- Submissions

Full Text
Progress in Petrochemical Science
Methanol Regeneration Technology for Compressor Stations of the Main Gas Pipeline
Paranuk AA1* and Khrisonidi VA2
1Department ONGP, Kuban State Technological University, Russia
2Branch of Maikop Technological University, Russia
*Corresponding author: Paranuk AA, Department ONGP, Kuban State Technological University, Russia
Submission: July 27, 2021;Published: August 30, 2021

ISSN 2637-8035Volume4 Issue2
Abstract
The authors have proposed an original scheme of methanol regeneration in the conditions of compressor stations, which makes it possible to separate the azeotropic solution by the adsorption method. When implementing this scheme, a certain grade of zeolite is used, which makes it possible to separate solutions at the molecular level using the molecular sieve properties of the adsorbent
Keywords:Regeneration gas; Adsorbent; Zeolite; Separator; Liquid hydrocarbons
Mini Review
The unique adsorption properties of natural zeolites open up new prospects for their
application in industry. For example, in such areas as natural gas dehydration, water
purification, removal of nitrogen compounds from wastewater [1,2]. Thus, the scope of their
application is very broad. Due to the structure of the framework of zeolites, most zeolites
can be used as molecular sieves, which opens up a whole area for the use of natural zeolites
as cheap adsorbents in technological processes. For example: A method for separating an
azeotropic solution by adsorption methods on natural zeolites. The initial azeotropic solution
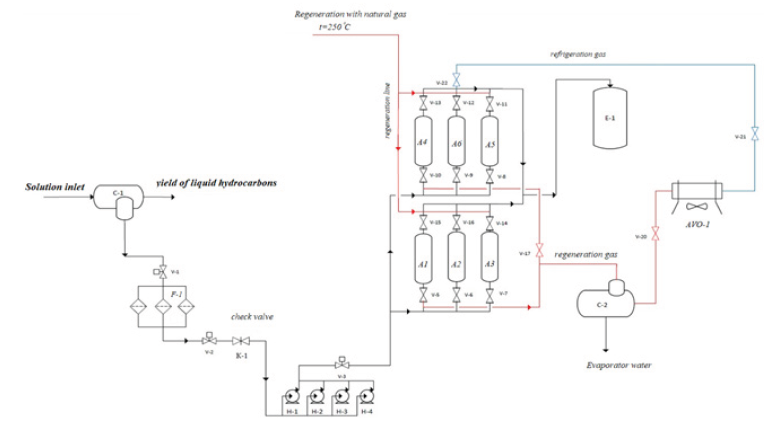
(Figure 1) from the separator for further processing is fed into the pipeline (1) by means of
pumps (2) through the pipeline into the adsorbers with zeolite (3) under the action of the
pumps, the solution is forced from the bottom up through the block of adsorbers into the
pipeline (5). After saturation of the adsorbent with a solution, it is necessary to switch the
taps and stop the pumping for the regeneration of the zeolite. Zeolite can be regenerated in
2 ways.
The first method is provided for the cases of the implementation of this technological
scheme in the conditions of the main compressor station with its own drying system using
solid absorbers, since in such schemes there is a natural gas heating furnace for their own
needs. Therefore, it is possible to use part of the regeneration gas for the desorption of the
zeolite [3-5]. To implement the stages of desorption, it is necessary to supply natural gas
to the adsorber from top to bottom (4) at a temperature of 250 0C. After desorption, the
mixture is fed to a separator, where droplet moisture is taken, and after the separator to a heat
exchanger where the gas is cooled, and then back to the adsorber for cooling. Thus, the system
turns out to be closed [6,7].
The second method provides for the creation of its own installation for obtaining
regeneration gas, and since the zeolite is well desorbed by nitrogen at a temperature of 250
0C. This scheme can be implemented as follows: the installation for producing nitrogen from
air supplies nitrogen to the heater and after the heater the nitrogen heated to the required temperatures is supplied to the adsorber. After desorption, the
mixture enters the separator, where the liquid fraction is discarded,
and then enters the heat exchanger where it is cooled to the required
temperature and then returned to the adsorber for cooling [8-10].
Figure 1: Technological scheme of the unit for the recovery of methanol from aqueous solutions. С-1-three-phase separator; V-1, V-2, V-3, V-4, V-5, V-6, V-8, V-9, V-10, V-11, V-12, V-13, V- 14, V-15, V-16, V-17, V-20, V-21, V-22 -shut-off and control valves with remote control; Н-1, Н-2, Н-3, Н-4 - pump unit; F-1-block of filters; A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6 - block of adsorbers; С-2 - two-phase separator; E-1 - methanol collection tank; К-1 - check valve; AVO-1 - air cooler.
Conclusion
The authors have proposed a new technology that has been tested in laboratory conditions and is unique; this technology has a number of features that are not presented in this work. In general, it can be noted that the proposed regeneration scheme has a number of features over other methods of methanol regeneration and is more environmentally friendly and energy efficient, in particular, compared to the rectification method of methanol regeneration.
References
- Paranuk AA, Khrisonidi VA (2018) A promising method for separating binary methanol–water solutions. Chemical and Petroleum Engineering 53(11-12): 773-777.
- Paranuk AA, Krisonidi VA, Ponomareva (2016) GV KAco zeolite adsorption of ethyl alcoho Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 11(13): 2876-2877.
- Paranuk AA, Khrisonidi VA, Skhalyakho ZC, Shugalei AI (2016) Technological scheme development of the azeotropic mix separation. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 11(13): 2878-2880.
- Paranuk AA (2017) A mathematical model for calculating the adsorbers for drying and concentration of methanol on zeolites. Chemical and Petroleum Engineering 53(1-2): 41-43.
- Zhdanov SP, Khvoshchev SS, Samulevich NN (1981) Synthetic zeolites: Crystallization, structural and chemical modification and adsorption properties. M Chemistry, 10-11.
- Keltsev NV (1984) Basics of adsorption technology. (2nd edn), M Chemistry, 85-87.
- Donald WB (1973) Zeolite molecular sieves: Structure, chemistry. Wiley, USA, pp. 1-771.
- Kabanova N (2015) A dissertation work for a candidate of chemical sciences on the topic crystallochemical methods for the analysis of free space in the structure of a crystal and their application for the study of certain classes of solid electrolytes and zeolites. Inorganic chemistry.
- Karnaukhov AP (1999) Adsorption: The texture of dispersed and porous materials. Novosibirsk: Science Sib Prev RAS, Russia, 33-63.
- Kiselev AV (1953) Methods for studying the structure of highly dispersed and porous bodies. Moscow: Publishing house of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Russia, pp. 1-
© 2021 Paranuk AA. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






