- Submissions

Full Text
Novel Research in Sciences
Medical Treatments for Chronic or Aggressive Diseases, Palliative Therapy and Nursery
Da Yong Lu1*, Yu Zheng Chen2, Ying Shen3, Bin Xu4 and Da Feng Lu2
1School of Life Sciences, China
2The Second Hospital of Neijiang District, China
3Medical School, China
4Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, China
*Corresponding author:Da Yong Lu, School of Life Sciences, Shanghai, China
Submission: November 28, 2019;Published: January 22, 2020
.jpg)
Volume3 Issue2January, 2020
Abstract
Chronic and aggressive diseases are commonly incurable. Palliative and nursery care are widest practiced. Better medical service of chronic and aggressive diseases can satisfy more patients and reduce therapeutic costs in a long run. In this article, relevant medical disciplines and drug developments are provided-from technique detail to medical knowledge.
Keywords:Healthcare; Nursing; Service promotion; Herbal medicine; Modern technology; Palliative treatment; Personalized medicine; Obesity; Psycho analysis
Introduction
Current situation
Chronic and aggressive diseases are commonly incurable. Palliative and nursery care are widest practiced. Better medical service of chronic and aggressive diseases can satisfy more patients and reduce therapeutic costs in a long run. In this article, relevant medical disciplines and drug developments are provided-from technique detail to medical knowledge. Palliative care and nursing advances help patient’s recovery and disease controls in the clinic. The medical significance of the quality improvements of medical healthcare and nursing activity is notable [1-12].
General methodology in different medical discipline
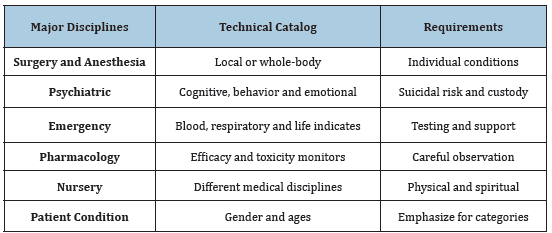
Table 1 shows major categories of acute or chronic disease treatments [13-35]. To general medical cares, different categories of medical disciplines are different characterized. However, it needs palliative treatments for incurable diseases. They are multi-disciplinary.
Table 1:Medical service from technical and health-care requirements.
Methods
Major parts of palliative treatments
A. Nutritional fortification
B. Herbal medicine
C. Life-style
D. High quality of nursing
E. Symptom alleviation (pain or lean)
F. Psychiatric control
G. Assistant therapy
H. Therapeutic or drug combination
I. Disease maintaining [36-57]
Discussion
Palliative medicine is very useful in the clinical trials. They are commonly less harmful for patients. But most of palliative treatments need to long-term utility because the disease origins and pathogens are not removed by these treatments. They are commonly not expensive. They assist to main-stream therapy. In summary, doctors and nurses should be familiar with all these knowledge of medical disciplines and execute their service in high quality and satisfy more patients.
Conclusion
Palliative service plays key roles in modern hospitals. After all, doctors and nursery training should be more emphasized for all medical disciplines. Commonly, a great difference can be made by these therapeutic efforts and creativity. There is a long way to move forwards and fill the gap between therapeutic convention and palliative treatments.
References
- Lu DY, Chen YZ, Lu DF, Che JY (2019) Patient’s care and nursery in different diseases. Hospice & Palliative Medicine International Journal. 3(1): 28-30.
- Lu DY, Chen YZ, Lu DF, Che JY (2019) Patient’s care and nursery in modern medicine. Nursery Practice and Health Care 1(1): 1-2.
- Lu DY, Chen YZ, Lu DF (2019) Nursery education, capability and service promotion. Open Access J Nursing 2(2): 1-4.
- Iqbal U, Humayyn A, Li YC (2019) Healthcare quality improvement and measurement strategies and its challenges ahead. Int J Quality in Health Care 31(1): 1.
- Iqbal U, Rabrenovic M, Li YC (2019) Healthcare quality challenges in low-and middle-income countries. International Journal for Quality In Health Care 31(3): 165.
- Lu DY, Che JY, Putta S, Wu HY, Shen Y (2019) How to improve the quality of pharmacotherapy for bone diseases. EC Orthopeadicis 10(6): 366-369.
- Leebov W, Scott G (1996) Service quality improvement: The customer satisfaction strategy for healthcare. J Healthcare Quality 18(4): 35.
- Kwag YK (2019) A study of clinical nurses perception on nursing student character development levels and requirement of character education virtue for nursing students. J Comprehensive Nursing Res Care 4: 147.
- Alzghool MM, Al Bakiri AM (2019) The future of mental health nursing practice in Saudi Arabia: A delphi study. J Comprehensive Nursing Res Care 4(3): 132.
- Lu DY, Chen YZ, Lu DF (2019) Nursery service, quality promotion. Hospice & Palliative Medicine International J 3(3): 97-98.
- Lu DY, Chen YZ, Lu DF, Che JY (2019) Nursery service in modern day. Adv Biomedical Engineering Biotechnology 1(3): 1-2.
- Lu DY, Shen Y, Xu B (2019) Heart and brain stroke, a paramount task for emergency medication. EC Emergency Medicine and Critical Care 3(11): 785
- Khan M, Silver B (2019) Editorial:Stroke in elderly: Current status and future direction. Frontier in Neurology 10: 177.
- Lu DY, Shen Y, Xu B (2019) Brain stroke, emergency management and drug developments. EC Pharmacology Toxicology 7(11).
- Lu DY, Wu HY, Yarla NS, Xu B, Ding J, et al. (2018) HAART in HIV/AIDS treatments: Future trends. Infectious Disorders-Drug Targets 18(1): 15-22.
- Lu DY, Wu HY, Ding J, Sastry N, Lu TR (2016) HIV vaccine for prevention and cure, a mission possible. Rev Recent Clini Trials 11(4): 290-296.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Wu HY, Yarla NS, Ding J, et al. (2018) HIV/AIDS curable study: New forms of therapeutic trinity. Rec Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov 13(3): 217-227.
- Lu DY, Wu Hy, Yarla NS, Lu TR, Xu B, et al. (2019) Ebola therapeutic study and future directions. Infect Disorder Drug Targets 19 (1): 17-29.
- Serafini G, Salano P, Amore M (2015) Suicidal ideation: A comprehensive overview. Suicidal ideation: Predictors, prevalence and prevention. Ed. Bradley Weaver, Nova Science Publishing US. pp: 1-42.
- While D, Bickley H, Roscoe A, Windfuhr K, Rahman S, et al. (2012) Implementation of mental health service recommendations in England and Wales and suicide rates, 1997-2006: A cross-sectional and before-and-after observational study. Lancet 379(9820): 1005-1012.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Lu Y, Cao S (2017) Introduction for suicide study. Journal Metabolic Syndrome 6(2): 227.
- Lu DY, Zhu PP, Wu HY, Yarla NS, Xu B, et al. (2018) Human suicide risk and treatment study. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 18(3): 206-212.
- Melton J (1993) Hip fractures; a worldwide problem today and tomorrow. Bone 14(1): S1-S8.
- Silva DMW (2018) Diagnosis of osteoporosis; bone mineral density, risk factors, or both. EC Orthopaedics 9(7): 500-502.
- Lu DY, Che JY, Shen Y (2018) Clinical treatments of osteoporosis, how to target co-morbidities. EC Orthopaedics 9(11): 781-782.
- Putta S, Peluso I, Yarla NS, Kilari EK, Bishayee A, et al. (2017) Diabetes mellitus and male aging: Pharmacotherapeutics and clinical implications. Current Pharmaceutical Design 23(30): 4475-4483.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Wu HY, Cao S (2013) Cancer metastasis treatments. Current Drug Therapy 8(1): 24-29.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Xu B, Qi RX, Sastry NY, et al. (2016) Cancer metastasis, a clinical dilemma for therapeutics. Current Drug Therapy 11(2): 163-169.
- Lu DY, Xu B, Ding J (2004) Antitumor effects of two bisdioxopiperazines against two experimental lung cancer models in vivo. BMC Pharmacology 4: 32.
- Lu DY, Huang M, Hu CX, Yang WY, Hu CX, et al. (2005) Anti-proliferative effects, cell cycle G2/M phase arrest and blocking of chromosome segregation by probimane and MST-16 in human tumor cell lines. BMC Pharmacology 5: 11.
- Lu DY, Chen XL, Ding J (2007) Treatment of solid tumors and metastases by fibrinogen-targeted anticancer drug therapy. Medical Hypotheses 68(1): 188-193.
- Lu DY, Lu TR (2010) Antimetastatic activities and mechanisms of bisdioxopiperazine compounds. Anti-Cancer Agent Medicinal Chemistry 10(7): 564-570.
- Lambert, AW, Pattabiraman DR, Weinberg RA (2017) Emerging biological principles of metastasis. Cell 168(4): 670-691.
- Putta S, Yarla NS, Peluso I, Tiwari DK, Reddy GV,et al. (2017) Anthocyanins: Possible role as multitarget therapeutic agents for prevention and therapy of chronic diseases. Current Pharmaceutical Design 23(30): 4475-4483.
- (2013) In: Shamm Ahmad (Ed.), An Old Disease, A New Insights, Springer Science, Germany.
- Zimmet PZ, Magliano DJ, Herman WH, Shaw JE (2014) Diabetes: A 21st century challenge. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(1): 56-64.
- Grimaccia F, Kanavos P (2014) Cost, outcome, treatment pathways and challenges for diabetes care in Italy. Global Health 10(1): 58
- Lu DY (2017) Suicide risks and treatments, new ideas and future perspectives. In: Ed Da-Yong Lu (Ed.), Nova Science Publishers, New York, USA.
- Lu DY (2017) HIV/AIDS treatments, fight for a cure. In: Ed Da-Yong Lu (Ed.), LAMBERT Academic Publishing. Germany.
- Lu DY (2014) Personalized cancer chemotherapy, an effective way for enhancing outcomes in clinics. Woodhead Publishing, Elsevier, UK.
- Lu DY, Chen XL, Ding J (2006) Individualized cancer chemotherapy integrating drug sensitivity tests, pathological profile analysis and computational coordination-an effective strategy to improve clinical treatment. Medical Hypotheses 66(1): 45-51.
- Lu DY, Lu TR (2019) Herbal medicine in new era. Hospice Palliative Medicine International J 3(4): 125-130.
- Lu DY, Chen EH, Wu HY, Lu TR, Xu B, et al. (2017) Anticancer drug combination, how far we can go through? Anticancer Agents Med Chem 17(1): 21-28.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Yarla NS, Wu HY, Xu B, et al. (2017) Drug combination in clinical cancer treatment. Reviews on Recent Clinical Trials 12(3): 202-211.
- Yang G, Li X, Li X, Wang L, Li J, et al. (2012) Traditional Chinese medicine in cancer care: A review of case series published in the Chinese literature. Evid Based Complement Alternate Med.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Putta S, Xu B, Wu HY (2019) Anticancer drug discoveries from herbal medicine. EC Pharmacology Toxicology 7 (9): 990-994.
- Parasuraman S (2018) Herbal drug discovery: challenges and perspectives. Current Pharmacogenetics Personalized Medicine 16(1): 63-68.
- Kocatepe D (2019) Importance of fish-oil consumption. EC Nutrition 14(2): 120-121.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Chen XL, Xu B, Ding J (2015) Plasma fibrinogen concentrations in patients with solid tumor and therapeutic improvements by combining anticoagulants and fibrinolytical agents. Advances in Pharmacoepidemiology & Drug Safety 4(4): e133.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Chen EH, Ding J, Xu B (2015) Tumor fibrin/fibrinogen matrix as a unique therapeutic target for pulmonary cancer growth and metastases. Clin Res Pulmonology 3(1): 1027.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Ding J, Xu B, Che JY (2015) Anticancer drug sensitivity testing, a historical review and future perspectives. Current Drug Therapy 10(1): 44-55.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Xu B, Ding J (2015) Pharmacogenetics of cancer therapy: breakthroughs from beyond? Future Science OA 1(4): FSO80.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Che JY, Yarla NS (2018) Individualized cancer therapy, what is the next generation? EC Cancer 2(6): 286-297.
- Lu DY, Xu B, Ding J, Lu TR, Yarla NS, et al. (2018) Cancer bioinformatics in cancer therapy. Adv Proteomics Bioinformatics 1(11): 1-7.
- Lu DY, Lu TR, Che JY, Shen Y, Yarla NS (2018) Individualized cancer therapy, future approaches. Current Pharmacogenomics & Personalized Medicine 16(2): 156-163.
- Lu DY, Che JY, Yarla NS, Zhu H, Lu TR, et al. (2018) Type 2 diabetes study, introduction and perspective. The Open Diabetes Journal 8: 13-21.
- Lu DY, Che JY, Yarla NS, Wu HY, Lu TR, et al. (2018) Type 2 diabetes treatment and drug development study. The Open Diabetes J 8: 22-33.
© 2020 Da Yong Lu. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






