- Submissions

Full Text
Novel Research in Sciences
The Critical Analysis of Comparative Eastern Africa Corporate Governance Standards After Financial Crisis–Malawi and Kenya Cases
Dinh Tran Ngoc Huy*
Faculty of Economics, Japan
*Corresponding author: Dinh Tran Ngoc Huy, Lecturer, Economic Faculty, Graduate School of International Management, Niigata, Japan
Submission: August 06, 2019; Published: September 23, 2019
.jpg)
Volume2 Issue2September 23, 2019
Abstract
Even though corporate scandals and bankruptcy in US and Europe and Asia show some certain evidence on weak corporate governance, weak internal control system and weak audit, Global corporate governance forum noted corporate governance has become an issue of worldwide importance. Therefore, this paper chooses a different analytical approach and among its aims is to give some systematic opinions. First, it classifies Eastern Africa representative Corporate Governance (CG) standards into groups: Malawi and Kenya latest CG principles covered in group 1, while it uses ACCA and CFA principles as reference. Second, it, through analysis, shows differences between above set of standards which are and have been used as reference principles for many relevant organizations. Third, it establishes a selected comparative set of standards for Eastern Africa representative corporate governance system in accordance to international standards. Last but not least, this paper covers some ideas and policy suggestions.
Keywords: Corporate governance standards; Board structure; Code of best practice; Financial crisis; Corporate scandals; Market manipulation; Internal audit; JEL Classification: G00; G3; G30
Introduction
After corporate scandals and bankruptcy taking place recently, such as Tyco, Enron, Worldcom, we find out that there are signals of accounting frauds, and market manipulation as well. This leads to a question on qualification of top management team which is soon replaced by new members in a hope that the business market value can be recovered. Despite of trying to select an easy-reading writing style, there is still some academic words need to be explained in further.
The organization of paper contents is as following. As our previous series of paper, Research literature and theories are covered in the first two sessions. Next, it followed by introduction of our research methodology in session 3 (3rd). Continuously, session four (4) covers our familiar four (4) groups of empirical findings. And our conclusion and policy suggestion are covered in the fifth (5th) session. Before last, there are exhibit session which covers some summary of this paper’s analysis and comparison. And lastly, a glossary notes are provided with information for reference and because of reducing repeating terminology.
Research literature review
There are many and controversial opinions on corporate governance theories and practices. For example, Jensen and Meckling (1976) presented their conceptual agency theory on the separation of ownership and management. Lin, Andrew Jen-Guang (2007) pointed that Corporate Governance will maintain its vital position in corporate law and securities law with the simple focus on investors. Besides, Commonwealth Association (1999) pointed the fact that every country and businesses nowadays need good corporate governance practices and theories as a necessity. Moreover, the South Africa King Code (2009) mentioned the terms of “corporate citizenship” and CSR or Corporate Social Responsibility and stated Corporate responsibility is the responsibility of the company for the impacts of its decisions and activities on society and the environment, through transparent and ethical behavior that: contributes to sustainable development, including health and the welfare of society; Furthermore, exhibit 2 shows us different parties and components, internal and external, should be involved in a policy or system of corporate governance. And certainly, global crisis and scandals recently such as Enron, Tyco, and Philadelphia partially signify the importance of corporate governance. As Demirag and Solomon, 2003 stated, The Asian crisis in 1997-1999 and corporate scandals such as Barings and WorldCom enhanced the need for corporate governance reform at a global level.
Additionally, Becht, Marco, Bolton, Patrick, Roel, Ailsa, (2005) developed corporate governance, the term is related with the resolution of collective action problems among dispersed investors, as well as the reconciliation of conflicts of interest between various corporate claimholders. They also pointed that when the outside investors have conflicts of interest with and want to exercise control differently from what the managers do, it will be among causes of corporate governance problems. Moreover, Adams, Renee B, Hermalin, Benjamin E, and Weisbach, Michael S, (2009) realized that as a consequence of corporate scandals and relevant corporate governance issues, boards have been at the center of the policy debate concerning governance reform and many further researches should deal with it.
Then, Ahmed [1] mentioned in nearly five decades of its existence, Islamic finance has gained only one percent of the global market share for finance. While some of this can be chalked up to the relative newness of the industry, some of its problems stem from ambiguous corporate governance model and less than stellar commitment to ethics. Bekiaris et al. [2] pointed budgets on internal audit have increased significantly, both in national and international level, while in the future the internal audit itself should have as a priority to consult the board, in order to identify, manage and monitor the key risks. Because there are not many researches and surveys done in Eastern Africa, next, what is the limited comparative standardized set of so-called comparative Eastern Africa corporate governance standards?
Theory of corporate governance, scandal and market manipulation
Theory of manipulation: There are different views on Manipulation subjects because of different types of it. Market manipulation covers errors in interfering the market operation and creates false information on price or market for a financial commodity such as stock. Besides, the involvement of financial intermediaries and brokers may contribute to manipulate market price while maintaining their credibility. Last but not least, there is a role of speculators in manipulation transactions to cause the increasing in investment flow into the invested company when speculators produce enough, or as much and sufficient as possible, information [3].
Theory of corporate governance and financial crisis: In 2008, OECD also stated that the financial crisis revealed severe shortcomings in corporate governance. During the financial crisis, some stock markets experienced downturn in stock price volatility and little or quite small fluctuation of price volatility. And although corporate governance in some financial markets has a lot of strengths, there are still a few weaknesses. Besides, corporate governance in a globalization trend has many things to work with building a good internal system and quality flows of information inside the business to face the challenges which comes from the external factors of globalization [4]. Hence, we can see, there exist various views on corporate governance and its importance.
Research Methodology
Firstly, we analyze and compare corporate governance principles in each of different groups including: Group 1-Eastern Africa CG representative standards including Malawi Code 2010 and Kenya 2002 Corporate Governance Principles; We also use, but not limited to, international standards of corporate governance such as: World Bank, and Mc Kinsey corporate governance principles and surveys as reference, as well as ICGN and OECD Corporate Governance Principles which have many modifications in corporate governance principles after the crisis period [5]. Then, we suggest on what so-called limited comparative Eastern Africa corporate governance principles which is aiming to create a basic background for relevant corporations interesting in different aspects of corporate governance subjects and functions as the recommendation to relevant countries’ government and other relevant organizations for public policy and necessary evaluation [6]. Last but not least, for a summary of our standards, see Exhibit and the below [Figure 1,2] in relevant sessions.
Figure 1:Exhibit 1-Corporate Governance system (source: Brazil Code of Best Practice of CG).
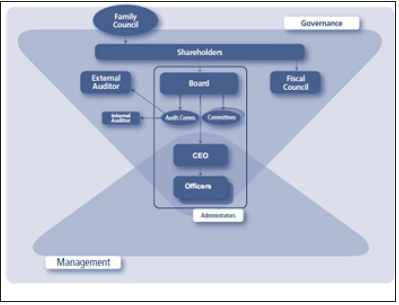
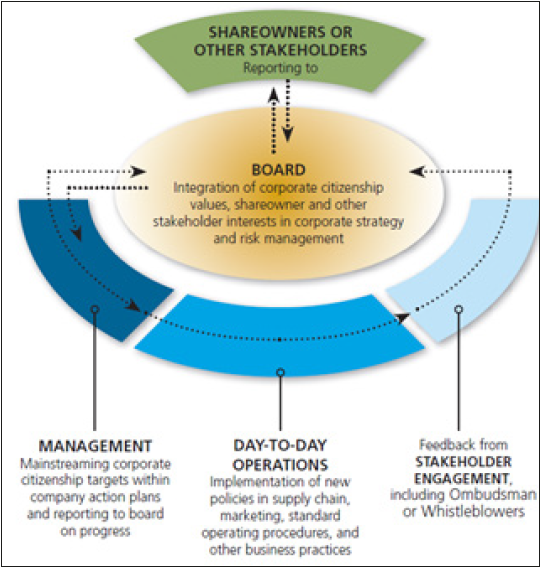
Figure 2:Exhibit 3-How responsible business embedded into function of BD (source: IFC and Global Compact 2009).
Empirical findings
Findings on Corporate governance issues after financial crisis, corporate scandals and market manipulation: Several popular issues including: the responsibility of the Board of Directors, both as a whole and as individual, to the mission of protecting and growing net value of total company asset. This is clearly identified after many crises and scandals recently. To break this issue in more details, we can see there is the un-effectiveness of Board, CEO and Board processes, as well as the inefficiency roles of audit function in dealing with matters relevant to Board effectiveness. Also, we can find out another Corporate Governance (CG) issue. It is, the lack of effective mechanism to protect well net value of company and investors and shareholders’ asset and investment. Another one is the transparency mechanism still existing with errors that lead to declining company’s credibility to investors [7]. Moreover, the lack of an effective Code of Ethics and Code of Conduct might be a cause contributing to failures, frauds and bankruptcy recently and after financial crisis time [Table 1,2].
Table 1:The 2010 Malawi code of governance for South Africa (a short summary evaluation).
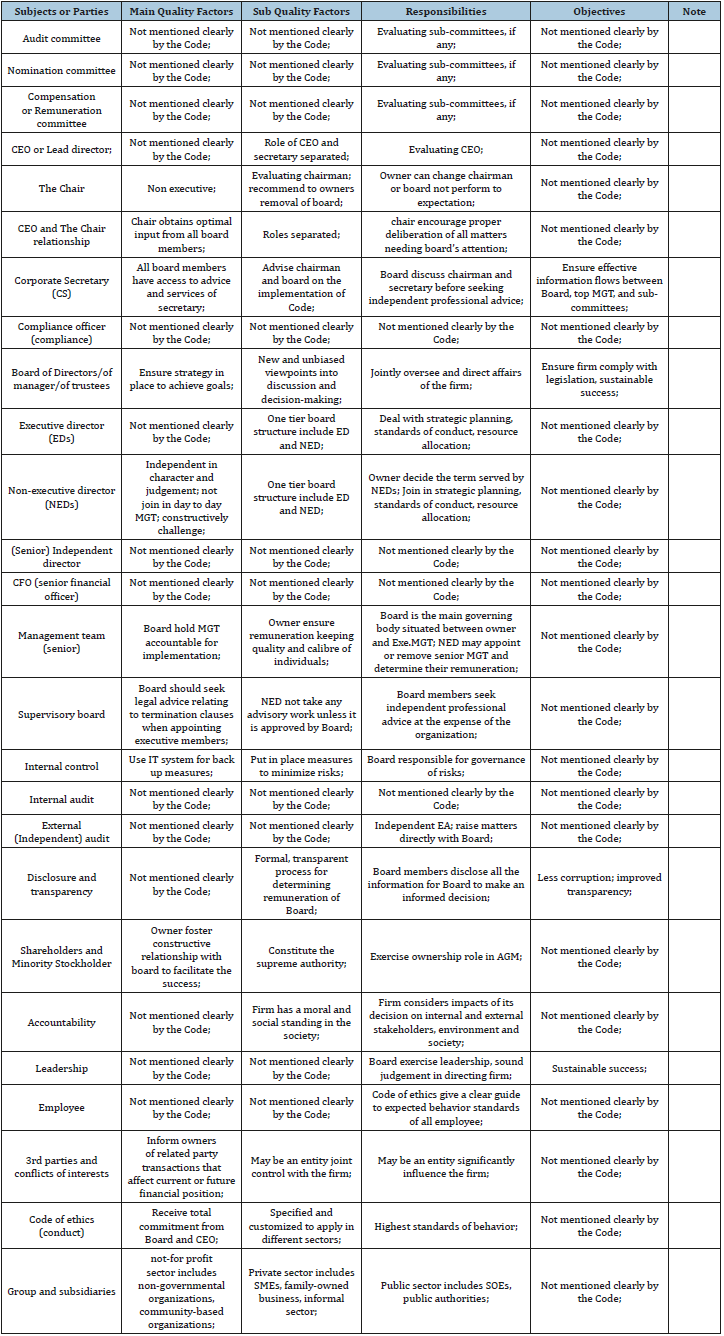
Table 2:The 2010 Malawi code of governance for South Africa (a short summary evaluation).

Findings on Ways of Manipulation during Corporate Scandals: Several Manipulation Techniques found out during corporate scandals involve, but not limited to:
A. The manipulation techniques in the income statement: Here, the technique is used to manipulate either income or expense or profit to maximize benefits for both Board and investors. In the scandal of Zhengzhou Baiwen company in China, the firm success is reported based on creative accounting and fraudulent practices. Falsifying financial statements were used for maintaining its stock exchange listing. And it made up artificial sale record and excluded 22 subsidiaries because of their poor performance between 1996 and 1998.
B. The manipulation techniques in both the income statement and balance sheet: In ABB scandal, although the technological company performed very well in previous years, until its hid losses and reported the first loss in 2002 but actually it is for 2001. Also, in the year 2000, ABB forgot the loss from divestments when it reported the benefits from acquisition. Hence, the result for the 2nd quarter is much worse than that in the 1st quarter. Another scandal in China, in Hongguang case in 2001 or previous years, it was discovered to inflate or manipulate profits of RMB 150 million by forging sales, manipulating depreciation, and overstating inventory.
C. The manipulation techniques relevant to international accounting practice code: There is a going controversial concern between some different practices in IFRs and GAAP standards. Furthermore, in the case of ABB scandal in Sweden, the company switched from IAS to US GAAP to be listed on the US stock exchange. And it is said that under IAS (International Accounting Standards), ABB could use gains from selling various assets to inflate its operating income while this accounting practice is not allowed under US GAAP.
D. Other manipulation techniques net belongs to above classifications: Financial manager could make use of irregular accounting rules to manipulate assets in accounting number not in its real life number, for example, Waste Management Inc case show us the depreciation time length of property is expanded in the year 2002. On the other hand, financial managers can manipulate interest rates to earn profits and these are fraudulent actions. For example, in scandals relevant to Libor (London interbank rate), banks were falsely inflating or deflating their rates so as to profit from trades or in order to create impression that they are more creditworthy than they were.
Actions on Preventing or Controlling negative manipulation: Firstly, it is necessary to have a controlling mechanism on accounting processes and procedures and the proper use of international accounting standards. Other necessary actions to control negative market manipulation are, enhancing capability of the board and management, as well as the capability of internal control system.
Findings on Construction of Comparative International Corporate Governance Standards: These findings will be shown in a detailed analysis of a model indicated in the later sessions.
A. Group 1–Eastern Africa Corporate Governance standards analysis
I. The Malawi Code of Governance 2010
This is the modified Code since its first publication in 2001. Among its advantages are, but not limited to, clear descriptions of Board duties including developing policies to minimize conflicts of interest. Additionally, it is good to state that the Board need to develop a board charter based on articles of association and organization’s constitution. Besides, it has involved detailed roles of Board including ensuring appropriate procedures protecting firm assets, resources and reputation. Generally speaking, the 2010 Code has certain different strong points including Board ensuring members playing a full role in the affairs of firm. However, it would be better to identify roles of CFO [8].
II. The 2002 Kenya Corporate Governance principles
One of its distinctions is mentioning good CG based on advancing long term shareholder value and human-centered development. And it also pointed good CG could create competitive companies and promote effective use of limited resources. Besides, the Kenya Code mentioned BD ensure no one person or group has unfettered power. For more information, please see Exhibit 2. However, it would be better to clarify duties of a compliance officer.
III. Comparison between the Malawi and Kenya Corporate Governance principles
Different from most of Asian Codes, there is a focus in Malawi Code 2010 on clear illustration of roles of Board of directors. Also, it makes a sound point when it considers the firm as a good corporate citizen.
On the other hand, the Kenya Code 2002 refers CG to promoting an efficient process of value adding and creation [9].
Conclusion
Among several key corporate governance issues is, but not limited to, the leadership roles and the effectiveness of top management team, including CEO, chair, Board and outside directors. To reduce its impacts, The Malawi code 2010 mentioned CG practices can support sustainable development and greater access to capital. Besides, the Kenya Code emphasized role of governance in management of economic and social resources for sustainable human development. Past surveys from McKinsey in 2000 showed results such as investors willing pay 24% premium for good CG in South Korea and 18% premium for that in UK [10,11]. In consideration of corporate governance issues analyzed in the previous sessions, we proposed the main and sub quality factors in this paper a set of general Eastern Africa corporate governance standards in a limited Eastern Africa model with selected countries. Though limited, it has some implications for further research and proper recommendations to relevant government and organizations. And it also provides relevant academic and nonacademic, lawyer and consultant, board and non-board people with minimum information for further researches [12].
Acknowledgement
I would like to take this opportunity to express my warm thanks to Board of Editors and Colleagues at Citibank –HCMC, SCB and BIDV-HCMC, Dr. Chen and Dr. Yu Hai-Chin at Chung Yuan Christian University for class lectures, also Dr Chet Borucki, Dr Jay and my ex- Corporate Governance sensei, Dr. Shingo Takahashi at International University of Japan. My sincere thanks are for the editorial office, for their work during my research. Also, my warm thanks are for Dr. Ngo Huong, Dr. Ho Dieu, Dr. Ly H. Anh, Dr Nguyen V. Phuc and my lecturers at Banking University – HCMC, Viet Nam for their help. Lastly, thank you very much for my family, colleagues, and brother in assisting convenient conditions for my research paper.
References
© 2019 Dinh Tran Ngoc Huy. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






