- Submissions

Full Text
Modern Applications in Pharmacy & Pharmacology
Contemporary Scenario of SSFFC Medicines: A Systematic Review
Farah Iram, Sana Iram and Asif Husain*
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Jamia Hamdard, India
*Corresponding author: Asif Husain, Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, SPER, Jamia Hamdard, New Delhi-110062, India
Submission: March 01, 2018; Published: March 16, 2018

ISSN 2637-7756Volume1 Issue4
Abstract
Health care professionals (HCPs) play most significant role in health care system and provide medicines to cure and heal diseases, lessen symptoms, relieve pain, avoid disease or symptoms and slow down the disease process. Unfortunately, sometimes medicines not found to be potent due to the problem of substandard/spurious/falsely labeled/falsified/counterfeit medicines (SSFFC). The issue is widely spread globally and affects both developing and developed nations. In India every year several incidences of SSFFC medicines were reported, which tremendously affects the health of the public. SSFFC medicines not only affect public health but it also results in the economic crises. This concern cannot be neglected any more. A comprehensive study on the contemporary scenario of the problem, its recognition and detection with respect to locality, medication category, and drug form investigation is not present. Our purpose is to thoroughly explore and investigate the evidence available on SSFFC in the period of 2013-2016. Reports suggest the incidence occurrence in their region wise manner.
Keywords: SSFFC; Adulterated; WHO; CDSCO
Introduction
Globally every year dubious quality drugs affect a large number of populations. Drug safety, efficacy, and quality are the prior responsibilities of health care professionals [1]. However, substandard/spurious/falsely labeled/falsified/counterfeit medicines (SSFFC) make it hard for HCPs to provide trust worthy and resolute health care system [2,3]. Countries including developing and developed endure many health issues due to counterfeit/ substandard/ spurious drugs. Victim of these drugs faces life threatening issues, financial crises and loss trust on the health system. SSFFC could be branded or generic drug. Weak regulatory guidelines and their enforcement in the manufacture, storage, importation, distribution, supply and sale of drugs result in the poor quality or NSQ (Not of Standard Quality) drugs [4]. Globally counterfeiting covers a large market and is complicated to distinguish, detect, inspect, enumerate and prevent them [5-7]. Thus this co-nundrum of the poor quality of drugs should be minimized by rigorous regulation and legal actions. The purpose of this review is to investigate the incidence of substandard/spurious/falsely labelled/falsified/counterfeit medicines for the duration of 20132016. Data from 2013 to 2016 were assembled and disclosed the actual status of poor quality drugs in India.
SSFFC Definition
WHO in 1992 describe counterfeit medicine as medicine which is intentionally and deceptively mislabelled with respect to identity and/ or source [8]. WHO in 2011 define counterfeit and substandard medicines in new term 'substandard/spurious/ falsely-labelled/falsified/counterfeit medical products' (SSFFC) [912]. SSFFC includes generic as well as branded drugs. SSFFC may be with the correct ingredients or with the incorrect ingredients, devoid of active ingredients, with inadequate active ingredients or with fake packaging [13]. Counterfeit products can be categorised as:
a. Drug ingredients are wrong.
b. Insufficient amount of ingredients present.
c. Drug product with no drug ingredients.
d. Drug ingredients differ from which it is mentioned on label.
e. Drug products with fake and inappropriate packaging.
f. Drug products which have been expired and which do not have expiry date.
g. Drug products with high content of impurities.
Type of SSFFC
Drug and Cosmetic Act, 1940 states that counterfeit, misbranded, spurious, adulterated and fake drugs and not good quality drugs are of three types [14].
I. Type A: It includes spurious and adulterated drug product. The actual characteristics of drug product obscure and mislead it with several identified brand. Active ingredients may not be present in mislead products. Mostly the manufacturers of these products are unknown and unlicensed authorities. Type A consists of adulterated products with harmful ingredients [15].
II. Type B: It includes grossly substandard drug product. These products mainly fail in their various evaluatory parameters like disintegration or dissolution test in case of tablets and pyrogen/endotoxin test in case of parenteral preparation. Broadly it includes [16].
a. Active ingredient: less than 70% and 5% for thermally labile and thermally stable products.
b. Tablets/Capsules: disintegration/dissolution not passes.
c. Liquid preparations: fungus occurrence.
d. Parental preparations and Vaccines: sterility, pyrogen/ endotoxin test not passes.
e. Adulterant: present of any substance which is injurious to health.
III. Type C: It includes products with insignificant fault. These categories of products do not cause significant harm. The insignificant imperfection of dosage form includes like picking, cracking, change in formulation colour, smell, sedimentation, weight variation and errors in the label. Example includes [17].
a. If tablets are broken or chipped,
b. If the coating is uneven or spot is present.
c. Cracking of emulsions.
d. Presence of sedimentation in any clear liquid dosage form.
e. Net content deviation.
f. Drug products fail in weight variation, colour test and deviation in net content.
g. Any labelling errors.
Preventive measures for SSFFC
Regulatory guidelines: There should be appropriate regulatory guidelines to prevent SSFFC, which should be followed rigorously. There should be penalties and imprisonment for felony related to manufacture, distribution and sale of spurious or adulterated drugs. There should be Standard Operative Procedures [SOP] in each region to observe if there is any violation of the provision of the Act [14,18].
Source integrity and Supply chain: The obtain source of medicine should be reliable. There should be possible regulatory guidelines to avoid counterfeit drugs. Particular measures should be taken for state licensed pharmacies. Some initiatives that devote reliable supply chain includes [16,19]:
a. Tool and techniques to enable the traceability and localization of drug
b. A limited number of intermediates in supply chain system while preserving free competition.
c. Rapidly and successfully analyze the suspect drug
d. Authenticate internet pharmacies and websites by awarding logo to the site. Presence of online official trustworthy sites.
By this step; one can get the medicine from a reputed source.
Pricing: Relatively cheaper price available drug product should be treated with extra cautions. Sometimes supplier trades the medicines at price more than its original one. The consumer should make sure to authenticate the price before the purchase [20].
Consumer awareness: Consumer should know the drug to be consumed. Any time when prescription refilled colour, odour, taste, the texture should be observed carefully. If there is any mystification then talk to the supplier. The appropriate campaign should be launched for the awareness of society against SSFFC [14,16].
Health care professionals' obligation: HCP should embrace entire stakeholders concerned with conception, making, regulation, allocation and sale of medicines. From the pharmaceutical laboratories that produce the medicines to the patients, all these professionals should be qualified and trained to identify and track SSFFC medicines [21].
Product reliability: SSFFC easily averts from the society if the medicinal products are reliable to consume. One should observe the medicine cautiously and evaluate it on following basis [14,22]
a. Label: Commonly original label removed and replace with a counterfeit label. Always look for holograms, sealing tape tears and seal. Observe the label carefully.
b. Expiry date: Be active to view expiry date. Mainly expiry date was altered in label to sell expired drugs.
c. Packaging: Packaging of the product should be observed meticulously. Several advanced packaging technologies proved helpful in combating this issue. Some of them are:
i. Acous to magnetic identification (AMID)
ii. Bar code
iii. Electro-magnetic identification (EMID)
iv. Holograms
v. Pedigree system of labelling
vi. Pilfer-proof packing
vii. Pharma code
viii. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
ix. Security label
x. Verification Systems
Vigilance and feedbacks: To assure the safety and efficacy of the drug there should be organized vigilance, monitor incidents and systematize feedback of the patients. The pharmaceutical company should [23].
a. Make and update the list of most likely medicines to be forged.
b. Thoroughly report the concern authorities regarding the entire incidence related to the product.
c. Systematically recall suspect batches and maintain the product transparency.
d. For rapid analysis of suspect drug, permanent all time available hotlines should be present in pharmaceutical companies.
The coordinated use of these technologies within the official and parallel trade distribution channels increase the chance to identify and eliminate forged drugs before they reach to the patient.
Method
This report is prepared from published materials collected over the internet and on web portals in the India. Further Google web hunt was conducted using seven keywords viz. 'spurious drug, spurious medicine, counterfeit drug, counterfeit medicine, fake drug, fake medicine, fake cosmetic' in combination with the year 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 and country name India. Up to 50 pages were searched under 'web' and 'news' section of Google. The search covered a period of four years data (2013-2016). This review contains SSFFC drugs incidence found in India as well as Indian SSFFC drugs which have been reported worldwide during four years (2013-2016).
Reports on SSFFC Drugs in India
(Table 1-5)
Table 1: SSFFC in year 2016.
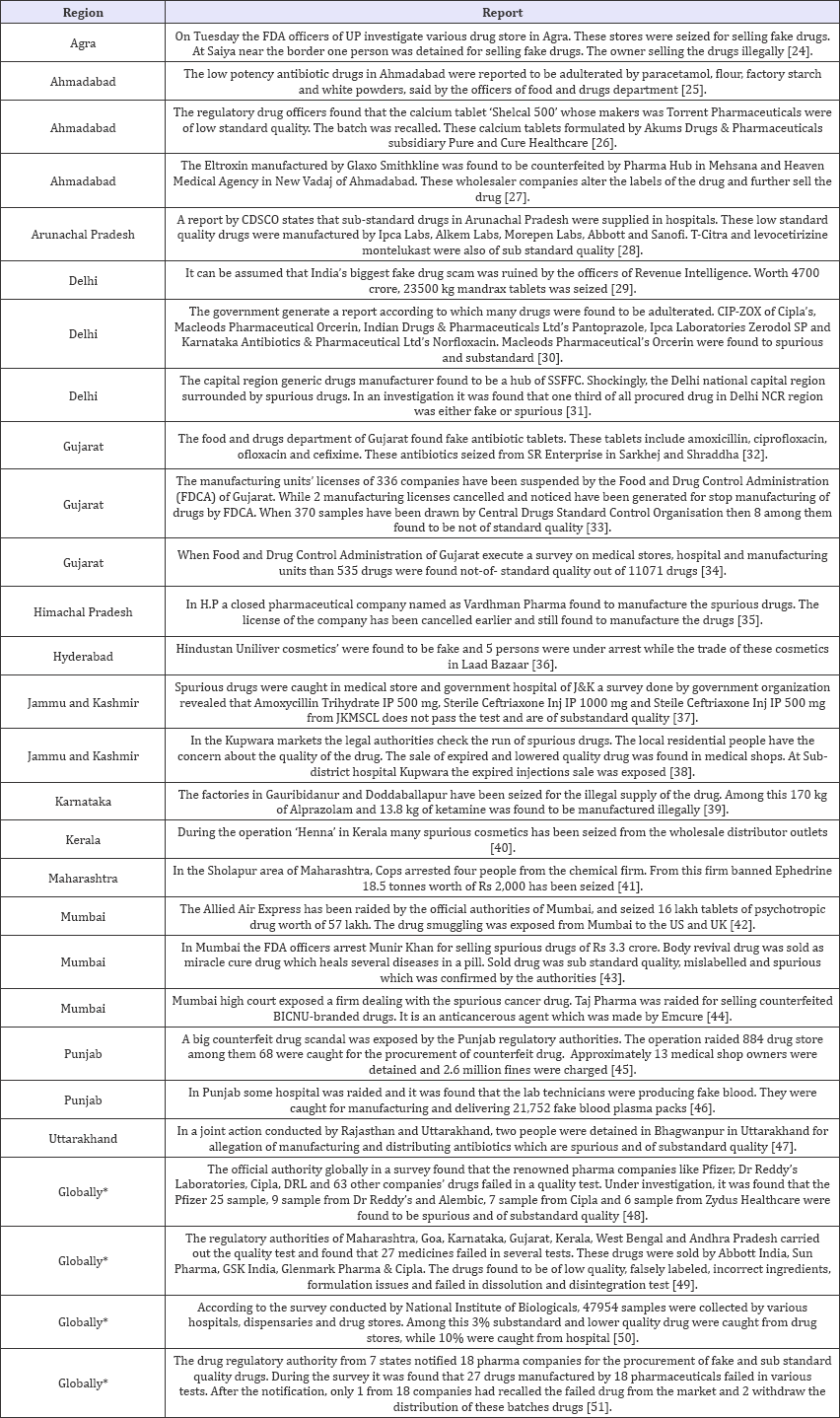
Table 2: SSFFC in year 2015.
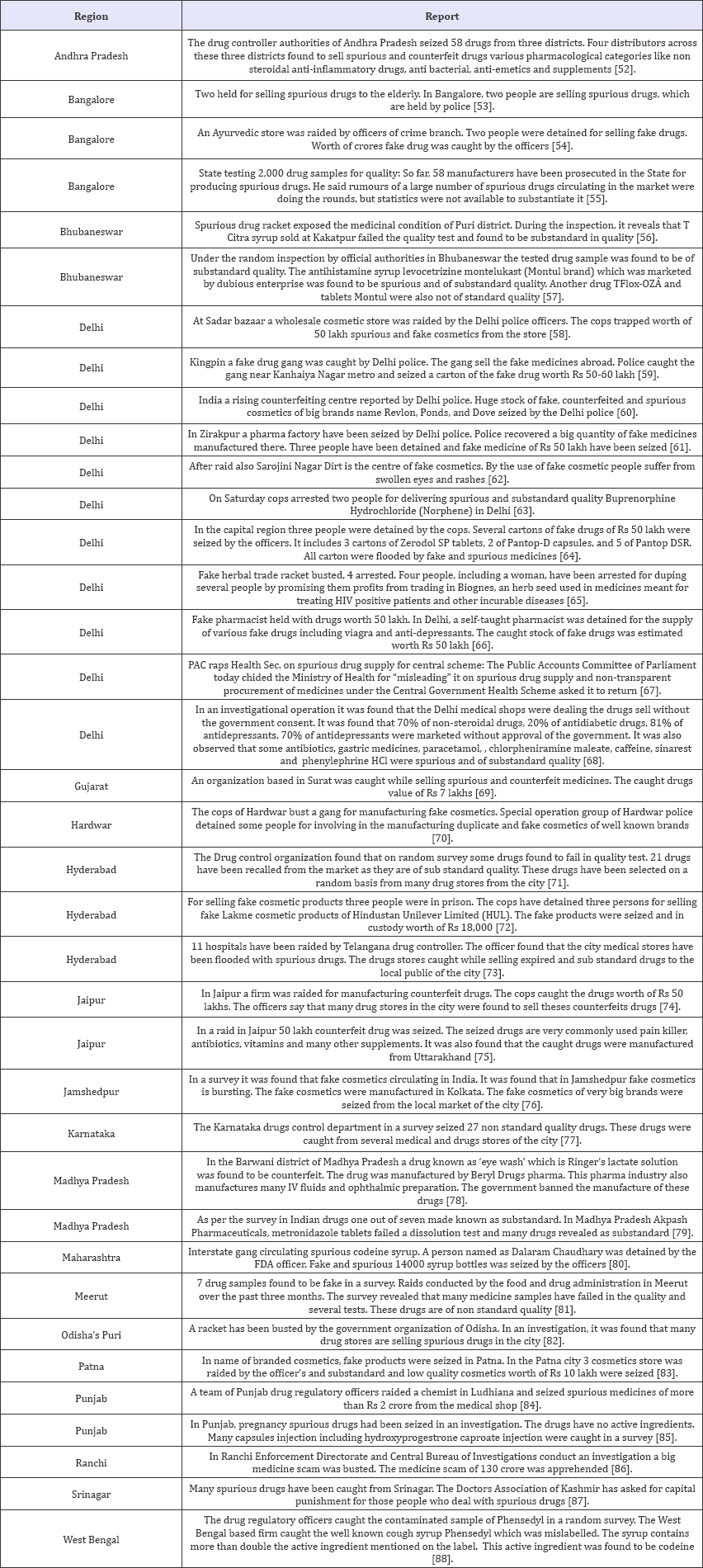
Table 3: SSFFC in year 2014.
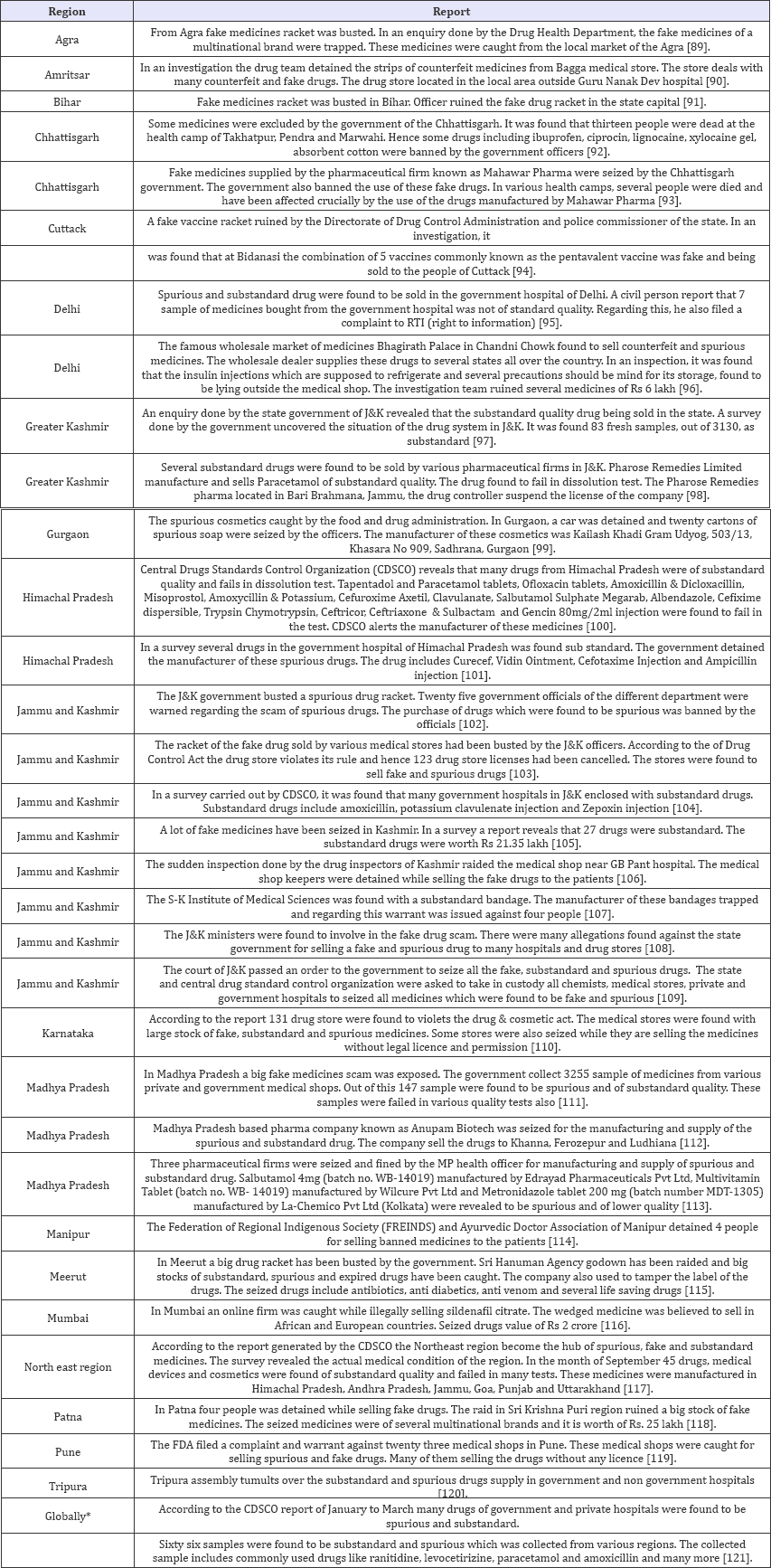
Table 4: SSFFC in year 2013.
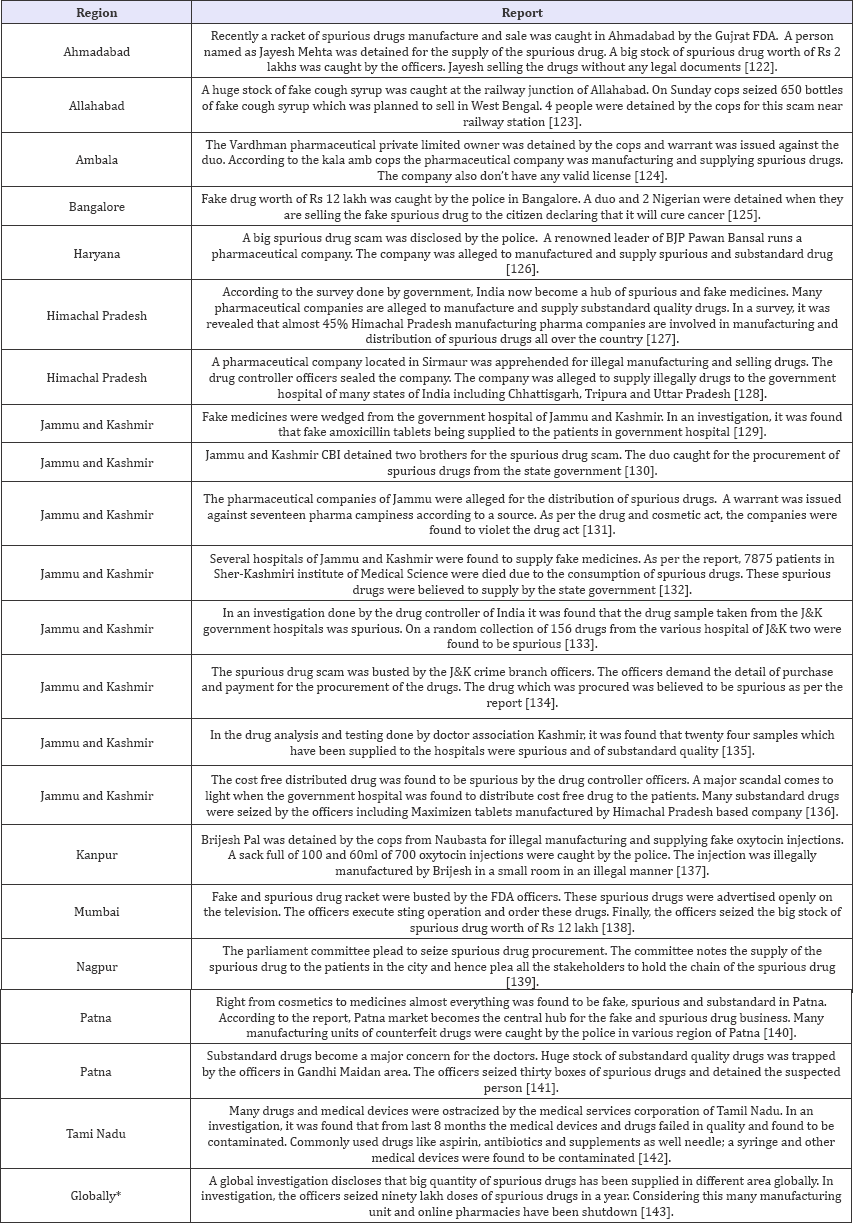
Table 5: SSFFC Indian report found world widely.
Overview
(Figure 1)
Figure 1: SSFFC incidence in 2013-2016.
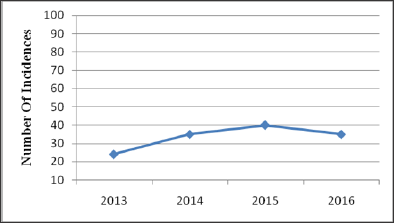
Figure 2: Region wise percentage of SSFFC in India.

Consequences of SSFFC
SSFFC drugs have several numbers of adverse effects, which not only affects the health but also the economic aspects of the society. It results in various difficulties for patients like treatment failure, end organ damage, toxicity and sometimes death also. Adverse effects caused by SSFFC causes unfaithfulness in the health care system. The name of the original medicine was ruined up and the company bears the loss. Some time pharmaceutical company faces financial crises as the products are being counterfeited and sold at a relatively cheaper price [158]. In some cases counterfeit products neither have active ingredients nor harmful, then does it not harm the patient health but it overdue the treatment process [159]. Whereas if the product has no active ingredient and harmful ingredients were present then it may result in mortality and morbidity [160]. If an inappropriate quantity of active ingredients were present then it either results into treatment failure or it may cause drug resistance. Consequential patient feel betray from the health care system. In return, it causes financial losses for patient, producers, traders and whole health care system. Eventually, it increases economic burden for the society [161].
Result
After observation of above data, it can be seen clearly that SSFFC has propagated all over the regions in India. Total 134 incidences have been reported from four years (2013-2016). In the year 2013, 22 and 2 reports within and outside India respectively have been observed. In the year 2014 within India 33 and outside India 2 report have been observed. Whereas the data enlarged in 2015 and 2016, includes 37; 28 reports in India and 3; 7 outside India respectively. Data revealed the alarming situation of SSFFC in India. In view of data, it is exposed that highest reports were from the North region (52%) which includes Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Punjab, Delhi, Jammu & Kashmir and Uttar Pradesh. Further observed reports cover East region (16%) Jharkhand, Bihar, West Bengal and Odisha. Remaining reports cover South region (13%) Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and West region (11%) includes Rajasthan, Maharashtra and Gujarat. In central region (8%) that is Madhya Pradesh & Chhattisgarh show the least incidence as per the data (Figure 2).
Conclusion
SSFFC drugs exceedingly affect the health of the society. This problem is the primary concern for all the health care professionals' worldwide. Frequently SSFFC reports have been noticed in India every year. Several classes of drug found to be spurious, including antibiotics, anti depressant, anti-histamics, anti-emetics, anti-cough and cold, anti-protozoal, anti-ulcers, pain killers, CNS stimulants, vaccines, vitamins, supplements and cosmetics. This is the time to aware the society against SSFFC more vigorously. Furthermore, research is essential to report SSFFC incidence to evade it in future. Medicines quality surveys are encouraged to avoid this conundrum of society. Various physical/chemical analysis and all the key initiatives and preventive measures should be considered to avoid substandard & counterfeit medicines. Mutual collaboration of all stakeholders required to achieve success against SSFFC. Through this we can anticipate the SSFFC free world.
References
- Caudron JM, Ford N, Henkens M, Mace C, Kiddle Monroe R, et al. (2008) Substandard medicines in resource-poor settings: a problem that can no longer be ignored. Trop Med Int Health 13(8): 1062-1072.
- Newton PN, Green MD, Fernandez FM (2010) Impact of poor-quality medicines in the 'developing' world. Trends Pharmacol Sci 31(3): 99
- Attaran A, Barry D, Basheer S, Bate R, Benton D, et al. (2012) How to achieve international action on falsified and substandard medicines. BMJ 345: e7381.
- Waller P (2001) Pharmacoepidemiology-a tool for public health. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 10(2): 165-172.
- Yankus W, Marks S (2009) Counterfeit drugs: coming to a pharmacy near you with an update for 2009. American Council on Science and Health, USA.
- Wertheimer AI, Norris J (2009) Safeguarding against substandard/ counterfeit drugs: mitigating a macroeconomic pandemic. Res Social Adm Pharm 5(1): 4-16.
- (1997) International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Associations. Counterfeiting of medicinal products, International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association, Switzerland.
- WHO (1999) Counterfeit drugs. Guidelines for the development of measures to combat counterfeit drugs.
- WHO, What are substandard medicines?
- Furnham A, Valgeirsson H (2007) The effect of life values and materialism on buying counterfeit products. The Journal of Socio-Economics 36(5): 677-685.
- Nayyar GML, Breman JG, Newton PN, Herrington J (2012) Poorquality antimalarial drugs in southeast Asia and sub saharan Africa. Lancet Infect Dis 12(6): 488-496.
- World Health Organization (2012) Medicines: spurious/falsely labeled/ falsified/counterfeit (SFFC) medicines, Switzerland.
- WHO (2014) General information on counterfeit medicines.
- Khan AN, Khar RK (2015) Current scenario of spurious and substandard medicines in India: a systematic review. Indian J Pharm Sci 77(1): 2-7.
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (2005) The drugs and cosmetics act and rules (Amendment), India.
- CDSCO (2008) Guidelines for taking action on samples of drugs declared spurious or not of standard quality in the light of enhanced penalties under The Drug and Cosmetic (Amendment) Act, pp. 1-13.
- Morris J, Philip S (2006) Counterfeit medicines in less developed countries.
- Murphy T (2014) Poison pills in your medicine cabinet: counterfeiters deliver deadly drugs.
- Cobert B (2011) Colbert's manual of drug safety and pharmacovigilance, (2nd edn), Jones & Bartlett Learning, USA.
- Gillette F (2013) Inside Pfizer's fight against counterfeit drugs. Bloomberg Business week, USA.
- Tim Murphy (2014) Opening statement before the subcommittee on oversight and investigations of the house committee on energy and commerce at the hearing on counterfeit drugs: fighting illegal supply chains.
- Coustasse A, Arvidson C, Rutsohn P (2010) Pharmaceutical counterfeiting and the RFID technology intervention. J Hosp Mark Public Relations 20(2): 100-115.
- Palmer E (2012) Drug shortages ease but remain serious problem. Fierce Pharma.
- Drive against fake drugs. Chemists' shops raided
- From flour to starch, fake antibiotic drugs have them all.
- Torrent pharmaceuticals.
- Racket in spurious drug unearthed.
- Indian government moves to tackle substandard drugs.
- India's 'biggest' drug racket busted, Bollywood producer nabbed.
- It's not only combiflam, more drugs under regulator's radar
- Need for policies and guidelines for diabetes management in public sector enterprises.
- Fake antibiotics worth Rs 51 lakh seized.
- Gujarat FDCA suspends licenses of 336 mfg units, cancels two mfg licenses for non-compliance to D&C Act.
- Gujarat FDCA detects 535 NSQ drugs in state 2016-17 as against last year's 365.
- Closed pharma unit found making drugs.
- Five held for selling fake cosmetic products.
- Vigilance raids in Jammu over sale of spurious drugs.
- Spurious' drugs flood Kupwara markets.
- City, outskirts becoming hub for manufacture of spurious drugs.
- Spurious cosmetics wreck Kerala beauty parlours, state launches operation henna.
- Banned drug Ephedrine worth Rs 2,000cr seized.
- DRI unearths Rs 57lakh drug smuggling racket; 8 held.
- FDA raids fake doctor's office, seized drugs worth Rs 3.3cr.
- HC hauls up firm exporting spurious cancer drugs.
- Counterfeit drugs: 884 medical stores raided in Punjab.
- Not just drugs, fake blood also running through Punjab's veins.
- Two arrested for making spurious drugs in Uttarakhand.
- Medicine! Pfizer, Cipla, DRL, other 63 drug firms fail quality test
- Drug regulation: 27 medicines sold by top firms 'fail' quality tests in seven states.
- Majority of the drugs found in India are either fake or ineffective.
- Official warns pharma units on spurious drugs.
- APDCA seizes spurious drugs worth Rs.5 lakhs from 3 districts in AP
- Two held for selling spurious drugs to the elderly
- Duo selling fake ayurveda drugs to senior citizens.
- State testing 2,000 drug samples for quality.
- 340 Routine check unearths spurious drugs racket.
- Drugs of fake firm found to be substandard, spurious.
- Fake cosmetics worth Rs 50lakh seized from Sadar Bazar, two held.
- Fake drug export racket busted; kingpin held.
- India police bust counterfeit "factory” for Revlon, Ponds, and Dove labels.
- Delhi cops raid Zirakpur factory, seize fake medicines, and arrest three.
- Dirt cheap and fake cosmetics.
- Two held for selling fake norphene injections in Delhi.
- 3 held with fake drugs worth Rs. 50lakh.
- Fake herbal trade racket busted, 4 arrested.
- Fake pharmacist held with drugs worth 50L.
- PAC raps Health Sec. on spurious drug supply for central scheme.
- City chemists selling common drugs without government approval.
- Spurious medicines worth Rs.7 lakhs were being sold.
- Haridwar cops bust gang making fake cosmetics.
- DCA recalls 21 spurious drugs.
- Three arrested for selling fake cosmetic products.
- Hyderabad: Telangana Drug Control Administration team raids 11 hospitals.
- Rs. 50lakh worth fake drugs seized.
- Counterfeit drugs worth Rs 50lakh seized in raid.
- Fake cosmetics circulating in India.
- Karnataka drugs control dept seizes 27 NSQ drugs.
- Congress demands criminal case against drug manufacturers over botched cataract surgery.
- 1 In 7 Indian drugs revealed as substandard.
- Interstate gang circulating spurious codeine syrup: Girish Bapat.
- 7 drug samples found to be fake.
- Odisha's fake medicine bust leads to inter-state racket.
- Fake cosmetics acting as top brands seized in India.
- A team of Punjab drug regulatory officers today raided a chemist.
- Spurious pregnancy drug being sold in state markets.
- Two caught in medicine scam net.
- Doctors seek death penalty for spurious drug dealers.
- Drug police asks abbott pharma to explain tainted cough syrup sample.
- Fake medicines supplied from Agra.
- Counterfeit medicines seized from three shops.
- Illegal, fake drug racket rocks Bihar assembly.
- Chhattisgarh government bans 4 medicines.
- Mahawar pharma medicines banned in Chhattisgarh following sterilisation deaths.
- Police get lead in fake vaccine case.
- Keep an eye out for spurious medicines.
- Business as usual after raid at Bhagirath Palace.
- 83 more drugs found substandard.
- 83 more drugs found substandard.
- FDA intercept car, seize 20 cartons of spurious cosmetics soap.
- 14 drugs made in Himachal Pradesh fail tests.
- Government orders drugs from 'dubious' companies.
- Spurious drugs: 25 government officials face action.
- Licenses of 134 drug shops suspended, fake drug seized in Kashmir
- Drugs in JK's government hospitals substandard, says CDSCO report.
- Kashmir's have consumed large stocks of fake medicines: DFCO.
- Spurious drugs sold outside GB Pant.
- SKIMS get sub-standard supply.
- J&K ministers involved in selling substandard drug in Kashmir
- Court asks Government to seize all identified drugs from market.
- 131 medical shops prosecuted for violating drugs act.
- Madhya Pradesh: 147 medicine samples in hospitals of inferior quality.
- 7 booked for selling false drugs. MP health dept slaps fine on 3 firms for supplying substandard drugs.
- MP health department slaps fine on 3 firms for supplying substandard drugs.
- Four held for selling spurious medicines.
- Drug racket had links with Meerut, Nepal.
- FDA busts online trade of Viagra.
- Northeast a dumping ground for inferior drugs.
- Fake drugs over Rs. 25lakh seized, four arrested.
- 23 chemists prosecuted, 4 convicted.
- Tripura assembly uproars on spurious drug issue.
- 66 drug samples found sub-standard.
- Guj FDCA busts racket in Ahmedabad selling spurious drugs of top brands.
- 650 bottles of fake cough syrup seized, four held.
- Spurious drugs case Hue and cry notice issued to Ambala couple.
- Bangalore couple, two Nigerians arrested for selling fake drugs.
- Bansal's kin makes spurious medicines.
- Major pharmaceutical firm under scrutiny for producing spurious drugs.
- Illegally operating drug factory sealed.
- Jammu and Kashmir government hospitals give away fake medicines to patients.
- Jammu and Kashmir drugs case: Two held.
- J&K drug control organization moves court against 17 Firms.
- Valley falls prey to deadly spurious drugs.
- 2 drugs found spurious in Jammu and Kashmir
- Spurious drug scam CB seeks details of purchases, payements 'urgently'.
- 24 more drugs found fake DAK.
- Sub standard drugs supplied to government hospitals seized.
- Manufacturer of fake oxytocin held.
- FDA sting traps makers of 'bogus' Drug.
- Parliament committee holds parleys on spurious drugs in markets.
- Fake cosmetics, medicines flood Patna Market.
- Inferior drugs disturb doctors.
- Tamil Nadu blacklists 25 substandard drug devices.
- Cracking down on spurious medicines.
- Alert! Fake Quinine sulphate in circulation.
- Fake Valium pills cause five deaths in one day as grieving families.
- Large haul of fake erectile stimulants seized.
- Around 35 percent of medicines imported into Guyana are fake and unsafe.
- Indian-made fake ED meds seized in Switzerland en route from Serbia.
- 'Viagra' factory feeding randy Brits' endless appetite for erection pills busted in Poland.
- Counterfeiting loopholes.
- ABC news investigation into counterfeit prescription drug operations in the US.
- US district judge Donetta Ambrose imposed that sentence.
- Record 'fake drugs' haul worth £16m by UK agency.
- Indian firm sues local medicine distributor over counterfeits.
- The Myanmar food and drug administration detected about 63 kinds of fake or unregistered medicine.
- Four Indian drug companies blacklisted.
- India made anti malaria drug banned in Ghana.
- Blackstone EA, Fuhr JP, Pociask S (2013) Intellectual property: facts and consumer opinions on counterfeit and pirated goods. American Consumer Institute, USA, pp. 1-28.
- Koczwara A, Dressman J (2017) Poor Quality and Counterfeit Drugs: a systematic assessment of prevalence and risks based on data published from 2007 to 2016. J Pharm Sci 106(10): 2921-2929.
- Jain SK (2006) The spurious drug menace and remedy. Health Administrator 19(1): 29-40.
- Love A, McIndoe S (2016) Counterfeit drugs and product serialisation- an overview of serialisation requirements. GMP Review 15(2): 9-11.
© 2018 Farah Iram, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






