Eds.), Emotions in Sport Champaign, Human Kinetics, Illinois, USA, pp. 93- 111.
- Arlington (2013) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Association (5th edn), American Psychiatric Publishing, USA, pp. 189-195.
- Stannard L (2013) Effects of Anxiety on the Body.
- Bouras N, Holt G (2007) Psychiatric and Behavioral Disorders in Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities (2nd edn), Cambridge University Press, New York, USA.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






