- Submissions

Full Text
Novel Research in Sciences
The Integration, Exploration and Practice of Blended Learning in the Post-Pandemic Era: Taking “Fundamentals of Architectural Design” as an Example
Hui-Peng Zeng1, Wei Li2, Hong-Liang Zeng3, Dong-Yao Liang4, Zhe Chen4, and Hui-Wen Huang5*
1Lecturer, School of Architecture and Civil Engineering, China
2Professor, School of Architecture and Civil Engineering, China
3Senior Engineer, National 1st class Registered Architect, School of Architecture and Civil Engineering, China
4Assistant, School of Architecture and Civil Engineering, China
5Associate Professor, School of Architecture and Civil Engineering, China
*Corresponding author:Hui-Wen Huang, Associate Professor, School of Architecture and Civil Engineering, China
Submission: March 15, 2023;Published: March 15, 2023
.jpg)
Volume14 Issue3March, 2023
Abstract
Fundamentals of Architectural Design is a compulsory basic course in the field of architecture, which requires certain craftsmanship and engineering thinking. It serves as an introductory practice course for students to learn architectural drawing. This paper explores and expands the practice of blended learning in professional education by utilizing the advantages of different teaching methods and aiming to enhance the cultivation of students’ professional qualities.
Keywords:Architectural drawing; Integrated design; Blended learning
Course Design Concept and Framework
The educational pattern of “Two Financing and Four Entering, Five-level Progression” is the core of the construction of this course [1]. The content of “Architectural Drawing” is a microcosm of the course reform exploration. Based on this, this course is built on the foundation of “Architectural Drawing”, with “Moral Education and Talent Cultivation” as the center, and explores the teaching mode of “Blended Learning Reform, Integration and Complementarity of In-class and Out-of-class Learning”. The entire process follows the “P-C-D-I-O” teaching mode [2], aiming to achieve the unified educational goal of “Knowledge Dissemination, Ability Formation, Explicit Education of the Curriculum, and Implicit Ideological and Political Education”(Figure 1).
Figure 1: Classroom instructional design matrix.
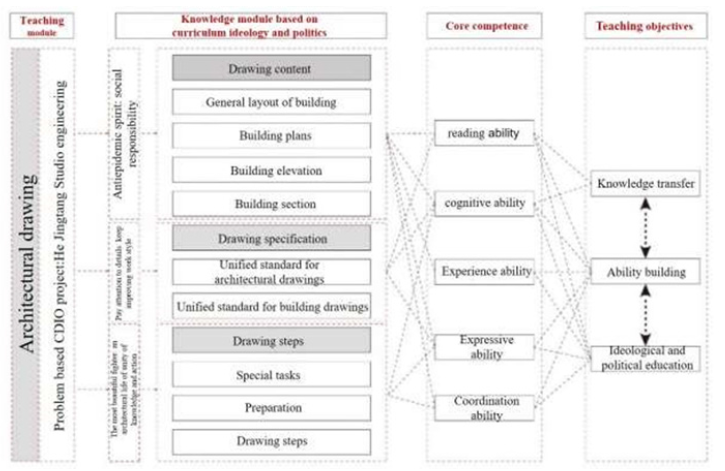
Integration of implicit ideological and political education into design teaching practice inquiry-based teaching, cultivating students’ scientific and academic thinking
In the teaching process, teachers, based on teaching tasks and objective laws of learning, use various methods to inspire students’ thinking as the core, mobilize students’ learning initiative and enthusiasm, and guide students to actively explore through reading, observation, experiments, thinking, discussion, etc., discovering and mastering knowledge and skills on their own, which is a teaching philosophy that encourages lively and active learning. It is also an effective teaching method for teachers to guide students to master knowledge actively, positively, and consciously according to the objective laws of the learning process.
PCDIO teaching, cultivating students’ engineering and design thinking
Centered around students, using the PCDIO (Problem-Based Learning) and CDIO (Conceive-Design Implement-Operate) models [3], the course teaching procedure is optimized to enhance the exploration, interaction, innovation, and challenge of the course, cultivating students’ comprehensive ability to solve complex problems. Teachers guide the teaching process through “problem guidance, support, building, process organization, pointing out and correcting errors, assessment, and evaluation” to develop students’ comprehensive abilities to solve complex problems and design innovative thinking
Peer teaching, cultivating students’ engineering thinking
Students who perform exceptionally well in the course and have outstanding academic achievements (including senior students) are selected as peer teaching assistants. As a supplement to the teaching team, peer teaching assistants guide students by asking questions and inspiring them, and guide them to master the problem-solving approach [4]. Students participating in peer teaching projects are usually divided into multiple small groups, each consisting of 6-8 people, and learn in the form of group discussions, with one peer teaching assistant responsible for each group. As an organizer, the peer teaching assistant discusses the core knowledge of the course with the group members, helping them answer questions related to the course content.
Blended Teaching [5] Improves Students’ Independent Learning Abilities
In response to the post-pandemic era, the future trend in education lies in the multi-dimensional classroom format, which integrates information technology with traditional subject classrooms through innovative methods such as complementary online and offline resources. Learning can extend from the classroom and campus to places outside the classroom and campus (including virtual space). Blended teaching can amplify the characteristics of the subject, carry more educational functions, enhance students’ independent learning abilities, and better achieve the curriculum’s educational goals. It is convenient for personalized learning, such as group discussions and individual tutoring. It also promotes the professional development of teachers and integrates online and offline training. Furthermore, it helps to highlight the features and standards of the curriculum.
Teaching Effectiveness and Reflection
Innovative teaching model improves the “Two Gender One Degree” of the curriculum
In this course, different teaching strategies were adopted in the classroom of teacher Cai, emphasizing the important role of student-centered, learning-centered, and participatory interaction in the process of teaching effectiveness. We value breaking the limitations of traditional classroom teaching content by attempting to enrich classroom forms, enliven classroom atmospheres, and expand new forms of curriculum teaching. The presentation method of the integration points adopted by different course teaching activity organization strategies is different, and students’ sensory experience of knowledge acquisition is also different, which improves the teaching effectiveness of the classroom and realizes the entire process of curriculum education [6].
The course team has been focusing on the exploration and practice of blended teaching reform using digital technology for many years. Through three teaching cycles of practice, the course has improved its high-order, innovative, and challenging characteristics and summarized and refined the “PBL+CDIO Integration Innovation Architectural Design Foundation Blended Teaching Model.” The teaching effect is significant: emphasizing the internalization of the learned knowledge, broadening the vision, increasing knowledge, enhancing the understanding of theory, and more deeply affecting the ideological awareness and behavior of young college students.
Reflection
Curriculum-based ideological and political education is a new concept and model for contemporary universities to carry out ideological and political work. Curriculum education is the fundamental purpose of education [7,8]. Exploring the ideological and political elements contained in the curriculum, integrating ideological and political education into the entire process of professional course education and teaching, and achieving fullprocess education and all-around education are essential for creating a new situation in the development of China’s higher education. In order to achieve this goal, the university actively explores the construction of a “professional course+curriculum for ideological and political education” double-integrated curriculum teaching system. The development and exploration process of the “Architectural Design Foundation” course of ideological and political education is full of harvest and expectations. Based on practice and focused on improving and upgrading, deeply reflecting on the double integration exploration of curriculum ideological and political education and professional education will help to continue the comprehensive promotion and high-quality development of curriculum ideological and political education.
Acknowledgement
This article supported by several projects, including the Guangdong Provincial Teaching Quality and Teaching Reform Engineering Project “Research on the Blended Teaching Mode of PBL+CDIO Integration Innovation in Fundamentals of Architectural Design” (15110210026), the Guangdong Provincial Demonstration Project of Curriculum Ideology and Politics Reform “Fundamentals of Architectural Design (Architectural Drawing)” (15109220379), the Research Project of the Guidance Committee for Online Open Courses in Undergraduate Universities in Guangdong Province “Research on the Construction Path of Online Open Course for ‘Fundamentals of Architectural Design’ under the Guideline of First- Class Courses” (2022ZXKC438), Research Project of the Guidance Committee for Online Open Courses in Undergraduate Universities in Guangdong Province “Research on the Construction of Online Open Courses Based on OBE” (2022ZXKC437),the “Professorial and Doctoral.
Scientific Research Foundation of Huizhou University
Project” (No. 2020JB062), the Teaching Reform Project “Apply
STEAM Maker Education to improve students’ cross-field ability”
(X-JYJG2021024) and “Construction of Flipped Classroom Teaching
Model Based on Cognitive Structure Transfer Theory -- Taking
the Course “History of Chinese and Foreign Architecture” as an
Example”(X-JYJG2021021)./p>
References
- Gao G, Pang M, Peng J (2022) The Course Architecture is Key to Guarantee the Education Outcome of University Online Courses. Education Theory: Teaching and Learning.
- Dzung TT (2022) A cooperative learning model combines between PBL and CDIO. JST: Engineering and Technology for Sustainable Development 32(1): 79-85.
- Magalhães JM, Pinto AP, Costa MT (2018) Implementation of a PBL/CDIO methodology at ISEP-P.PORTO Systems Engineering Course . 2018 3rd International Conference of the Portuguese Society for Engineering Education (CISPEE), Portugal. pp. 1-8.
- Mazurek R, Arvinen-Barrow M, Huddleston W (2021) Beyond traditional peer-to-peer teaching evaluation: Using pedagogical theory in conceptualizing a collaborative teaching development program. Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice 18(6): 1-18.
- Shohel MMC, Ashrafuzzaman M, Islam MT (2021) Blended teaching and learning in higher education. Handbook of Research on Developing a Post-Pandemic Paradigm for Virtual Technologies in Higher Education
- Eryong X, Li J (2021) What is the ultimate education task in China? Exploring “strengthen moral education for cultivating people” (“Li De Shu Ren”). Educational Philosophy and Theory 53(2): 128-139.
- OECD (2019) Conceptual learning framework: Core foundations for 2030, Future of Education & Skills 2030 Concept Note.
- OECD (2021) Embedding values and attitudes in curriculum shaping a better future.
© 2023 Hui-Wen Huang. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






