- Submissions

Full Text
Novel Approaches in Cancer Study
A Novel Eclectic Approach for Cancer Therapy with Liquid Knife & Immuno Therapy: UMIPIC, it may Overtake many Surgery, Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy for all Stages of Solid Tumor
Baofa Yu*
Beijing Baofa Cancer Hospital, China
*Corresponding author: Baofa Yu, Beijing Baofa Cancer Hospital, Beijing, China
Submission: April 02, 2020Published: April 16, 2020

ISSN:2637-773XVolume4 Issue3
Introduction
Recent years cancer immunological therapy is getting very popular and many new drug have been approved by FDA like PD1 and PDl-1, however, in clinical practice of cancer treatment, it looks very limited efficacy for advanced cancer, so that physician started to use comprehensive plan by combination chemotherapy with PD1 as a novel strategy with a better clinical benefit. Since chemotherapy and radiation therapy always produce the side effect like loss hair, vomit and neutropenia, and surgery is limited for many later stages of cancers, also surgery damages body shapes with functions, esophageal cancer was removed with reconstruction and put stomach into chest and stomach never has normal function; a lot of cases showed surgery can’t be performed because tumor location in special site, like tumor location in posterior vaginal wall or vaginal carnal, surgery just is not allowed to do the procedure, if remove the tumor in these location, it will make a hole to connect to the rectal. Because of the extremely toxic side effects, many cancer patients cannot be successfully completed a surgery or a complete course of chemotherapy or radiation therapy, and some cases even die from the side effects of surgery or chemotherapy or radiation therapy due to a patient’s poor tolerance. The extreme side effects of anti-cancer drugs are often caused by the poor target specificity of such drugs regarding the tumor in the patient’s body. The drugs circulate through most normal organs of patients as well as the intended target tumors (less than 5% of the drug reach the tumor), while over 95% of the drug circulates through the whole body of the patient.
Today, the more and more cancer patients do not like to choose to surgery and chemotherapy, even radiation therapy due to different reason, it is pushing the oncologists to be in the embarrassed situation to suggest the therapy for the patient who lost or do not like surgery opportunity, chemotherapy or radiation therapy, in the fact for most late stages of cancer, elder patients or patients with severe other disease, how many choices our oncologists can give? A few choices, today I do like to introduce one novel approach which is suitable for the most of earlier or late stages of almost solid tumor with benefit, no matter where the tumor located the body of patient, UMIPIC, ultra minimum incision personalized intratumoral chemo immunotherapy.
UMIPIC is a eclectic unique approach for cancer treatment utilizing the intratumoral injection of a combination of chemotherapy drugs (including Dox and Ara-C), coagulant agent oxidant to maintain the chemo agents at the injection site for a longer period of time, and a hapten for hapenation with intracellular tumor-associated antigens to stimulate the patient’s immune response while the tumor is been de-bulking like liquid surgery knife. Safer and more aggressive (higher dose) administration of toxic chemotherapy drugs that go directly into a tumor site with slow release, is an obvious and beneficial alternative to systemic treatment. The local retention afforded by intratumoral administration results in slowed and/or reduced entry of drug into the systemic circulation, minimizing exposure of distant tissues to the drug, and thus, resulting in a lower incidence of systemic side effects and more tumor cells be killed. So far, there are 56 clinical trials found for intratumoral chemotherapy (ITCT) by visiting the website at the following: https://clinicaltrials.gov. But there is not one integrated with immuno therapy and surgery knife to action like de-bulk.
In 1994, Yu B [1] developed the new concept of using the tumor itself as a drug carrier. Injection of anti-cancer drug ethanol saturated liquid into the tumor can generate a kind of intratumoral autologous therapeutic coagulum which can function as an antitumor drug depot. This autologous therapeutic coagulum can sustain or store anticancer drug in tumor and the surrounding tumor tissues to kill the tumor cells that have not been killed through ethanol coagulation treatment. It makes a fitting complement for the inadequacy of pure ethanol tumor treatment. A study of retaining drug in injected tumor demonstrated that the retention half-life of anticancer drug Ara-C in the tumor was 160 minutes following depot injection compared to only 6 minutes following intratumoral injection of Ara-C aqueous solution, thus increasing the drug retention by approximately 27 times [1]. The problem of using ethanol is that is is limited by the dosage for the patient and is also limited by tumor size (when the volume of tumor is large, it can dilute ethanol making it inefficient). Now Yu B [2] found oxidant is good role to replace the ethanol to coagulation of tumor as a drug carrier for slow releasing.
From 2003 to 2006, Yu B [3] also published many papers showing that the combination of intratumoral drug with hapten modification improves the immunogenicity of tumor cells, effectively inducing or activating body’s antitumor immune response and had 276 patients with cancer reported with good results [3-5]. It indicates that when hapten is added to the UMIPIC, it plays an important role in stimulating immune response.
The UMIPIC is comprised of commercially available drugs for intratumoral injection which includes oxidant as coagulant, chemotherapy drugs and hapten. Intratumoral injection with UMIPIC, it produces its antitumor role in the following aspects:
The first aspect is coagulation by the oxidant. “Tumor coagulation” refers the process by which the blood clots to form solid masses, or clots, and their components and extracellular matrix are transformed into a kind of soft, semi-solid, or solid block. This transformation is induced by oxidation, which makes openings in the membrane of tumor cells. This creates higher permeability of membrane that allows the drugs to penetrate into tumor cells and eventually leads to the death of coagulated tumor cells and enhancement of the cancer drug entering agglomerated tumor cells, most tumor cells killed like liquid surgery knife.
The second aspect is the concentration and sustainability of the drugs, the two key elements: Drug dosage and amount of time for destruction of cancer cells. Tumor coagulation also creates a “drug depot” which not only increases local drug action concentration (dozens or even hundreds of times more than the normal concentration by intravenous chemotherapy) to kill the tumor, but also retains the drugs within the tumor and gradually releases them from inside to the outside to kill residual tumor cells around tumor tissue. This “drug depot” not only extends drug action time in the tumor, but also prevents the leakage of anti-cancer drugs from the tumor, and lowers systemic drug concentration, toxicity and side effects since drug depot created slow release of drugs in the tumor site or the surrounding of tumor.
The third aspect is stimulation of immune response. Tumor cells killed by the tumor coagulation effect and the chemotherapeutic agents could release intracellular proteins including tumor-associated antigens, which may already interact with hapten in that active reaction with tumor oxidation. The tumor antigens induce a personalized systemic immune response and the haptenation of tumor antigens could further stimulate immune response, thereby eliminating recurring or metastatic tumor cells.
The schematic diagram is shown with the function of components in UMIPIC and the Procedure of UMIPIC: Guided by CT, find the optimal route and angle for introducing the needle intratumoral, the needle is inserted into the tumor, connected to the inflator, the regimens of UMIPIC were slowly delivered into the tumor; a high pressure supplied by the inflator; the solution (UMIPIC) can penetrate into the extracellular matrix of tumor and facilitate forced diffusion. Same injection could be repeated to same tumor or other tumor several times according to evaluating by CT and physician or investigator brochures [6-9].
In the past years, UMIPIC treated lung cancer, median overall survival was 11.23 months in the UMIPIC (test) group and 5.62 months in the ITCT (control) group (P<0.01). The 6-month and 1-year survival rates of the UMIPIC and ITCT groups were 76.36% versus 45.23% (P<0.01) and 45.45% versus 23.81% (P<0.05), respectively. Two cycles of UMIPIC treatment (N=19) conferred a significant survival benefit compared with two cycles of ITCT (N=29); significant benefits in survival time were also found with UMIPIC (N=20) compared with ITCT (N=13) when both were utilized without hapten treatment.
Also UMIPIC for liver cancer with good result: the benefit rates (complete response + partial response + stable disease) were 78.68% and 81.52% in the UMIPIC and ITCT groups, respectively, with no statistically significant difference; however, the median overall survival was 7 months for UMIPIC (test) and 4 months for ITCT (control), respectively (P<0.01). The 6-month and 1-year survival rates for UMIPIC and ITCT were 58.88% vs 32.3% and 30.37% vs 13.6%, respectively (P<0.01). Single and multiple UMIPIC revealed significant improvement in overall survival compared to that of ITCT.
In the past years, UMIPIC treated pancreatic cancer, for single drug, median survival was 6.45 months for UMIPIC-S vs 4.98 months for ITCT-S, (P<0.05), one year survival rate was 28% for UMIPIC-S vs 5% for ITCT-S (P<0.05). For double drugs, median survival was 15.5 months for UMIPIC-D vs 3 months in ITCT-D (P<0.01). The 6-month survival rate was 76.67% for UMIPIC-D vs 18.18% for ITCT-D (P<0.01) and 1-year survival rate for 56.67% UMIPIC-D vs 9.09% ITCT (P<0.01).
In the past twenty two years, UMIPIC is used for over 60,000 cancer patients with late stages or patient do not like to take surgery or chemo & radiation therapy, it resulted in good benefits and extended their life. Today it is analyzed the data included 2594 patients (unpublished), including 27 common cancer diseases such as lung cancer, esophageal cancer, primary liver cancer, and pancreatic cancer, gastric cancer, rectal cancer, breast cancer, cardia cancer, colon cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, kidney cancer, hypopharynx carcinoma, lymphoma, bladder Cancer, gallbladder cancer, thyroid cancer, malignant melanoma, prostate cancer.
After the patient was admitted to hospital and signed the patient's UMIPIC agreement, The UMIPIC of the UMIPIC guide, collection data of patients, and follow-up of the patients, statistical analysis found:
- For all of solid tumor, the lowest incidence of adverse reactions was rash, the incidence was 0, the highest incidence of adverse reactions was fever for the incidence of 31.08%; moderate severe adverse reactions was the lowest incidence of rash for the incidence of 0, the highest incidence of severe adverse reactions was fever for 8.61%. For pancreatic cancer, the main adverse reactions was mild fever (27.78%) and moderate severe fever (8.33%), mild pain (24.49%) and moderate severe (1.02%), there was also a decrease in hemoglobin (13.95%) because 39% of patients was anemic before UMIPIC. There is no other adverse reaction related to UMIPIC or life-risking adverse reaction related to UMIPIC.
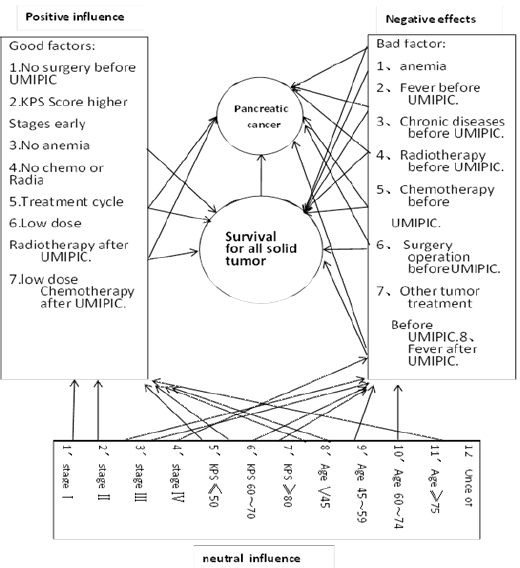
- According to the statistics of patients' baseline period, anemia and fever and cancer stages before UMIPIC have a great influence on the incidence of adverse reactions after UMIPIC, while KPS score, gender, age, chronic disease, prior UMIPIC chemotherapy, prior UMIPIC radiotherapy and prior UMIPIC surgery, these factors are influence to the incidence of adverse reactions but the impact is small.
- After statistical analysis of the overall best efficacy, it is found that before UMIPIC patients with anemia, fever, chronic disease, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, tumor surgery, low KPS score, clinical stage is advanced, it will reduce the UMIPIC effect to varying degrees; KPS score is high, after UMIPIC low-dose radiotherapy, low-dose chemotherapy, and early clinical stage will increase the therapeutic effect of UMIPIC in different degrees, and the therapeutic survival will increase with the increase of UMIPIC cycle and UMIPIC times; pancreatic cancer has the similar observation as above. From patients diagnosed to receive UMIPIC, the average time was 5.6 months, during this period patient ma got traditional chemo or radiation therapy.
- After follow-up UMIPIC patients, the median survival time was 11.03 months and The 1-, 2-, 3-, 4-, and 5-year survival rates were 45.15%, 24.90%, 20.59%, 20.09% and 18.98% in general analysis of 2594 patients. This results of survival is comparable to any therapy of surgry, chemo& radiation therapy.The average time from diagnosis to UMICIP treatment was 3.59 months for pancreatic cancer patients. The median survival time after treatment was 7.60 months. The 6-month, 1-year, and 2-year survival rates were 60.00%, 29.00%, and 15.00%.
- The main factors that reduce the survival time and survival rate of patients are anemia, low KPS score, advanced clinical stage, prior treatment fever, prior treatment chronic disease, prior treatment radiotherapy, chemotherapy, surgery and post-treatment fever, improve patient survival time and survival. The main factors of the rate were high KPS score, early clinical stage, the low-dose radiotherapy after treatment and low-dose chemotherapy. Survival time and survival rate increased with the number of treatments and cycles; pancreatic cancer was the same as above, all factor influence to UMIPIC efficacy and survival, see bellowing.
UMIPIC is a simple, clinically effective drug for a broad spectrum of tumors with minimal side effects through ultra-minimal invasive surgery under the guide of CT or ultrasound. In conclusion, UMIPIC provides a new method of decreasing tumor mass while boost the patient’s own immunological power to fight against micro tumor cells in a specific and innovative manner, which is one of its advantages over any treatment. Another advantage is that it is not limited in terms of tumor size, number, or location in the lung, liver, pancreatic or any location of tumor (Table 1). In future, it is possible that UMIPIC may overtake in the treatment of all stages of tumor in the lung, liver, pancreatic or any location of tumor, sometimes it may take over in the treatment of earlier stages of cancer. UMIPIC can take the place of surgery and chemotherapy or radiation therapy in patients who are not suited for surgery or chemotherapy and radiation therapy. We hope to continue to investigate UMIPIC therapy with double cytotoxic drugs with double hapten under clinical study to improve effectiveness (Figure 1).
Table 1:
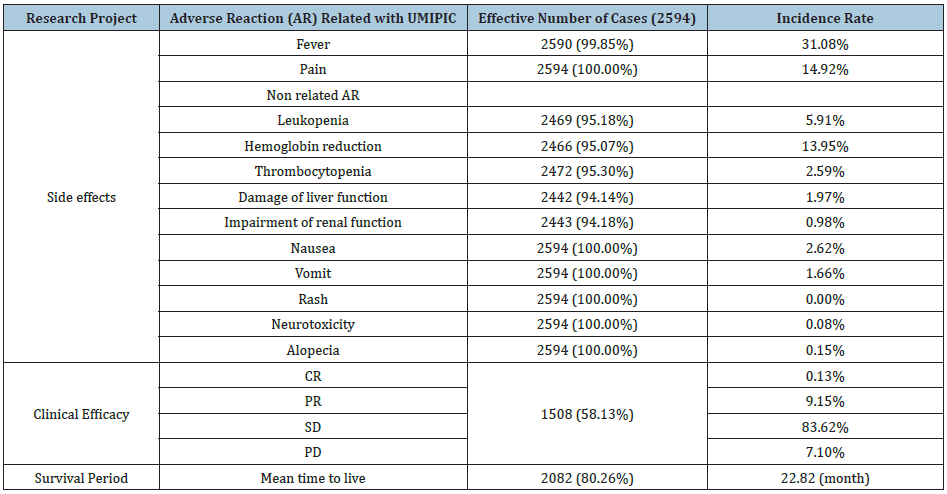
Figure 1: Neutral Influence.
Today, it is time to think how to replace the surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy which produce a damage of patient with cancer, we believe UMIPIC has provided a new eclectic approach for the treatment of primary all solid tumor at anywhere of body at earlier stages, even pre surgery and during of operation produce a immunological response while the surgery. UMIPIC is safe, easy to operate, and reproducible with good benefit for all solid tumor.
References
- Yu B, Kim S (1994) Alcohol with intratumoral drug injection and pharmacokinetics of drug after intratumoral injection: A new concept of intraturmoal autologous therapeutic coagulum with drug depots. Journal of Current Oncology 1(2): 97-100.
- Bu Jieqiong, Baofa Yu (2007) Slow intra-tumor release of drugs on B16 melanoma in Mice. Journal of Shandong University (Health Sciences) 45(10): 988-991.
- Yu B, Ma Z, Guan C (2003) Observation of 751 cases of malignant tumors treated with drug depot therapy. Journal of Shandong University (Health Sciences) 41 (Addition): 14-8.
- Baofa Yu, Yan Han, Guoliang Liu (2003) Animal Experiment of Intratumoral Drug (ARA-C) slow release depot therapy. Journal of Shandong University (Health Science), Jinan China, 41(Suppl): 1-3.
- Guan C, Yang G, Zhang J (2006) Observation of 276 cases of advanced liver tumors treated with drug depot therapy. Chinese Journal of Celiopathy 6(3): 160-162.
- Bf Yu, et al. (2014) Interventional Oncology & Chemoimmunotherapy 9.
- Baofa Yu, Yuanfei Lu, Feng Gao, Peng Jing, Han Wei, et al. (2015) Hapten-enhanced therapeutic effect in advanced stages of lung cancer by ultra-minimum incision personalized intratumoral chemoimmunotherapy. Lung Cancer: Target and Therapy 6: 1-11.
- Feng Gao, Peng Jing, Jian Liu, Yuanfei Lu, Peicheng Zhang, et al. (2015) (Hapten-enhanced overall survival time in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma by ultra-minimum incision personalized intratumoral chemoimmunotherapy. Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma 2: 57-68.
- Peng Jing, Jian Li, Feng Gao, Yuanfei Lu, Jian liu, et al. (2015) Use of hapten combinded Catatonic drugs for enhancing therapeutic effect in advanced stages of pancreatic cancer. Journal of Liver Research, Disorders & Therapy 1(3): 63-69.
© 2020. Baofa Yu. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






