- Submissions

Full Text
Research & Development in Material Science
Antiferromagnetic Insulator Double Perovskite La2CoZrO6
Ting-Kai Cheng1, Albert Zhong-Ze Yan1, Po-Han Lee1* and Yin-Kuo Wang2*
1Affiliated Senior High School of National Taiwan Normal University, Taiwan
2Center of General Education, National Taiwan Normal University, Taiwan
*Corresponding author: Po-Han Lee, Affiliated Senior High School of National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei 10658, Taiwan
Submission: April 03, 2018;Published: April 18, 2018

ISSN: 2576-8840
Volume5 Issue4
Abstract
Density functional theory and generalized gradient approximation (GGA) with onsite Coulomb interaction (GGA+U) is used to calculate the magnetic properties of new material La2CoZrO6. Here, we considered the possibilities of four magnetic orderings: ferromagnetic, ferrimagnetic, antiferromagnetic, and nonmagnetic states. Under the GGA+U scheme, we finally find that the antiferromagnetic insulator stands out as the most stable state among these four states.
Keywords: Half-metal; Double perovskite; First principle calculations
Abbreviations: AFM: Antiferromagnetic; HM: Half Metal; IS: Insulator; FM: Ferromagnetic
Introduction
Recently, magnetic half-metals have been in high interest in spintronic applications [1], such as magneto dielectric capacitors [2,3] and spin filtering tunnel junctions [4-8]. Double perovskites, compared with other complex crystal structures, are relatively simple and convenient for integration [9]. Double perovskite halfmetals have three attributes:
1. Quantization of the magnetic moment
2. 100% spin polarization at the Fermi level
3. Zero spin susceptibility
Their special attributes have brought about many experimental and theoretical researches, with various findings including Ferromagnetic half-metals with near room temperature Curie temperatures found in ordered double perovskites such as La2NiMnO6 (TC=280K) [10] and Bi2NiMnO6 (TC=340K) [11]. However, some double perovskite magnetic insulators are antiferromagnetic (AFM) and not ferromagnetic (FM), such as in the cases of La2VTcO6 and La2VCuO6 [12]. In many cases, the existence of half-metal (HM) is related to double-exchange or super exchange interactions. Sr2CoZrO6 and A2CrRuO6 (A=Si, Ge, Sn, and Pb) are both half-metals attributed to super exchange and generalized doubleexchange mechanism [4,13]. When structuring A2BB’O6 half-metal materials [14], A is usually exchanged with alkaline metals or rare earth metals (Ca, La, Ce etc.), while A=La in this paper. BB’ can be any combination of the 29 transitional metal elements other than A (Ca, Ce etc.).
It is a time-consuming task to calculate the 406 C229 combinations, and when searching for magnetic properties, we first used VASP code to calculate the self-consistent electronic structure of all 406 La2BB’O6 compounds. Fuh et al. [15] have mentioned that the states of FM-semiconductor states in the BB’ pairs of Fe (Co, Rh, Ir) are stable against antiferromagnetism and hence we do not consider them any further.
The aim of this paper is to search for new antiferromagnetic insulators from double-perovskite oxides. Here, we use first principle theory to calculate and explore potential insulating material La2CoZrO6. In transition metal oxides, the fact that strong electron correlation cannot be observed with GGA calculations should be corrected with GGA+U [16-19]. In GGA+U, the effective parameter Ueff=U–J is used [16], with U and J being coulombs and exchange parameters, respectively. In this paper, for simplicity, we use U to represent Ueff. In the following discussion, we focus on the physical properties and correction effect on the electronic structures of possible AFM insulator La2CoZrO6.
Discussion
Computational method
The first principle DFT calculations for theoretical calculations and the electronic structure calculations with generalized gradient correction (GGA) [17] plus on-site Coulomb interaction U (GGA+U) [18-20] are used. Structural optimization calculations (i.e., relaxation for both lattice constants and atomic positions) were carried out with the all full-potential projector-augmented wave (PAW) [21,22] method, carried out with the VASP package [23,24]. We used the conjugate-gradient (CG) method to find the stable ionic positions, and the energy convergence criteria for self-consistent calculations were set to 10-6 eV. We also used the 8*8*6 k-point grids in the Brillouin zone and set the cut-off energy of the plane wave basis to 450eV. To determine the theoretical lattice constants and atomic positions through structural optimization calculations, a conjugated-gradient method was used under the conditions of forces and stresses lower than 0.03eV/A and 0.9kBar, respectively. To reduce symmetry by relaxing the structure, we used a larger unit cell with two f.u., as shown in Figure 1. The crystal parameters from full optimization calculations are listed in Table 1. La2CoZrO6 has a c/a ratio close to the ideal value of √2, meaning that the structural shape is close to the ideal double perovskite structure. We not only carried out full structural optimizations, but also put into consideration the possibility of four distinct magnetic orderings: nonmagnetic (NM), ferromagnetic (FM), ferrimagnetic (FiM), and antiferromagnetic (AFM) phases in Figure 2.
Figure 1: An ideal double perovskite ordered structure, La2CoZrO6, where there are 4 kinds of O, O1(0, 0, 0.2434), O2(0.5, 0.5, 0.2566), O3(0.2428, 0.2428, 0), O4(0.2572, 0.2572, 0.5).

Figure 2: The schematic diagram of 4 magnetic states: FM, FiM, AF and NM.

Table 1: Structural parameters of the possible AFM-Is material in the fully optimized structure.
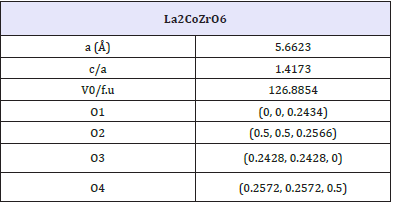
La2CoZrO6 are in space group (123 P4/mmm) where La(x, y, z) = (0, 0.5, 0.75), Co1(x, y, z) = (0, 0, 0), Co2(x, y, z) = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5), Zr1(x, y, z) = (0.5, 0.5, 0), and Zr2(x, y, z) = (0, 0, 0.5). O1(x, y, z) = (0, 0, O1z). O2(x, y, z) = (0.5, 0.5, O2z). O3(x, y, z) = (O3x, O3y, 0). O4(x, y, z) = (O4x, O4y, 0.5).
Results
Table 1: Calculated physical properties of the La2CoZrO6 in double perovskite structure in the full structural optimization calculation of GGA (+U).

AFM: Antiferromagnetic; FM: Ferromagnetic
Table 2 shows the calculated quantities of electronic and magnetic properties. In the AFM ordering, La2CoZrO6 shows conducting metal and insulating attributes in the GGA and GGA+U scheme respectively. La2CoZrO6 has the lowest energy state in the AFM-Is ordering under GGA+U, at 647meV below the FM state’s energy. With GGA, in the AFM ordering, La2CoZrO6 is conducting in both spin channels, resulting in a metal, at 219meV below the FM state’s energy. The band gap for both spin channel opens to 0.95eV in the AFM ordering after +U, resulting in an AFM insulator.
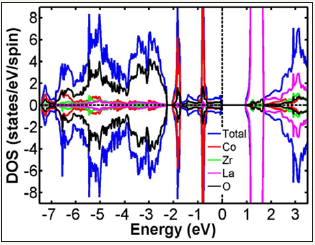
The total DOS in the GGA scheme for La2CoZrO6 is presented in Figure 3a, and the total DOS in the GGA+U scheme for La2CoZrO6 is presented in Figure 3b. The charge configuration in GGA is Co1.653 (3d7.347) and Zr2.320+ (4d1.680). The charge configuration in GGA+U is Co1.702 (3d7.298) and Zr2.402+ (4d1.598).
Figure 3a: Total DOS of AFM-state La2CoZrO6 in the GGA scheme.
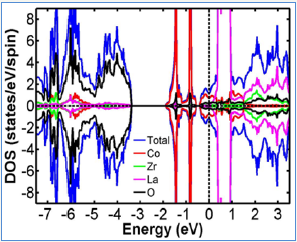
Figure 3b: Total DOS of AFM-state La2CoZrO6 in the GGA+U scheme.
Conclusion
We have carried out full research of ordered double perovskite La2CoZrO6. The full structural optimization calculations results show La2CoZrO6 has potential to be an antiferromagnetic insulator. According to the energy levels, AFM-Is is the most stable state. We hope that these findings can encourage further experimental research on antiferromagnetic insulators.
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge support from the National Center for Theoretical Sciences of Taiwan, National Taiwan Science Education Center in Taiwan (P. H. Lee), and the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology under Grants Nos. MOST-105-2112-M- 003-006 (Y. K. Wang), and MOST-106-2514- S-788-002 (P. H. Lee). Support from the National Center for High-performance Computing of Taiwan in providing computing resources to facilitate this research is also gratefully acknowledged.
References
- Hu X (2012) Half-metallic antiferromagnet as a prospective material for spintronics. Adv Mater 24: 294-298.
- Cheong SW, Mostovoy M (2007) Multiferroics: A magnetic twist for ferroelectricity. Nat Mater 6(1): 13.
- Ramesh R, Spaldin NA (2007) Multiferroics: progress and prospects in thin films. Nat Mater 6: 21.
- Gajek M, Bibes M, Barthèlèmy A, Bouzehouane K, Fusil S (2005) Spin filtering through ferromagnetic BiMnO3 tunnel barriers. Phys Rev B 72: 020406R.
- Tsymbal EY, Kohlstedt H (2006) Tunneling across a ferroelectric. Science 313: 181.
- Santos TS, Moodera JS (2004) Observation of spin filtering with a ferromagnetic EuO tunnel barrier. Phys Rev B 69: 241203(R).
- Zhuravlev MY, Sabirianov RF, Jaswal SS, Tsymbal EY (2005) Giant electroresistance in ferroelectric tunnel junctions. Phys Rev Lett 94: 246802.
- Ju S, Cai TY, Guo GY, Li ZY (2007) Electrically controllable spin filtering and switching in multiferroic tunneling junctions. Phys Rev B 75: 064419.
- Halder A, Nafday D, Sanyal P, Dasgupta ST (2018) Computer predictions on RH-based double perovskites with unusual electronic and magnetic properties. NPJ Quantum Materials 3: 17.
- Rogado NS, Li J, Sleight AW, Subramanian MA (2005) Magnetocapacitance and magnetoresistance near room temperature in a ferromagnetic semiconductor: La2NiMnO6. Adv Mater 17(18): 2225-2227.
- Padhan P, LeClair P, Gupta A, Subramanian MA, Srinivasan G (2009) Magnetodielectric effect in Bi2NiMnO6-La2NiMnO6 superlattices. J Phys Condens Matter 21: 306004.
- Wang YK, Lee PH, Guo GY (2009) Half-metallic antiferromagnetic nature of La2VTcO6, La2VCuO6 from ab initio calculations. Phys Rev B 80: 224418.
- Liu YP, Fuh HR, Xiao ZR, Wang YK (2014) Theoretical prediction of halfmetallic materials in double perovskites Sr2Cr(Co)B’O6 (B’=Y, La, Zr, and Hf) and Sr2V(Fe)B’O6 (B’=Zr and Hf). J of Alloys and Compounds 586: 289-294.
- Liu YP, Fuh HR, Wang YK (2014) Expansion research on half-metallic materials in double perovskites of Sr2BB’O6 (B=Co, Cu, and Ni; B’=Mo, W, Tc, and Re; and BB’=FeTc). Comp Materials Science 92: 63-68.
- Fuh HR, Weng KC, Liu YP, Wang YK (2015) New ferromagnetic semiconductor double perovskites: La2VCuO6 (M=Co, Rh, and Ir). J of Alloys and Compounds 622: 657-661.
- Solovyev IV, Dederichs PH, Anisimov VI (1994) Corrected atomic limit in the local-density approximation and the electronic structure of d impurities in Rb. Phys Rev B Condens Matter 50(23): 16861-16871.
- Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77(18): 3865-3868.
- Chen SH, Xiao ZR, Liu YP, Wang YK (2013) Investigation of possible halfmetallic antiferromagnets on double perovskites A2BB’O6 (A=Ca, Sr Ba; B,B’=transition metal elements). Comm of Comp Phys 13(2): 526-539.
- Liu YP, Chen SH, Fuh HR, Wang YK (2013) First-principle calculations of half-metallic double perovskite La2BB’O6 (B,B’=3d transition metal). Comm of Comp Phys 14(1): 174-185.
- Holman KL, Huang Q, Klimczuk T, Trzebiatowski K, Bos JWG, et al. (2007) Synthesis and properties of the double perovskites La2NiVO6, La2CoVO6, and La2CoTiO6. J of Solid State Chem 180: 75-83.
- Kresse G, Joubert D (1999) From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 59(3): 1758.
- Blöchl PE (1994) Projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B Condens Matter 50(24): 17953-17979.
- Kresse G, Hafner J (1993) Ab initio molecular dynamics for open-shell transition metals. Phys Rev B Condens Matter 48(7): 13115-13118.
- Kresse G, Furthmller J (1996) Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput Mater Sci 6(1): 15-50.
© 2018 Po-Han Lee. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






