- Submissions

Full Text
Novel Research in Sciences
One-Pot Multicomponent Synthesis of Novel 2-Imino-1,3-Thiazolidin-4-One
Abdelhamid AA*, Salah HA, Amany SE and Amer AA
Department of Chemistry, Egypt
*Corresponding author:Abdelhamid AA, Department of Chemistry, Egypt
Submission: October 21, 2019;Published: November 12, 2019
.jpg)
Volume2 Issue3November, 2019
Abstract
A novel series of 2-imino-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one were synthesized via simple efficient method through one-pot three-component reaction of phenyl isothiocyanate, primary amines and dimethyl acetylene dicarboxylate. The same products were synthesized via conventional route by reaction of the corresponding thiourea derivatives with dimethyl acetylene dicarboxylate
Keywords: 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one; Dimethyl acetylene dicarboxylate (DMAD); One-pot multicomponent reaction; Thiourea derivatives; Phenyl isothiocyanate
Introduction
Researcher’s interest in the chemistry of thiazolidine families has increased recently, due to a wide spectrum of biological properties shown by them [1,2]. Their derivatives were found in large numbers of biologically active compounds, including antifungal [3], anti-inflammatory [4,5], anti-diabetic [6], antimicrobial [7,8], antioxidant [9], antimalarials [10], anticancer [11-13], anti-HIV [14], and anticonvulsant [15,16] agents. Recent studies have also exposed that thiazolidine scaffolds have inhibitory effects towards the cytosolic CA II and hCA IX [17]. Thiourea derivatives are very important starting material in organic synthesis; they are simply synthesized with great variableness at the two substituents, also they provide a bifunctional site for 1,3-bielectrophiles yielding numerous heterocyclic products. From chemical view, dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate (DMAD) can be used as 1,3-bielectrophiles and react with thiourea derivatives to afford 1,3-thiazolidin-4-ones. Following up our previous findings on the improvement of new methods for the production of new heterocyclic compounds such as; pyridine, imidazole and anilinopyrimidine derivatives [18-21] and due to pharmaceutical applications of 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one, herein we aimed to further investigate the synthesis of novel 2-imino-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives by simple one-pot method from readily available starting materials under catalyst free condition, which involves the direct interaction between phenyl isothiocyanate, primary amines and dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate.
Result and Discussion
In this work, we wish to report a new route for synthesis a novel series of highly functionalized 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives by facile method through one-pot three-component reaction of phenyl isothiocyanate, primary amines and dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate. This protocol offers flexibility in tuning the molecular complexity and diversity. The reactions proceeded to completion almost in 2.0hrs. and pure products were obtained in good to excellent yields, without using any chromatographic techniques, simply by filtration and recrystallization. As an initial test, we run a model reaction by stirring an equimolecular aramounts of phenyl isothiocyanate 1 and phenethylamine 2a in ethanol at room temperature for about one hour then dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate 3 was added and the reaction mixture was stirred for one hour, that afforded desired product methyl 4-oxo-3-(2-phenylethyl)-2-(phenylimino)- 1,3-thiazolidin-5-ylidene]acetate 4a in excellent yield. After optimization of the procedure, the scope of the technique was investigated with a series of primary aliphatic and aromatic amines to yield the corresponding 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one 4b-k, (Method A, Figure 1). The same 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one 4a-k was also synthesized by an classical route via reaction of corresponding thioureas 5a-k with dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate 3 (Method B, Figure 1). Also, we found that, phenyl hydrazine reacts with phenyl isothiocyanate 1 and dimethyl acetylene dicarboxylates 3 by the same manner to give 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one 4i. While hydrazine hydrate and ethylenediamine react with phenyl isothiocyanate 1 and DMAD 3 to produce dimer of 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one 4j and 4k, respectively (Table 1). It is reasonable to assume that the formation of 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one 4 begins with the formation of thiourea 5 by reaction between phenyl isothiocyanate and primary amine followed by nucleophilic attack of thiourea’s sulfur atom on the C≡C bond of DMAD to give intermediate I, which undergoes intramolecular cyclization through nucleophilic attack of the NH group onto the carbonyl group, followed by elimination of methanol to yield 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one 4. (Figure 2).
Figure 1:Synthesis of 2-imino-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one.
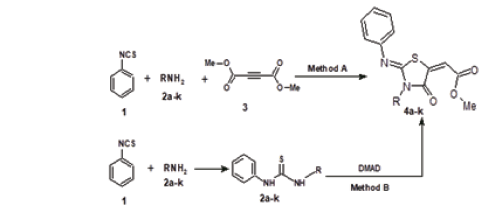
Figure 2:Reaction mechanism for the formation of 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one 4.

Table 1:Synthesis of 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one 4a-k.

Figure 3:1HNMR and 13CNMR chemical shift of 4a.
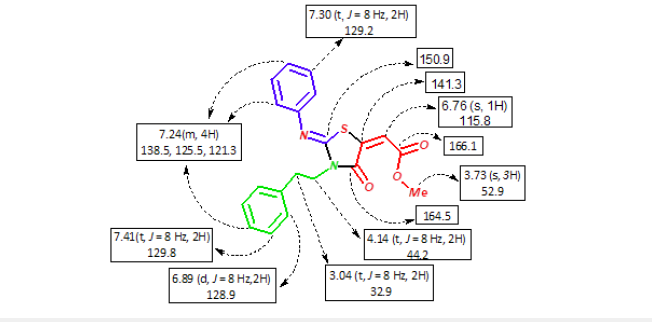
The chemical structures of 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one 4a-k were confirmed based on their spectral (IR, 1H, 13C NMR) and elemental analysis data. For example, the IR spectrum of 4a showed an absorption bands at 1716, 1665cm-1 due to the two carbonyl groups. Its 1H NMR spectrum showed the presence of two triplet signals at δ 3.04, 4.14ppm with coupling constant J=8Hz, characteristic of two methylene protons; a singlet signal at 3.73ppm for the methoxyl protons; it also exhibited a singlet signal at δ6.76ppm due to the vinylic proton; also it showed four signals at 7.41-6.89ppm characteristic for aromatic protons. The 13C NMR spectrum of 4a showed thirteen signals at 166.1, 164.5, 150.9, 147.8, 141.3, 138.5, 129.8, 129.2, 128.9, 126.9, 125.5, 121.3, 115.8 which are assigned to carbons of the carbonyl, aromatic and vinyl groups, while the H3CO is characterized by signal at 52.9ppm, finally the two methylene groups appears at 44.2, 18.9ppm (Figure 3).
Conclusion
A new series of the 1,3-thiazolidin-4-one were prepared from available starting materials via one-pot three-component reaction of phenyl isothiocyanate, primary amines and dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate. The same products were prepared via traditional method by reaction of the corresponding thiourea derivatives with dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate.
Supporting information
Experimental procedures and characterization data for new compounds 4a-k associated with this manuscript can be found via the supplementary content section of this article’s webpage.
Experimental
General procedure for synthesis of compounds 4a-k:
a) Method A
A mixture of phenyl isothiocyanate1(5.0mmol) and primary amine 2(5.0mmol) was stirred in ethanol (40ml) at room temperature for about 1hr. and then dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate (5.0mmol)3 was added. The reaction mixture was stirred for about 1hr. under an air atmosphere. After completion of reaction (monitored by TLC), the precipitate was filtered and recrystallized from appropriate solvent to give 4a-k.
b) Method B
Equimolecular amounts (5.0mmol) of thiourea derivatives 5 and dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate 3 in ethanol (40ml) were stirred for about 1hr. at room temperature under an air atmosphere. After completion of reaction (monitored by TLC), the precipitate was filtered and recrystallized from appropriate solvent to give 4a-k.
Methyl [4-oxo-3-(2-phenylethyl)-2-(phenylimino)-1,3- thiazolidin-5-ylidene] acetate (4a)
(Method A76 %, Method B 80) as a white solid, mp: 129- 130 °C; ϑmax(ATR) 3076, 2971, 2911, 1716, 1665cm-1. 1H NMR (400Hz,DMSO-d6) δ7.41(t, J=8Hz, 2H,CHarom), 7.30 (t, J=8Hz, 2H, CHarom), 7.24(m, 4H, CHarom), 6.89(d, J=8Hz, 2H, CHarom), 6.76(s, 1H, CHvinyl), 4.14 (t, J=8Hz, 2H,CH2), 3.73 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.04 (t, J=8Hz, 2H,CH2). 13CNMR(100MHz, DMSO-d6) δ166.1, 164.5, 150.9, 147.8, 141.3, 138.5, 129.8, 129.2, 128.9, 126.9, 125.5, 121.3, 115.8, 52.9, 44.2, 32.9. Anal. Calcd. for C20H18N2O3S (366): C, 65.55; H, 4.95; N, 7.64. Found: C, 65.83; H, 4.79; N, 7.60 [21-23].
References
- Chhabria MT, Patel S, Modi P, PS (2016) Thiazole: A review on chemistry, synthesis and therapeutic importance of its derivatives. Curr Top Med Chem 16(26): 2841-2862.
- Jain AK, Vaidya A, Ravichandran V, Kashaw SK, Agrawal RK (2012) Recent developments and biological activities of thiazolidinone derivatives: A review. Bioorg Med Chem 20(11): 3378-3395.
- Łaczkowski KZ, Biernasiuk A, Łaczkowska BA, Zavyalova O, Redka M, et al. (2018) Synthesis, lipophilicity determination, DFT calculation, antifungal and DPPH radical scavenging activities of tetrahydrothiophen-3-one based thiazoles. Journal of Molecular Structure 1171(5): 717-725.
- Sinha S, Doble M, Manju SL (2018) Design, synthesis and identification of novel substituted 2-amino thiazole analogues as potential anti-inflammatory agents targeting 5-lipoxygenase. Eur J Med Chem 158(5): 34-50.
- Tageldin GN, Fahmy SM, Ashour HM, Khalil MA, Labouta IM, et al. (2018) Design, synthesis and evaluation of some pyrazolo[3,4-d] pyrimidine derivatives bearing thiazolidinone moiety as anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorganic Chemistry 80: 164-173.
- Bhutani R, Pathak DP, Kapoor G, Husain A, Azhar I (2019) Novel hybrids of benzothiazole-1,3,4-oxadiazole-4-thiazolidinone: Synthesis, in silico ADME study, molecular docking and in vivo anti-diabetic assessment. Bioorganic chemistry 83: 6-19.
- Tuncel ST, Gunal SE, Ekizoglu M, Kelekci NG, Erdem SS, et al. (2019) Thioureas and their cyclized derivatives: Synthesis, conformational analysis and antimicrobial evaluation. Journal of Molecular Structure 1179(5): 40-56.
- Patel D, Kumari P, Patel N (2012) Synthesis and biological evaluation of some thiazolidinones as antimicrobial agents. Eur J Med Chem 48: 354-362.
- Djukic M, Fesatidou M, Xenikakis I, Geronikaki A, Angelova VT, et al. (2018) In vitro antioxidant activity of thiazolidinone derivatives of 1,3-thiazole and 1,3,4-thiadiazole. Chemico-Biological Interactions 286(25): 119-131.
- Jain S, Kumar A, Saini D (2018) Novel arylidene derivatives of quinoline based thiazolidinones: Synthesis, in vitro, in vivo and in silico study as antimalarials. Experimental Parasitology 185: 107-114.
- Szychowski KA, Leja ML, Kaminskyy DV, Binduga UE, Pinyazhko OR, et al. (2017) Study of novel anticancer 4-thiazolidinone derivatives. B J Chemico-Biological Interactions 262(25): 46-56.
- Ansar MF, Idree D, Hassan I, Ahmad K, Avecilla F, et al. (2018) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel pyridine-thiazolidinone derivatives as anticancer agents: Targeting human carbonic anhydrase IX. Eur J Med Chem 144(20): 544-556.
- Szychowski KA, Leja ML, Kaminskyy DV, Kryshchyshyn AP, Binduga UE, et al. (2017) Anticancer properties of 4-thiazolidinone derivatives depend on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ). J Eur J Med Chem 141(1): 162-168.
- Rawal RK, Tripathi R, Katti SB, Pannecouque C, De Clercq E (2007) Design, synthesis, and evaluation of 2-aryl-3-heteroaryl-1,3-thiazolidin-4-ones as anti-HIV agents. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 15(14): 1725-1731.
- Carradori S, Secci D, Bolasco A, Rivanera D, Mari E, et al. (2013) Synthesis and cytotoxicity of novel (thiazol-2-yl) hydrazine derivatives as promising anti-Candida agents. Eur J Med Chem 65: 102-111.
- Salar U, Khan KM, Chigurupati S, Taha M, Wadood A, et al. (2017) New hybrid hydrazinyl thiazole substituted chromones: As potential α-amylase inhibitors and radical (DPPH & ABTS) scavengers. Scientific Reports 7: 16980.
- Mahmood S, Saeed A, Bua S, Nocentini A, Gratteri P, et al. (2018) Synthesis, biological evaluation and computational studies of novel iminothiazolidinone benzenesulfonamides as potent carbonic anhydrase II and IX Bioorganic Chemistry 77: 381-386.
- Amer AA, Abdelhamid AA (2017) Microwave‐assisted, one‐pot multicomponent synthesis of some new cyanopyridines. J Heterocyclic Chem 54: 3126-3132.
- Marzouk AA, Abu Dief AM, Abdelhamid AA (2018) Applied Organometallic Chemistry 32(1): 3794-3809.
- Moustafa AH, Amer AA (2018) Unexpected products from the reaction of chalcones with cyanoguanidine. Tetrahedron 74(2): 324-328.
- Amer AA (2018) Synthesis of some new polyfunctionalized pyridines. J Heterocyclic Chem 55(1): 297-301.
- Gargi P, Sanjay P, Asish RD (2014) A facile and efficient synthesis of functionalized 4-oxo-2-(phenylimino)thiazolidin-5-ylideneacetate derivatives via a CuFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles catalyzed regioselective pathway. New Journal of Chemistry 38: 2787-2792.
- Alaa AH, Kamal MA, Amal SA, Stefan B, Martin N (2015) Journal of Natural Science B 70: 243-248.
© 2019 Abdelhamid AA. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






