- Submissions

Full Text
Orthoplastic Surgery & Orthopedic Care International Journal
A Systematic Review of Beneficial Outcomes of Omega-3 Fatty Acid in Human Musculoskeletal Diseases
Zeenat Ara1, Shah Waliullah1*, Mohammed Lafi Al-Otaibi2 and Aftab Alam Khan3
1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, India
2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Saudi Arabia
3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Russia
*Corresponding author: Shah Waliullah, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, India
Submission: May 05, 2022;Published: June 10, 2022
ISSN 2578-0069Volume2 Issue5
Abstract
Omega 3 fatty acid are long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid found mostly in marine & Plant sources Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) are the classes of omega 3 fatty acid that are mostly derived from marine sources, whereas another class of omega 3 fatty acid i.e., Linolenic acid is mostly found in plant sources. Consumption of EPA & DHA daily approx. 3-4gm will help in lowering serum triglycerides level by 25-30%, and in subjects suffering from hypertriglyceridemia, there serum triglycerides level will be lowered approximately 50%. Essential fatty acid for human beings are Alpha-Linoleic Acid (ALA, omega-3) and Linoleic Acid (LA, omega-6) as they are not synthesized by human body, so they are consumed by them from exogeneous sources, for healthy brain higher amount of omega 3 must be include in our diet, for maintaining proper brain functioning specially in those having low baseline levels, and pregnant and lactating mothers and neuropsychiatric subjects need omega 3 fatty acid in sufficient quantity. Supplementation with omega 3 fatty acid helps to get rid from dementia, it’s having good antioxidant properties as well due to its anti-inflammatory action it proves to be best therapy for cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Omega 3 fatty acid; Linoleic acid; Salvia hispanica; Stearidonic acid
Abbreviations:EPA: Eicosapentaenoic Acid; DHA: Docosahexaenoic Acid; LA: Linoleic Acid; ALA: Alpha- Linoleic Acid; CHD: Coronary Heart Disease; BCC: Basal Cell Carcinoma; SCC: Squamous Cell Carcinoma; TLR4: Toll-Like Receptor 4; FFQ: Food Frequency Questionnaire; PPAR: Peroxisome Proliferators-Activated Receptor
Introduction
The two main families of PUFAs are the omega‐ 6 and the omega‐3 PUFAs, that are relevant to human health, linoleic acid (LA, 18:2ω‐6) and α‐linolenic acid (ALA, 18: 3ω‐3), are present in highest amount in most diets, both of them are not synthesized in animal body thus they are regarded as essential fatty acids [1], both are mostly synthesized by plants and found in high proportion in food of plant origin as in chia seeds (Salvia hispanica), nuts, and plant oils are rich in LA, these include safflower, sunflower and pumpkin seeds, walnuts, and corn, safflower and soybean oils, whereas soyabean, pumpkin seeds and walnut are also good source of ALA too [1], including flax seeds (Linum usitatissimum), and flaxseed oil garden cress (Lepidium sativum), richest source of omega-3 fatty acids is farmed mussels, that contains 300-800mg of omega-3 fatty acids which is equivalent to per 100g of cooked meat [2,4]. So, we can say that n-3 fatty acid is highly bioavailable as 50-60% of the lipid in mussel is phospholipid [2,5]. So sustainable source of long chain omega fatty acid is mussels, research has proved that consumption of mussel (81-289g/person/meal depending on study participants’ individual characteristics), as the protein complement of lunch time meals 3x/week is sufficient to meet the recommended intake of omega-3 and thus improves status of omega 3 index in body and contributes to heart health within two weeks [4]. Thus, encouraging mussels’ consumption in place of other proteins could be a viable strategy to easily fulfil omega 3 fatty acid need as per recommendation [2,6]. Omega 3 fatty acid both Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic (DHA) acid protects from various metabolic disorders [7].
Richest source of Stearidonic Acid (SDA) is seed oil of Echium plantagineum, Buglossoides arvensis, and Ribes sp. SDA helps in increasing EPA, DHA content in body more than ALA [7]. Whereas EPA & DHA in body is directly supplied by oil from microalgae and thraustochytrids [7]. Fishes are the richest source of omega 3 fatty acid especially fatty fishes such as salmon, mullet, and mackerel are the best sources of EPA & DHA in diet therefore expansion of the aquaculture industry is on demand, but fish having very long chain omega 3 fatty acid are not useful for vegans and vegetarians, so commercial production of n-3 PUFAs are focused through plant seeds rich in EPA & DHA, thraustochytrids and microalgae, and stearidonic acid (SDA, C18: 4, n-3) [7-10]. Composition of fatty acids in Palm (palmolein) oil is oleic (43%), palmitic (40%), and LA (11%) [11], whereas soyabean has high content of LA (54.17%) whereas, ALA is present in minor concentration therefore ratio of both PUFAs is (n-6/n-3 PUFAs ratio of 10.5) [11]. Algae such as brown, green, and red from North Queensland, Australia are also best sources of omega 3 fatty acids among which highest amount of EPA (3.30mg/g DW) was recorded from red seaweeds (Champia parvula) [12].
Women who mostly consume diet enriched in omega 3 fatty acid in comparison to omega 6 fatty acid have a reduced: Risk of having breast cancer [13]. In comparison to men, women have higher levels of EPA and DHA following equivalent dosing and in comparison, to younger women older women have high level of EPA & DHA [14]. Individuals who are taking fish oil supplement tend to take them daily whereas fish consumption may be more intermittent, both EPA and DHA are responsible for generating bioactive lipid mediators important in inflammation resolution [15], 25% reduction in breast cancer recurrence and improvement in mortality in a large cohort of over 3,000 women with early-stage breast cancer followed for a median of 7 years were observed who preferred higher intakes of EPA and DHA from dietary sources. Study by Patterson RE [16] demonstrated that consumption of fish oil (EPA+DHA) is not associated with breast cancer outcomes whereas consumption of marine fatty acids from food sources helps in reduction of additional breast cancer events and all-cause mortality.
Both Linoleic Acid (LA) and α-Linolenic Acid (ALA) are often abbreviated by their chemical designation, as LA is 18: 2n-6 here 18 represents length of the carbon chain, number of double bond is represented by 2 and the n-6 indicates that the first of the double bonds begins at the sixth carbon atom from the methyl end of the carbon chain, whereas ALA is abbreviated as 18: 3n-3, here n-3 represents that the first double bond is at the third carbon from the methyl end of the chain. In human beings from their respective essential fatty acid, longer chain Polyunsaturated FA (PUFA) can be synthesized by a series of elongation i.e., addition of carbon atoms and desaturation i.e., addition of a double bond, enzymatic reactions, these two series of EFA cannot be inter-converted in humans and thus compete for these enzymes.
In Western diets contain more LA (15-20 times) than ALA, therefore, there diet has high level of long-chain omega-6 FA (Arachidonic Acid, 20:4n-6), so, for maintaining good health under certain dietary conditions supplementation with EPA (Eicosatetraenoic Acid, 20:5n-3) and DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid, 22:6n-3) may be essential [17]. In most body organs including brain and retina of eye level of DHA is much higher in comparison of EPA, but in RBCs EPA level is higher [18-21]. Omega 3 fatty acid has immense role, so, have impact on reproductive system too, it effects Prostaglandin (PG) synthesis, steroidogenesis, transcription factors and membrane properties [22], Studies have shown that dietary supplementation of omega-3 (n-3) PUFAs enhances sperm fertility in birds [23,24] and boars [25,26]. Steroidogenesis is mostly affected by PUFAs such as Arachidonic Acid (AA) and its metabolites as they directly effect on Steroid Acute Regulator (StAR) and cytochrome P450, as both these play role in regulating steroid synthesis [22,27]. Direct precursors of PGs is 20-carbon PUFAs [28], and it participate in the regulation of reproductive endocrinology [29,30].
Feng Y [31] demonstrated the role of PUFA in regulating reproductive system, PUFA plays major role in testis development, ratio of omega 3 fatty acid to omega 6 fatty acid having ratio 4.15 have no significant effect on the testis index (P>0.05), increased germ layers cells, Spermatogonia development were seen, as well elevation in hormonal serum level (GnRH, FSH, LH and T) on 35th day were observed, PUFAs plays significant role in upregulating receptors expression and levels of mRNA of all these genes(GnRHR, FSHR, LHR and StAR), thus their study indicates that balanced between both PUFAs is beneficial in reproduction. Due to their anti-inflammatory effect, promoting pre Resolvins mediators and aggregation of platelets and thrombosis, Omega 3 fatty acid (EPA, DHA), might be a useful therapy against covid-19 as we known in this acute respiratory disease there is immune inflammatory response and uncontrolled production of pro inflammatory cytokine and excessive coagulation so due to their antioxidant PUFA (EPA, DHA) might be a boon therapy in this deadly disease [32].
Omega upregulates the function of neutrophils, macrophages, natural killer cells, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils cells. As we know subjects of Japan & Korea consumes fish one of the best sources of omega 3 fatty acid and thus their serum has elevated level of EPA and DHA and thus these countries have reported lowest severity of COVID-19 [33,34]. The most reliable surrogate marker of omega -3 status is the Omega-3 Index (O3I), represents EPA and DHA content of RBCs expressed as a percentage of the total weight of RBC membrane fatty acids, this index corelates with the omega 3 fatty acid level in the tissue, and with various disorders like CVDs,bipolar disorder etc [35] demonstrated in his cross sectional study on covid-19 pandemic that subjects worldwide are more prone to this deadly virus who have deficiency of omega 3 fatty acid thus have low O3I index, as this index had inverse relation between mechanical ventilation and death in case of covid subjects, but there is need of future research to assess the value of OSI to establish it as a biomarker in case of COVID-19.
Health Benefits of Omega 3 Fatty Acid
Based on geographic area and diet habits omega 3 fatty acids level vary in blood, as Japanese consumes marine diet, so their blood have high level of omega 3 fatty acid in comparison to subjects of Pennsylvania and Japanese Americans living in Honolulu [36]. In comparison to natives of Pennsylvania and Japanese Americans even the lower 5th percentile of blood n-3 fatty acid is higher in natives of Japan than there mean levels even when total fat is comparable [36]. Omega 3 fatty acid level in blood is inversely related to Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) as reported by the multiple risk factor intervention trial reported in 1995 [37]. Studies have demonstrated its beneficial and promising role in various diseases like hypertension, inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, respiratory disease like asthma and in Crohn’s disease [38]. Risk of primary cardiac arrest, coronary artery disease and suppression in serum triglycerides were seen in subjects consuming omega 3 fatty acid sources [38], abnormalities in fatty acid composition is related to mood disorders, studies have demonstrated that suppression in serum concentration of omega 3 fatty acid give rise to mood disorders. Hibbeln [39] showed in his study the relation between the prevalence rate of major depression is inversely proportional to amount of fish consumption.
Study by Peet M [40] demonstrated that major depressant subjects have lower concentration of omega 3 fatty acid in their erythrocyte membranes. Many studies have demonstrated that with increased severity of depression concentration of omega 3 dietary fatty acid level in blood, and in plasma decreased concentration of ratio of omega-3 fatty acids to omega-6 fatty acids is observed [41-43]. Positive impact may have been shown by the increased concentration of essential fatty acids on central serotonergic and dopaminergic neurotransmitter systems [44,45] demonstrated in his studies that dietary supplementation of omega 3 fatty acid supplementation especially DHA have demonstrated positive influence on central nervous system metabolism of serotonin and dopamine as in CSF of controls and abstinent alcoholics elevated level of metabolites of serotonin (5-HIAA) and dopamine (HVA) was observed [44]. According to the American Heart Association, addressing TGs and cardiovascular disease, the recommended dose to subjects needs to lower their TGs level is 2 to 4g/day of EPA plus DHA [46], Whereas according to the endocrine society for lowering TGs levels from moderate to severe stage combination of statin along with omega 3 fatty acid or alone consumption of omega 3 fatty acid is best treatment option [47]. Studies have demonstrated that TGs level in plasma in reduced by 25% to 34% if n-3 fatty acid is consumed as fish oil supplements or as prescription OM-3-A EE [48,49].
PUFA in Human Milk
Difference in composition of human milk from lactating mother is because of difference in fatty acid concentration [50]. By analysing sample of human milk from nine European countries it was found that concentration of both ALA and LA in milk is 0.9% wt/wt & 11.0% wt/wt respectively [50]. One of the meta-analysis by examining 65 data from 2400 women worldwide reveals that mean DHA concentration was 0.32±0.22% of total fatty acids having ranges from 0.06 to 1.4%, whereas elevation in concentration of DHA was found in human milk of subjects living sea shore due to high consumption of marine diet like fish and sea food [51,52] suggests that infants receiving infant formula in combination with PUFA till first year of their life had less allergic symptoms in comparison to infants who are only on infant formula until 4 years old. Even in children having at risk for atopy if they are consuming PUFA so they have less chances of having asthma.
In his double-blind randomized controlled trial on 420 infants who are at high atopic risk [53] demonstrated that when these children consumes a daily dose of fish oil containing 280mg docosahexaenoic acid and 110mg eicosatetraenoic acid or olive oil, since birth to 6 months of age, it was found that after 6 months of age in fish oil supplemented group elevated level of DHA &EPA in their blood (both P<05) whereas lower level of arachidonic acid in erythrocyte (P=003) were observed. This elevated level of PUFA till 6 months of age is associated with lower risk of eczema (P=033) and recurrent wheeze (P=027), whereas at 1 year follow up no clinical outcomes were observed. In case of organ transplantation like kidney and liver recipient are over 100 folds prone to develop skin cancer, one of the follow up study on 449 transplant subjects has observed that who are consuming long-chain omega-3 PUFAs and alpha linolenic acid have reduced risk to develop Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) and Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) respectively [54].
Studies have proved that nutritional diets rich in omega 3 fatty acid [55] may help to get rid from fatigue caused by cancer/ cancer related fatigue [56], Kleckner AS [57] demonstrated in his study that in cancer subjects if there nutritional status is improved then concentration of omega 3 fatty acid will increase that help them to get rid from cancer related fatigue, Breast cancer patients of 4-36 months post-treatment having moderate to severe fatigue were enrolled and for 6 weeks, group 1 & 2 were given 6g fish &soyabean oil respectively or 3g of each daily. They observed that subjects having good nutritional diet have increased total serum omega 3 level at baseline and after supplementation have more elevated level of n-3, subjects who were on fish oil diet have greater improvement in cancer related fatigue in comparison to subjects on soyabean oil.
Study by Shehab R [57] observed in his pilot study that omega 3 fatty acid helps in improving levels of Vitamin D & Calcium among childbearing age women who are suffering from deficiency of vitamin D when they were supplemented with omega 3 capsule 1 capsule twice daily (1000mg) for 12 weeks then elevation in the levels of vit D & Calcium and improved lipid profile as reduction in level of cholesterol, LDL-c, thus also exerts its cardioprotective effect and thus it indirectly play role in providing strength to bones [58] states in his cross-sectional Study that omega 3 fatty acid ratiobased intake is related in declining of CRP level which is related to inflammation thus exerts its cardioprotective effect but apparently declines subclinical inflammation mostly in healthy elderly males. As omega 3 fatty acid directly suppress the action of key modulator of pro-inflammatory cytokines Including Interleukin-6 (IL-6) i.e., Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4), thus reduce CRP level [59], many studies have demonstrated that inflammatory markers like interleukin-6 mostly activates the transcription rate of the CRP gene including the translation of CRP mRNA, even in endothelial cells and so by consuming diets rich in omega 3 fatty acid helps to get rid from this mechanism as it directly suppress levels of inflammatory markers [60-63].
In case of diabetic nephropathy, omega 3 fatty acid in combination with vitamin D3 exerts beneficial effects in improving hyperglycemia, renal function test, by decreasing urinary protein content and marker of podocyte injury & oxidative stress i.e., urinary nephrin all these mentioned changes were observed in rat model, as they were divided in 3 groups, first & second group was given oral supplementation of VD3 and O3-FAs separately whereas group third was receiving both in combination, and superior result was demonstrated in combined therapy [64]. Along with rosuvastatin omega 3 fatty acid helps in elevating adiponectin serum level thus protecting from coronary artery disease and insulin resistivity as [65] we know this adiponectin protein helps in preventing development of metabolic syndrome, in their study on 87 subjects with CAD & IR, Al-Kuraishy [64] divided them into 4 categories one receiving omega 3 fatty acid, other rosuvastatin, third group was receiving both drugs whereas fourth group was taken as control, they observed that group receiving combined treatment have elevated serum adiponectin levels and thus have significant cardiometabolic protection.
Fatty Acids for Wound Healing
It’s an anabolic process that needs nutrients such as glucose and fats for healing, glucose acts as energy source and fats pays major role in development of cell membrane & modulation of cell signaling, in case of wound healing [66], through beta oxidation and production of ATP by unique pathway by fats for energy production that allows available protein to be utilized in wound healing [66]. Both omega 3 fatty acid & omega 6 fatty acid are precursors of key mediators of inflammatory phase such as prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxane that plays role in wound healing [67], omega 3 fatty acid supplementation helps in suppressing the activities of genes involved in proinflammatory pathways and in addition helps to abolish lymphocyte proliferation and levels of inflammatory markers such as IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor α, and IL-6 [68]. But more studies on this topic needs to be conducted. Quality of fatty acid supplemented also have impact on wound healing, but large prospective case control studies and human trials are still needed to elaborate the role of fatty acid in wound healing.
One of the case report has demonstrated that in 21 year old Japanese female with lower body paralysis having pressure ulcer on heel and first toe when supplemented with omega-3-acid ethyl esters one of the analog of omega 3 fatty acid, complete healing of the ulcer of the first toe in 10 weeks was seen [69,70], demonstrated in his 8-week, placebo-controlled, double-blind study on borderline personality disorder in female subjects that Ethyl-Eicosatetraenoic Acid (E-EPA) have promising result against severe borderline personality development and it is also an effective and safest monotherapy. Study by Sublette [71] demonstrated in his study that low level of DHA and increased level of omega-6/omega-3 fatty acids in diet is associated with major depression and affected subject can commit suicide [79].
Relationship between Omega 3 Fatty Acid & Osteoporosis
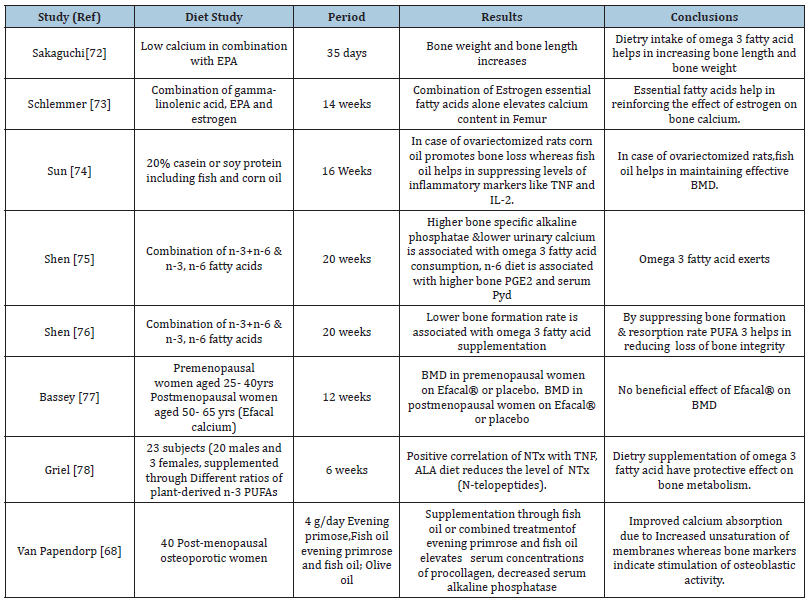
Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by having low bone mineral density and due to deterioration in microarchitectural of bone tissue that make bones fragile, and it easily get fracture, Omega 3 fatty acid affects bone remodeling by affecting mainly three pathways of action it mainly modulates activity of absorption of calcium, suppressing activity of inflammatory cytokine and Peroxisome Proliferators-Activated Receptor (PPAR). Absorption of calcium and urinary calcium levels are mostly affected by fat rich diets [80,81]. As consumption of PUFA helps in absorption of intestinal calcium, by enhancing the activity of enzyme Ca2+ATPase, as this enzyme plays major role in active absorption of calcium in intestine (Table 1). In one of the studies on 891 women during menopausal transition using Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) to evaluate food intake and measuring BMD with DEXA, in another study negative relationship was obtained between fatty acid consumption and femoral BMD loss, it was reported that in both sexes’ higher ratio of n-6 to n-3 fatty is mainly associated with lower BMD at the hip region [82,83].
Table 1:Relationship between omega 3 fatty acid &osteoporosis.
Role in Spinal Cord Injury
Acute spinal cord injury is very severe disability, it’s extremely complex disease having high mortality and morbidity [84,85] demonstrated the antioxidant & anti-inflammatory role of omega 3 fatty acid in spinal cord injury in rat model, their study showed that as concentration of omega 3 fatty was increased more effective result was obtained such as reduced oxidative stress markers, inflammatory markers, and apoptosis. As omega 3 fatty acid usually modify multiple pathways that are responsible for secondary damage following SCI. Studies have confirmed that subjects who are administrating long chain omega 3 fatty acid before injury they restore cord lipid homeostasis, exerts neuroprotection, dysfunction of sensorimotor, and neuropathic pain is prevented by omega 3 fatty acid as well it promotes locomotor recovery both in acute & sensory phase of SCI [74].
One of the studies on SCI induced rats has proved the neuroprotective effect of omega 3 fatty acid it mainly suppresses the activation of inflammasomes following SCI. Their study showed that PUFA mainly suppress activation of microgliosis, whereas oligodendrocytes number got increased with its consumption and demyelination got suppressed [86]. PUFA and its metabolites play major role against environment-related skin inflammation such as UV radiation due to sun exposure that cause acute skin inflammation, thus in such case MaR1one of the metabolite of PUFA suppressed swelling and infiltration of UVB irradiation induced macrophage in addition it also helps in inhibiting UVB irradiationinduced keratinocyte apoptosis and suppress production of inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and TNFα, and oxidative stress [87].
Conclusion
In the present review we try to conclude the structure, sources and health benefits in various diseases and disorders, but in case of cancer, pressure ulcer etc more human trials are needed to be conducted to establish its effect.
References
- Djuricic I, Calder PC (2021) Beneficial outcomes of omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on human health: An update for 2021. Nutrients 13(7): 2421.
- Yaghubi E, Carboni S, Snipe RM, Shaw CS, Fyfe JJ, et al. (2021) Farmed mussels: A nutritive protein source, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, with a low environmental footprint. Nutrients 13(4): 1124.
- Venugopal V, Gopakumar K (2017) Shellfish: Nutritive value, health benefits, and consumer safety. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 16(6): 1219-1242.
- Carboni S, Kaur G, Pryce A, McKee K, Desbois AP, et al. (2019) Mussel consumption as a “Food First” approach to improve omega-3 status. Nutrients 11(6): 1381.
- Ahmmed MK, Ahmmed F, Tian H, Carne A, Bekhit AE-D (2020) Marine omega-3 (n-3) phospholipids: A comprehensive review of their properties, sources, bioavailability, and relation to brain health. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 19(1): 64-123.
- Wijsman JWM, Troost K, Fang J, Roncarati (2019) A global production of marine bivalves. Trends and challenges. In: Smaal AC, Ferreira JG, Grant J, Petersen JK, Strand Ø (Eds.), Goods and Services of Marine Bivalves. Springer International Publishing, USA, p: 7-26.
- Saini RK, Prasad P, Sreedhar RV, Akhilender NK, Shang X, et al. (2021) Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs): Emerging plant and microbial sources, oxidative stability, bioavailability, and health benefits-A review. Antioxidants 10(10): 1627.
- Adarme-Vega T, Lim DKY, Timmins M, Vernen F, Li Y, et al. (2012) Microalgal biofactories: A promising approach towards sustainable omega-3 fatty acid production. Microb Cell Factories 11(96): 1-10.
- Wells ML, Potin P, Craigie JS, Raven JA, Merchant SS, et al. (2017) Algae as nutritional and functional food sources: Revisiting our understanding. J Appl Phycol 29(2): 949-982.
- Colonia OBS, Vinícius MPG, Soccol CR (2020) Omega-3 microbial oils from marine thraustochytrids as a sustainable and technological solution: A review and patent landscape. Trends Food Sci Technol 99: 244-256.
- Dorni C, Sharma P, Saikia G, Longvah T (2018) Fatty acid profile of edible oils and fats consumed in India. Food Chem 238: 9-15.
- Gosch BJ, Magnusson M, Paul NA, Nys DR (2012) Total lipid and fatty acid composition of seaweeds for the selection of species for oil-based biofuel and bioproducts. GCB Bioenergy 4(6): 919-930.
- Fabian, CJ, Kimler BF, Hursting SD (2015) Omega-3 fatty acids for breast cancer prevention and survivorship. Breast Cancer Res 17(2): 62-77.
- Walker CG, Browning LM, Mander AP, Madden J, West AL, et al. (2014) Age and sex differences in the incorporation of EPA and DHA into plasma fractions, cells and adipose tissue in humans. Br J Nutr 111(4): 679-89.
- Weylandt KH, Chiu CY, Gomolka B, Waechter SF, Wiedenmann B (2012) Omega-3 fatty acids and their lipid mediators: Towards an understanding of resolvin and protectin formation. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 97(3-4): 73-82.
- Patterson RE (2011) Marine fatty acid intake is associated with breast cancer prognosis. J Nutr 141(2): 201-206.
- Black HS, Rhodes LE (2016) Potential benefits of omega-3 fatty acids in non-melanoma skin cancer. Journal of clinical medicine 5(2): 23.
- Calder PC (2013) Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Nutrition or pharmacology? Br J Clin Pharmacol 75(32): 645-662.
- Arterburn LM, Hall EB, Oken H (2006) Distribution, interconversion, and dose response of n-3 fatty acids in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 83(6): 1467-1476.
- Browning LM, Walker CG, Mander AP, West AL, Madden J, et al. (2012) Incorporation of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids into lipid pools when given as supplements providing doses equivalent to typical intakes of oily fish. Am J Clin Nutr 96(4): 748-758.
- Kopecky J, Rossmeisl M, Flachs P, Kuda O, Brauner P, et al. (2009) N-3 PUFA: Bioavailability and modulation of adipose tissue function. Proc Nutr Soc 68(4): 361-369.
- Wathes DC, Abayasekara DR, Aitken RJ (2007) Polyunsaturated fatty acids in male and female reproduction. Biol Reprod 77(2):190-201.
- Zanini SF, Torres CA, Bragagnolo N, Turatti JM, Silva MG, et al. (2003) Evaluation of the ratio of omega (6: omega3 fatty acids and vitamin E levels in the diet on the reproductive performance of cockerels. Arch Tierernahr 57(6): 429-442.
- Kelso KA, Cerolini S, Speake BK, Cavalchini LG, Noble RC (1997) Effects of dietary supplementation with alpha-linolenic acid on the phospholipid fatty acid composition and quality of spermatozoa in cockerel from 24 to 72 weeks of age. J Reprod Fertil 110(1): 53-59.
- Estienne MJ, Harper AF, Crawford RJ (2008) Dietary supplementation with a source of omega-3 fatty acids increases sperm number and the duration of ejaculation in boars. Theriogenology 70(1): 70-76.
- Strzezek J, Fraser L, Kuklinska M, Dziekonska A, Lecewicz M (2004) Effects of dietary supplementation with polyunsaturated fatty acids and antioxidants on biochemical characteristics of boar semen. Reprod Biol 4(3): 271-287
- Stocco DM, Wang X, Jo Y, Manna PR (2005) Multiple signaling pathways regulating steroidogenesis and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression: More complicated than we thought. Molecular endocrinology 19(11): 2647-2659.
- Needleman P, Turk J, Jakschik BA, Morrison AR, Lefkowith JB (1986) Arachidonic acid metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem 55: 69-102.
- Wang XJ, Dyson MT, Jo Y, Eubank DW, Stocco DM (2003) Involvement of 5- lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid in cyclic AMP-stimulated steroidogenesis and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene expression. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 85(2–5): 159-166.
- Fiedler EP, Plouffe Jr L, Hales DB, Hales KH, Khan I (1999) Prostaglandin F (2alpha) induces a rapid decline in progesterone production and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression in isolated rat corpus luteum without altering messenger ribonucleic acid expression. Biol Reprod 61(3): 643-650.
- Feng Y, Ding Y, Liu J, Tian Y, Yang Y (2015) Effects of dietary omega-3/omega-6 fatty acid ratios on reproduction in the young breeder rooster. BMC Veterinary Research 11(1): 1-7.
- Hathaway D, Pandav K, Patel M, Riva-Moscoso A, Singh BM, et al. (2020) Omega 3 fatty acids and COVID-19: A comprehensive review. Infect Chemother 52(4): 478.
- Amengual O, Atsumi T (2021) COVID-19 pandemic in Japan. Rheumatol Int 41: 1-5.
- Kim SW, Kim SM, Kim YK (2021) Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 cohort patients in daegu metropolitan city outbreak in 2020. J Korean Med Sci 36(1): 1-15.
- Zapata BR, Müller JM, Vásquez JE, Ravera F, Lago G, et al. (2021) Omega-3 index and clinical outcomes of severe covid-19: Preliminary results of a cross-sectional study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18(15): 7722.
- Sekikawa A, Curb JD, Ueshima H, El-Saed A, Kadowaki T, et al. (2008) Marine-derived n-3 fatty acids and atherosclerosis in Japanese, Japanese-American, and white men: A cross-sectional study. J Am Coll Cardiol 52(6): 417-424.
- Simon JA, Hodgkins ML, Browner WS, Neuhaus JM, Bernert JT, et al. (1995) Serum fatty acids and the risk of coronary heart disease. Am J Epidemiol 142(5): 469-476.
- Freeman MP (2000) Omega-3 fatty acids in psychiatry: A review. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry 12(3): 159-165.
- Hibbeln JR (1998) Fish consumption and major depression. Lancet 351(9110): 71-72.
- Peet M, Murphy B, Shay J, Horrobin D (1998) Depletion of omega3 fatty acid levels in red blood cell membranes of depressive patients. Biol Psychiatry 43(5): 315-319.
- Maes M, Smith R, Christophe A, Cosyns P, Desnyder R, et al. (1996) Fatty acid composition in major depression: Decreased omega-3 fractions in cholesteryl esters and increased C20:4 omega 6/C20:5 omega 3 ratio in cholesteryl esters and phospholipids. J Affect Disord 38(1): 35-46.
- Adams PB, Lawson S, Sanigorski A, Sinclair AJ (1996) Arachadonic acid to eicosapentaenoic acid ration in blood correlates positively with clinical symptoms of depression. Lipids 31: 157-161.
- Edwards R, Peet M, Shay J, Horrobin D (1998) Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the diet and in the red blood cell membranes of depressed patients. J Affect Disord 48(2-3): 149-155.
- Hibbeln JR, Linnoila M, Umhau JC, Rawlings R, George DT, et al. (1998) Essential fatty acids predict metabolites of serotonin and dopamine in cerebrospinal fluid among healthy control subjects, and early- and late-onset alcoholics. Biol Psychiatry 44(4): 235-242.
- Hibbeln JR, Umhau JC, Linnoila M, George DT, Ragan PW, et al. (1998) A replication study of violent and nonviolent subjects: Cerebrospinal fluid metabolites of serotonin and dopamine are predicted by plasma essential fatty acids. Biol Psychiatry 44(4): 243-249.
- Miller M, Stone NJ, Ballantyne C (2011) Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 123(20): 2292-2333.
- Berglund L, Brunzell JD, Goldberg AC (2012) Evaluation and treatment of hypertriglyceridemia: An endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(9): 2969-2989.
- Harris WS (1997) N-3 fatty acids and serum lipoproteins: Human studies. Am J Clin Nutr 65(5): 1645-1654.
- Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, Appel LJ (2002) Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 106(21): 2747-2757.
- Sartorio MU, Pendezza E, Coppola S, Paparo L, D’Auria E, et al. (2021) Potential role of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in pediatric food allergy. Nutrients 14(1): 152.
- Brenna JT, Varamini B, Jensen RG, Diersen-Schade DA, Boettcher JA, et al. (2007) Docosahexaenoic and arachidonic acid concentrations in human breast milk worldwide. Am J Clin Nutr 85(6) 1457-1464.
- Foiles AM, Kerling EH, Wick JA, Scalabrin DMF, Colombo J, et al. (2016) Formula with long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids reduces incidence of allergy in early childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 27(2): 156-161.
- Meldrum SJ, Dunstan JA, Martino D, McCarthy S, Metcalfe J, et al. (2012) Postnatal fish oil supplementation in high-risk infants to prevent allergy: Randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics 130(4): 674-682.
- Miura K, Way M, Jiyad Z, Marquart L, Plasmeijer EI, et al. (2021) Omega-3 fatty acid intake and decreased risk of skin cancer in organ transplant recipients. European Journal of Nutrition 60(4): 1897-1905.
- Podpeskar A, Crazzolara R, Kropshofer G, Hetzer B, Meister B, et al. (2021) Omega-3 fatty acids and their role in pediatric cancer. Nutrients 13(6):1800.
- Kleckner AS, Culakova E, Kleckner IR, Belcher EK, Demark-Wahnefried W, et al. (2022) Nutritional status predicts fatty acid uptake from fish and soybean oil supplements for treatment of cancer-related fatigue: results from a phase II nationwide study. Nutrients 14(1): 184
- Shehab R, Saleh M, Al-Hamati K, Halboup A (2021) Role of Omega-3 fatty acid in childbearing age women with vitamin D deficiency in Sana’a City. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 11(1): 118-122.
- Yang W, Lee JH, Lee JW, Kim Y, Kim YS, et al. (2021) Increased omega-3 fatty acid intake is inversely associated with subclinical inflammation in healthy elderly men, based on the 2015-2018 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutrients 13(2): 338.
- Liu H-Q, Qiu Y, Mu Y, Zhang XJ, Liu L, et al. (2013) A high ratio of dietary n-3/n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids improves obesity-linked inflammation and insulin resistance through suppressing activation of TLR4 in SD rats. Nutr Res 33(10): 849-858.
- Caterina DR, Cybulsky MI, Clinton SK, Gimbrone MA, Libby P (1994) The omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoate reduces cytokine-induced expression of proatherogenic and proinflammatory proteins in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb J Vasc Biol 14(11): 1829-1836.
- Khalfoun B, Thibault F, Watier H, Bardos P, Lebranchu Y (1997) Docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids inhibit in vitro human endothelial cell production of interleukin-6. Adv Exp Med Biol 400: 589-597.
- Haghiac M, Yang X-h, Presley L, Smith S, Dettelback S, et al. (2015) Dietary omega-3 fatty acid supplementation reduces inflammation in obese pregnant women: A randomized double-blind controlled clinical trial. Plos One 10(9).
- Calder PC (2012) The role of marine omega-3 (n-3) fatty acids in inflammatory processes, atherosclerosis and plaque stability. Mol Nutr Food Res 56(7): 1073-1080.
- El-Sokkary NH, Yusuf A, Abdel-Moneim RA, Abdulrazeg HS, Hassaan PS (2022) The possible ameliorative effect of vitamin D3 and/or omega-3 fatty acids in a rat model of type I early diabetic nephropathy: A physiological and histological study. Bulletin of Egyptian Society for Physiological Sciences 42(1): 101-117.
- Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI (2016) Effects of rosuvastatin alone or in combination with omega-3 fatty acid on adiponectin levels and cardiometabolic profile. Journal of basic and clinical pharmacy 8(1): 8-14.
- Quain AM, Khardori NM (2015) Nutrition in wound care management: A Comprehensive overview. Wounds 27(12): 327-335.
- Molnar JA, Underdown MJ, Clark WA (2014) Nutrition and chronic wounds. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle) 3(11): 663-681.
- Meydani SN, Endres S, Woods MM (1991) Oral (n-3) fatty acid supplementation suppresses cytokine production and lymphocyte proliferation: Comparison between young and older women. J Nutr 121(4): 547-555.
- Nagai K, Matsumaru K, Hirai I, Takae Y, Andoh K (2014) New therapy using omega-3-acid ethyl esters for decubitus ulcers and stasis dermatitis: A case report. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal 16(12):19500.
- Zanarini MC, Frankenburg FR (2003) Omega-3 fatty acid treatment of women with borderline personality disorder: A double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. American Journal of Psychiatry 160(1): 167-169.
- Sublette ME, Hibbeln JR, Galfalvy H, Oquendo MA, Mann JJ (2006) Omega-3 polyunsaturated essential fatty acid status as a predictor of future suicide risk. American Journal of Psychiatry 163(6): 1100-1102.
- Sakaguchi K, Morita I, Murota S (1994) Eicosapentaenoic acid inhibits bone loss due to ovariectomy in rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 50(2): 81-84.
- Schlemmer CK, Coetzer H, Claassen N, Kruger MC (1999) Oestrogen and essential fatty acid supplementation corrects bone loss due to ovariectomy in the female Sprague Dawley rat. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 61(6): 381-390.
- Sun D, Krishnan A, Zaman K, Lawrence R, Bhattacharya A, et al. (2003) Dietary n-3 fatty acids decrease osteoclastogenesis and loss of bone mass in ovariectomized mice. J Bone Miner Res 18(7): 1206-1216.
- Shen CL, Yeh JK, Rasty J, Li Y, Watkins BA (2006) Protective effect of dietary long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on bone loss in gonad-intact middle-aged male rats. Br J Nutr 95(3): 462-468.
- Shen CL, Yeh JK, Rasty J, Chyu MC, Dunn DM, et al. (2007) Improvement of bone quality in gonad-intact middle-aged male rats by long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid. Calcif Tissue Int 80(4): 286-293.
- Bassey E, Littlewood J, Rothwell M, Pye D (2000) Lack of effect of supplementation with essential fatty acids on bone mineral density in healthy pre- and post-menopausal women: two randomized controlled trials of Efacal® calcium alone. Br J Nutr 83(6): 629-635.
- Griel AE, Kris-Etherton PM, Hilpert KF, Zhao G, West SG, et al. (2007) An increase in dietary n-3 fatty acids decreases a marker of bone resorption in humans. Nutr J 6(2): 2.
- Papendorp DH, Coetzer H, Kruger MG (1995) Biochemical profile of osteoporotic patients on essential fatty acid supplementation. Nutr Res 15(3): 325-334.
- Claassen N, Coetzer H, Steinmann CM, Kruger MC (1995) The effect of different n-6/n-3 essential fatty acid ratios on calcium balance and bone in rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 53(1): 13-19.
- Macdonald HM, New SA, Golden MH, Campbell MK, Reid DM (2004) Nutritional associations with bone loss during the menopausal transition: Evidence of a beneficial effect of calcium, alcohol, and fruit and vegetable nutrients and of a detrimental effect of fatty acids. Am J Clin Nutr 79: 4-5.
- Weiss LA, Barrett-Connor E, Mühlen D (2005) Ratio of n-6 to n-3 fatty acids and bone mineral density in older adults: The Rancho Bernardo Study. Am J Clin Nutr 81(4): 934-938.
- Singh A, Srivastava RN, Chatterji T, Singh S, Raj L, et al. (2020) 1H NMR urine metabolomics is an effective prognostic indicator in Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI): A prospective case-control study. Journal of Metabolomics and Systems Biology 4(1): 1-21.
- Bi J, Chen C, Sun P, Tan H, Feng F, et al. (2019) Neuroprotective effect of omega‐3 fatty acids on spinal cord injury induced rats. Brain and behavior 9(8): 01339.
- Baazm M, Behrens V, Beyer C, Nikoubashman O, Zendedel A (2021) Regulation of inflammasomes by application of Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in a spinal cord injury model. Cells 10(11): 3147.
- Cezar TLC, Martinez RM, Rocha CD, Melo CPB, Vale DL, et al. (2019) Treatment with maresin 1, a docosahexaenoic acid-derived pro-resolution lipid, protects skin from inflammation and oxidative stress caused by UVB irradiation. Sci Rep 9(1): 3062.
- Bernard JJ, Gallo RL, Krutmann J (2019) Photoimmunology: How ultraviolet radiation affects the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 19(11): 688-701.
© 2022 Shah Waliullah. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






