- Submissions

Full Text
Open Journal of Cardiology & Heart Diseases
Widely Association Analysis and Identification New Early-Onset Factor for Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease
Yisheng Lu1, Jindong Ren2* and Lizhi Lu1,2
1 Wenzhou Medical University, China
2 Department of Animal Science and Technology, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China
*Corresponding author: Jindong Ren, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou, China
Submission: March 15, 2018;Published: September 04, 2018

ISSN 2578-0204Volume2 Issue4
Abstract
Hemorheological indexes, living habits, medical history and genetics factor are primary risk factors in Coronary Heart Disease (CHD). In the present study the relation of all factors to the severity of CHD was examined. The data of 282 patients (mean age: 60±9 years) diagnosed with CHD and 229 healthy controls (mean age: 59±7 years) from Wenzhou Medical University were analyzed. All detected hemorheological indexes (except for total bilirubin, fasting blood, uric acid and triglyceride) were determined associated with CHD (P< 0.01). The factors of smoking, hypertension, diabetes and gout reached statistical significant level (P< 0.05) in logistic regression analyses with CHD and four events reveal more than 99% accuracy for CHD prediction. The ten selected SNPs have not found closely related to CHD in Wenzhou people, but found that rs3782886, rs671, 4977574 and rs2383206, four SNPs locus can affect the uric acid content and rs1842896 can affect the LDL-CH concentration in blood and thus indirectly contribute to the incidence of CHD. These results indicate that these detected hemorheological indexes, living habits, medical history and genetics factor may have the possibility as an adjunct to early warning of CHD.
Keywords: Coronary heart disease; Hemorheological indexes; Living habits; Medical history; SNP
Abreviations: ALT: Alanine Transaminase; AST: Aspertate Amino Transferase; FBG: Fasting Blood-Glucose; SCr: Serum Creatinine; UA: Uric Acid; T-CH: Total Cholesterol; HDL-CH: High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; LDL-CH: Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; WBC: White Blood Cell; Hb: Hemoglobin; PLT: Blood Platelet; HVR4: Hypervariable Region 4; EDTA: Ethylene Di Amine Tetra Acetic Acid
Introduction
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), behind Stroke is the second leading cause of death of Chinese population, but the trend of number of death increase caused by CHD is significant in recently years [1,2]. It is a complex multifactorial disease in which habits, health states and genetic factors have a significant function in inducing [3-5]. Among these inducing factors, genetic factors are more significantly than other and known to influence the risk of CHD [6]. Abnormal physiobiochemic and hemorheological indexes, particularly, caused by genetic factor are important elements for the risk of CHD [7,8]. These genetic and other factors are associated with CHD and provides a possible for prediction of CHD in early onset. In previously study, some studies on the association with CHD have identified a few risk factors could be used as an index for prediction of CHD. The genetic factor, such as SNP, was paid lots of attention by researchers from medical area.
Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1, angiotensin-converting enzyme, High-Density lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C), Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone (RAAS) system gene and so on genetic factors have been found to have a significant associated relationship with CHD [9-11]. In addition, due to the advancement of genetic marker identification techniques, a large number of non-genotypic markers have also been found that have a significant association relationship with CHD and can be used to predict CHD in early onset [3,12,13]. Genetic factors, however, are not the only factor that causes and can predict to CHD, individual status and history of morbidity is also an important factor. For instance, decreasing physical activity and increasing of BMI (Body Mass Index) have significant effect on CHD [14], and family history of diabetes have influence the risk of CHD [15] that were investigated by medical researchers in previously studies.
Although a number of genetic and physiological factors have been found to have significant synergistic effects with CHD, the synergistic effect of the same factor in different populations is not necessarily the same. The coagulation factor VII gene Hypervariable Region 4 (HVR4) is one of them [16], and an allele on this gene revealed differential association with CHD in divergent ethnic groups. Therefore, when study on exploring the factors of CHD and the prediction in early onset, the difference of population should not be to directly flow the previous study. In this study, we took advantage of rich longitudinal data on CHD incident events in the Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University study and performed a SNaP Shot of incident CHD events in Chinese Han population of Wenzhou to identify potential factors for prediction of CHD in early onset.
Material and Methods
Data collection and phenotype analyses
From November 2015 to June 2016,281 patients were identified with CHD that included 120 patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI), 2 patients with old myocardial infarction, 159 patients with angina pectoris from the Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University were enrolled in our study. There are 229 cases for healthy control group collected through regular health screening of people with no history of CHD, diabetes mellitus, or dyslipidemia. All patients were identified according to the 1999 World Health Organization diagnostic criteria for CHD. Coronary angiography was performed in all patients. Background information included sex, BMI, age, whether or not smoking and drinking, and the history of hypertension, diabetes and gout of all investigators, patients and control cases, were collected as far as possible with diagnosing CHD and medical test. The study was approved by the ethics committee at the Wenzhou Medical University.
Hemorheological indexes and genotype analyses
For each patients and control case, 2ml and 5ml of peripheral fasting blood were collected into Ethylene Di Amine Tetra Acetic Acid (EDTA)-coated tubes and stored at -20 ℃ and used for hemorheological indexes testing and genotype analyses for each SNP. Within 1 h, the blood for hemorheological indexes was test by using the Abbott Architect i2000SR, Johnson and Vitus 5600 and Sysmex XE-5000 to analyze the indexes of TBiL (Total Bilirubin), ALT(Alanine Transaminase), AST(Aspertate Amino Transferase), FBG (Fasting Blood-Glucose), SCr (Serum Creatinine), UA (Uric Acid), T-CH(Total Cholesterol), TG (Triglyceride), HDL-CH(High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol), LDL-CH(Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol), WBC(White Blood Cell), Hb (Hemoglobin) and PLT (Blood Platelet), and recorded all the corresponding data.
DNA extraction
The total DNA of each sample was extracted using the Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega, USA). The DNA concentration of each sample was detected on a spectrophotometer (NanoVue; GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ, USA) and diluted to a working concentration of 5-10ng/μl.
Genotype analyses
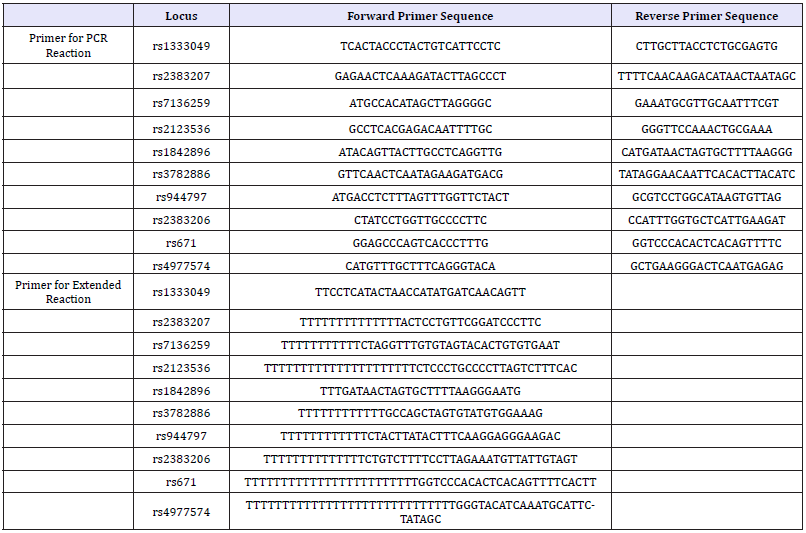
In this study, ten SNP locus were selected as candidate genes for prediction of CHD, and named rs2123536, rs1842896, rs671, rs3782886, rs1333049, rs4977574, rs944797, rs2383207, rs2383206, rs7136259, respectively. Among these SNP, seven SNP from three genes are BRAP (BRCA1 associated protein), ALDH2 (acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2) and CDKN2B-AS1. Polymorphisms of each locus were detected by a highly sensitive ligase detection reaction using the primers showed in Table 1. A 20μL PCR reaction was generated consisting of DNA (2μl), 4 ul Primer Mix (content same molecular mass of ten pair primer), 3mM Mg2+ (1.6μl), 10μl ExTaq (Takara, Japan) 2mM dNTP (2μl), and 10mM of each primer (4μl). The multiplex PCR reaction conditions were set as follows: 95 ℃ for 5min; 40 cycles of 10s at 95 ℃, 40s at 50 ℃, and 20s at 72 ℃, with the final step consisting of 7min at 72 ℃. After PCR reaction, 5U SAP enzyme and 2U Exonuclease I enzyme were added to 15μl of PCR product, incubated at 37 ℃ for 1 hour and then 75 ℃ for 15 min to purify PCR product. Then, 5μl SNaPshot Multiplex Kit (ABI, USA), 2ul purified multiplex PCR product and 1ul extension primer mixture were put together, and the mixture was conducted the extended reaction as follows procedure: 95 ℃ for 10s, 25 cycles of 10 s at 95 ℃, 5 s at 50 ℃, and 30sec at 60 ℃, with the final step consisting of 30s at 60 ℃. After extended reaction, the per 10μl product was added 1U SAP enzyme, incubated at 37 ℃ for 1 hour and then 85 ℃ for 15min to purify extended product. Take 1μl of the purified extended product was performed sequencing on ABI3730XL and analyzing the genotype of each locus of each sample by Gene Mapper 4.0 Applied Biosystems Co., Ltd., USA.
Table 1:The primers of ten locus used in this study.
Statistics
A quantitative difference among the means of different group was evaluated by one-way ANOVA. Homogeneity of variances among groups and genotypes was evaluated using the Duncan test. Multivariable logistic regression and principal component analyses were conducted using R 3.0 for Windows (R team). When one of variable in test have miss value, the corresponding sample was ignored to perform.
Results
Relationship between age BMI with CHD
figure 1:The impact of BMI and age on the probability of occurrence of CHD.
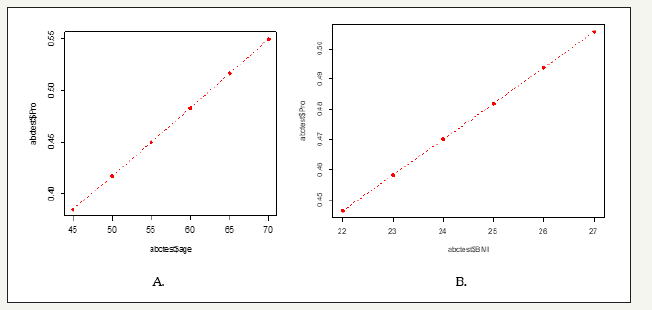
Table 2:The results of age, BMI one-way test between CHD patients and control group.
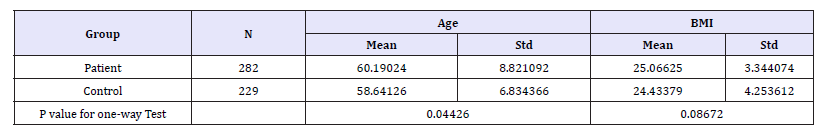
Through theone-waytest, it was found that both the age and BMI of CHD patients were increased compared with the control group. The mean age of the CHD group was over 60 years old, which was significantly higher than that of the control group (P< 0.05), but there was no significant difference in body mass index between the two groups. The logistic regression analysis showed that the estimated regression model of age and BMI in patient population was reached the statistical significance (Table 2). The risk of occurrence of CHD was increased by about 3% per 5 years from 45 to 70, and each unit increase in BMI the risk of CHD was increased more than one percent. Therefore, the impaction of age is greater than BMI according to the results (Figure 1).
Relationship between habits, medical history with CHD
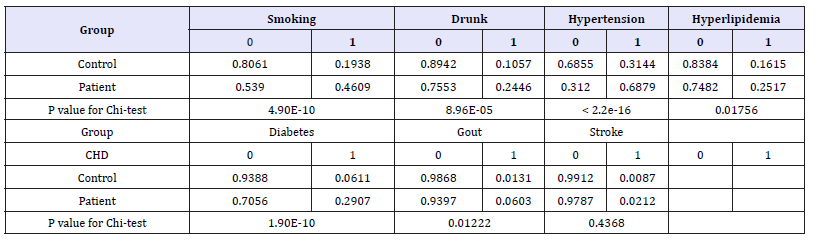
Based on chi-square test of profile habits and medical history between groups, it was found that there were significant differences in smoking, drink, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes and gout (Table 3). The regression coefficient of four indicators of smoking, hypertension, diabetes and gout reached statistical significant level (P< 0.05) by further logistic regression analysis. Through the model to predict the impact of four indicators on the probability of CHD, found that any three indicators at the same time in a person when the risk of CHD will reach more than 95%, and four indicators also have the risk of CHD up to more than 99%.
Table 3:The results of habits, medical history chi-square test between CHD patients and control group.
Hemorheological indexes impacted on CHD
Table 4:The results of hemorheological indexes One-way test between CHD patients and control group.
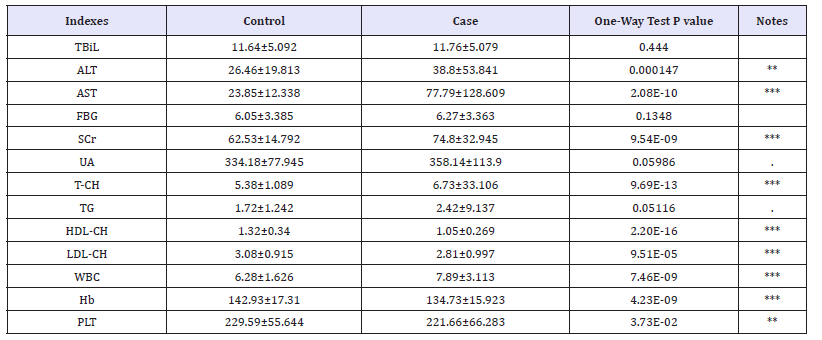
Table 5:The results of principal component analysis with significant different hemorheological indexes between CHD patients and control group.
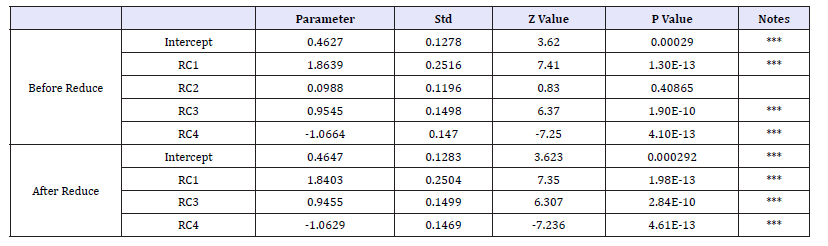
Statistics significant level (P< 0.05) or extremely significant (P< 0.01), except for TBiL, FBG, UA and TG, were found by one-way test of two group in all other hemorheological indexes (Table 4). According to the two-two correlation coefficient and matrix of the constructed hemorheological indexes, the correlation between most indexes is horizontal or vertical. In addition, the distribution of hemorheological indexes in the patients population and the control population showed a significant difference between the two groups, mainly in the control group, the relative correlation between the two groups was relatively scattered, and the risk of the population there are a number of significant correlation between the hemorheological indexes (Figure 1). Through the principal component analysis, it is found that all the hemorheological indexes with significant difference between CHD patients and control in oneway test can be attributed to the representative of the four principal components with cumulative contribution of 100%, of which the cumulative contribution of the first three principal components is more than 82%.Using the logistics regression model to analyze the four principal components and risk of CHD found that the second principal component and the risk of CHD did not exist significantly affect. The parameters of the regression model after RC2 removal are as showed in Table 5.
The RC1 and RC3 showed a linear increase in the risk of CHD in the regression model, but the RC4 showed negative correlation with the risk of CHD. According to this corrected regression model, the results showed that RC1 had the greatest influence on the risk of CHD, while the three greatest coefficient of indexes in RC1 were AST, ALT and WBC, respectively. The contribution of Hb to RC4 was the greatest in all biochemical indexes, indicating that Hb too much to reduce the risk of CHD have a certain inhibitory effect.
Association analyses between SNP and CHD, hemorheological indexes
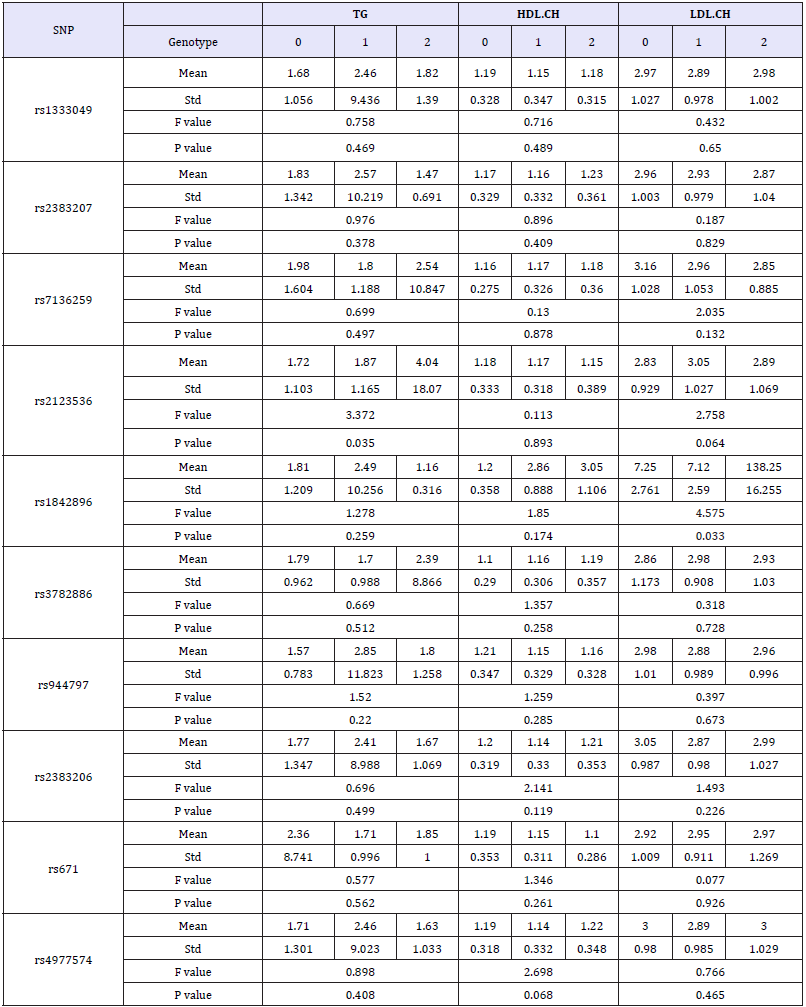
Each SNP genotype was scored as Myocardial Infarction Genetics Consortium published in previously [3]. In briefly, the score was composed of allelic dosage (assignment 0, 1, or 2 for three genotypes in each SNP locus), weighted by the effect size of that allele on the patient population. Based on the score of SNPs, ten SNP loci were not significantly different between the control and the group of CHD (Table 6). All the hemorheological indexes were analyzed by one-way ANOVA in each SNP. The results showed that rs3782886, rs671, 4977574 and rs2383206 had significant effect on UA, and the significant association between rs1842896 and LDLCH was found too (Table 7 & 7a).
Table 6:The results of association between the ten SNPs and CHD.
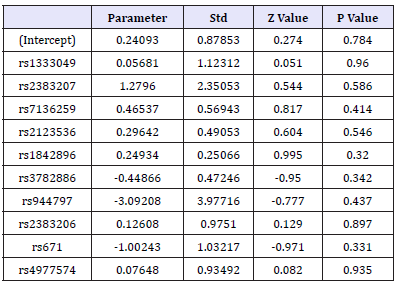
Table 7:The results of habits, medical history chi-square test between CHD patients and control group.
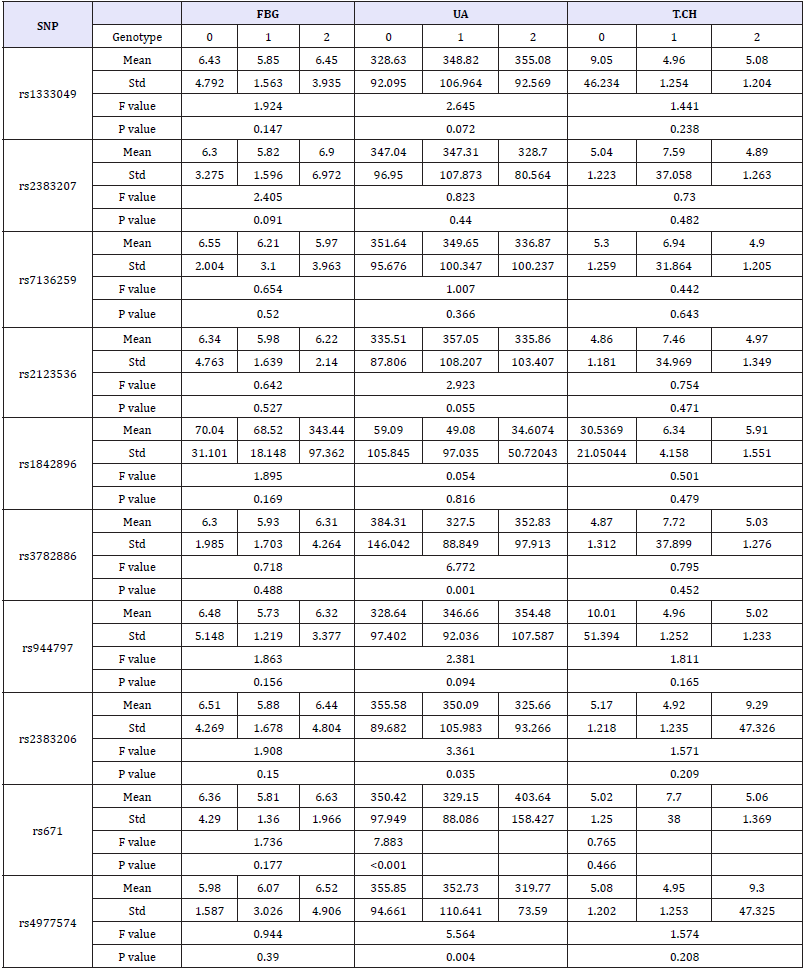
Table 7a:The results of association between the ten SNPs and hemorheological indexes.
Discussion
With the change of modern diet and the increase in the pressure of life, the incidence of CHD is rising, the research data show that if the myocardial infarction patients within one hour of onset of treatment, the mortality rate of up to about 30% [17,18], So early prediction, early prevention, effective control of the disease, improving the predictive ability of patients with CHD is a very significant study in medical area. In this study, Wenzhou Chinese patients with CHD were observed and found that the risk of CHD can reach more than 48% with age of 60 or more people, while the age per 5-year-old the risk of CHD will increase by more than 3% and more than 4% risk will reveal with BMI per one unit up on the basis of the average. The results demonstrated that Wenzhou Chinese have later than 10 year by previous reported age of onset in Chinese woman [19], which is also proved that the difference of population have divergent sensitive for CHD as previous study reported [18,20]. Wenzhou is a relatively economically developed city in China and the people have extra condition to pay attention on their healthy like developed country [21]. Therefore, it is not surprising that CHD is more later onset in the population of this area than the average of China in total. The better economic condition, however, will boast BMI increasing and then cause increasing risk of CHD particularly in developing country [22-24]. It demonstrated that both age and BMI have a certain supporting effect on the early prediction of CHD in Wenzhou Chinese, and suggested that when the person with age of 60 years or older, they need to strengthen the detection of CHD and improve the health status to prevent the occurrence of CHD, especially when the their BMI reaches 27 or more.
Moreover, bad habits, for instance smoking, is a strongest associated factor with CHD risk [24] what was also documented by our study. On the analysis of patients’ medical history with CHD, the effect of hypertension and diabetes on CHD is consistent with previous studies [25,26], but stroke history have not associated with CHD, even though, they share similar risk factors [27]. In addition, this study also identified that gout and CHD has a significant association relationship. Gout is a crystal-related joint disease caused by the deposition of monosodium monostate, which is directly related to hyperuricemia caused by purine metabolic disorders and/or uric acid excretion. The function of hyperuricemia increase the risk of CHD events have verified by Kim and his working team [28]. Although these factors have a relatively close impact on the likelihood of CHD and its morbidity, the incidence of CHD can reach more than 90% when any three of smoking, hypertension, diabetes and gout occurring/occurred simultaneously in one person, and the incidence of CHD will reach more than 99%. So these four events as early warning of CHD has a high degree of credibility in Wenzhou people.
Previous study has identified some hemorheological parameter associated with CHD, such as hematocrit, fibrinogen level, plasma viscosity and apparent whole blood viscosity [29] and proved that hemorheological indexes have a certain significance for the occurrence of CHD, and also have a greater effect in the prediction of CHD. In this study, the seven indexes of ALT, AST, SCr, T-CH, HDL-CH, LDL-CH, WBC, Hb and PLT in patients with CHD were significantly higher than those in the control group (P< 0.01), while the TBiL, FBG, UA and TG indexes in the patients group were not significantly different from those in the control group (P>0.05).In addition, through the principal component analysis and logistics model regression study found that the three top hemorheological indexes for increasing the risk of CHD were AST, UA and TG. In contrast the three top hemorheological indexes to reduce the risk of CHD has a significant function were PLT, HDL-CH and LDL-CH. AST and ALT have been verified that they can be used to predict the severity of CHD [30,31] what was documented in this study again in Wenzhou people. Although UA and TG do not directly affect the morbidity of CHD, but they have an indirect effect on CHD via improving the incidence of obesity and hyperuricemia [28,32,33]. Both HDL-CH and LDL-Ch are important factors that contribute to the regulation of the atherosclerotic process and have a significant reduction in the incidence of CHD [34,35]. Therefore, this study suggested that the early prediction of CHD should combine directly and indirectly hemorheological indexes that will be better to enhance the result for diagnosis, especially through the calculated value of principal component formula can gain greater accuracy than single index.
The ten selected SNPs have been proved the association between them with CHD in white people [3,36], but all of them have not found closely related to CHD in Wenzhou people. This result is sufficient to show the presence specific of CHD related SNP inspecificity population. Although the direct relationship between these SNPs and CHD was not detected, but found that rs3782886, rs671,4977574 and rs2383206, four SNPs locus can affect the UA content and rs1842896 can affect the LDL-CH concentration in blood and thus indirectly contribute to the incidence of CHD. However, the mechanism of found SNPs work on hemorheological indexes is not clearly in previous study.
References
- He Y, Lam TH (1999) A review on studies of smoking and coronary heart disease in China and Hong Kong. Chinese Medical Journal 112(1): 3-8.
- Zhang X, Lu ZL, Liu L (2008) Coronary heart disease in China. Heart 94(9): 1126-1131.
- Sekar K, Benjamin FV, Shaun Purcell, Peltonen L, Salomaa V, et al. (2009) Genome-wide association of early-onset myocardial infarction with single nucleotide polymorphisms and copy number variants. Nat Genet 41(3): 334-341.
- Kozarevic D, Demirovic J, Gordon T, Kaelber CT, Mc Gee D, et al. (1982) Drinking habits and coronary heart disease: the Yugoslavia cardiovascular disease study. American Journal of Epidemiology (5): 748-758.
- Wang Q (2005) Molecular genetics of coronary artery disease. Curr Opin Cardiol 20(3): 182-188.
- Lusis AJ, Mar R, Pajukanta P (2004) Genetics of atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 5: 189-218.
- Zhou T, Yan T (2010) Investigation on Hemorheological Indexes from 119 Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Practical Preventive Medicine, New York, USA.
- Wang Y, Li C, Chang H, Lu LH, Qiu Q, et al. (2016) Metabolomic profiling reveals distinct patterns of tricarboxylic acid disorders in blood stasis syndrome associated with coronary heart disease. Chin J Integr Med 22(8): 597-604.
- Loew M, Hoffmann MM, Hahmann H, Maerz W, Brenner H, et al. (2006) Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 13(3): 449-456.
- Kangas-Kontio T, Huotari A, Ruotsalainen H, Herzig KH, Tamminen M, et al. (2010) Genetic and environmental determinants of total and highmolecular weight adiponectin in families with low HDL-cholesterol and early onset coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis 210(2): 479-485.
- Ellis KL, Palmer BR, Frampton CM, Troughton RW, Doughty RN et al. (2013) Genetic variation in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is associated with cardiovascular risk factors and early mortality in established coronary heart disease. J Hum Hypertens 27(4): 237-244.
- Meng W, Hughes AE, Patterson CC, Belton C, Kee F, et al. (2008) Chromosome 9p21.3 is associated with early-onset coronary heart disease in the Irish population. Dis Markers 25(2): 81-85.
- Barbalic M, Reiner AP, Wu C, Hixson JE, Franceschini N, et al. (2011) Genome-wide association analysis of incident Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) in African Americans: a short report. PLoS Genet 7(8): e1002199.
- Britton A, Brunner E, Kivimaki M, Shipley MJ (2012) Limitations to functioning and independent living after the onset of coronary heart disease: What is the role of lifestyle factors and obesity? Eur J Public Health 22(6): 831-835.
- Scheuner MT, Setodji CM, Pankow JS, Blumenthal RS, Keeler E (2008) Relation of familial patterns of coronary heart disease, stroke, and diabetes to subclinical atherosclerosis: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Genet Med 10(12): 879-887.
- Wang LL, Ma B, Qian D, Pang J, Yao YL (2001) Correlation between polymorphisms in the coagulation factor VII gene hypervariable region 4 site and the risk of coronary heart disease in population with different ethnic backgrounds: A meta-analysis. 34(12): 1250-1254.
- Erikssen G, Liestøl K, Bjørnholt J V, Stormorken H, Thaulow E, et al. (2000) Erythrocyte sedimentation rate: A possible marker of atherosclerosis and a strong predictor of coronary heart disease mortality. European Heart Journal 21(19): 1614-1620.
- Wilhelmsen L, Rosengren A, Johansson S, Lappas G (1997) Coronary heart disease attack rate, incidence and mortality 1975-1994 in Goteborg, Sweden. European Heart Journal 18(4): 572-581.
- Shen L, Song L, Liu B, Li H, Zheng X et al. (2017) Effects of early age at natural menopause on coronary heart disease and stroke in Chinese women. International Journal of Cardiology 241: 6-11.
- Feinleib M (1984) The magnitude and nature of the decrease in coronary heart disease mortality rate. Am J Cardiol 54(5): 2C-6C.
- Becker S, Black RE, Brown KH, Nahar S (2013) Relations between socio-economic status and morbidity, food intake and growth in young children two villages in Bangladesh. Ecology of Food and Nutrition 18(4): 251-264.
- Lawson RA, Murphy RH, Williamson CR (2016) The relationship between income, economic freedom, and BMI. Public Health 134: 18-25.
- Abbasi F, Brown BW, Lamendola C, Mclaughlin T, Reaven GM (2002) Relationship between obesity, insulin resistance, and coronary heart disease risk. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 40(5): 937- 943.
- Fitzgerald AP, Jarrett RJ (1992) Body weight and coronary heart disease mortality: An analysis in relation to age and smoking habit, 15 years follow-up data from the Whitehall study. International Journal of Obesity & Related Metabolic Disorders Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 16(2): 119-123.
- Ibsen H, Hilden T (1990) New views on the relationship between coronary heart disease and hypertension. Journal of Internal Medicine 227(2): 77-79.
- Dong C, Tang L, Liu Z, Shizhong B, Qiong Liu, et al. (2014) Landscape of the relationship between type 2 diabetes and coronary heart disease through an integrated gene network analysis. Gene 539(1): 30-36.
- Conforto AB, Leite CC, Nomura CH, Bor-Seng-Shu E, Santos RD, et al. (2013) Is there a consistent association between coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke caused by intracranial atherosclerosis? Arquivos de neuro-psiquiatria 71(5): 320-336.
- Kim SY, Guevara JP, Kim KM, Choi HK, Heitjan DF, et al. (2010) Hyperuricemia and coronary heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res 62(2): 170-180.
- Kesmarky G, Toth K, Habon L, Vajda G, Juricskay I (1998) Hemorheological parameters in coronary artery disease. Clinical Hemorheology & Microcirculation 18(4): 245-251.
- Shen J, Zhang J, Wen J, Ming Q, Zhang J, et al. (2015) Correlation of serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase with coronary heart disease. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(3): 4399-4404.
- Schindhelm RK, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Bouter LM, Stehouwer CD, et al. (2007) Alanine aminotransferase predicts coronary heart disease events: A 10-year follow-up of the Hoorn Study. Atherosclerosis 191(2): 391-396.
- Halpern MJ, Miguel MSP (1974) Uric acid and coronary heart disease. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 22(2): 86-87.
- Mukherjee M, Desai H, Soneji SL (1994) Triglyceride and coronary heart disease. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 42(6): 463.
- Young CE, Karas RH, Kuvin JT (2004) High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and coronary heart disease. Cardiology in Review 12(2): 107-119.
- Curb JD, Abbott RD, Beatriz L, Rodriguez MD, Masaki K, et al. (2004) Prospective association between low and high total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and coronary heart disease in elderly men. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 52(12): 1975-1980.
- Lu X, Wang L, Chen S, He L, Yang X, et al. (2012) Genome-wide association study in Han chinese identifies four new susceptibility loci for coronary artery disease. Nature Genetics 44(8): 890-894.
© 2018 Jindong Ren. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






