- Submissions

Full Text
Intervention in Obesity & Diabetes
The Indian Fruit Phyllanthus Emblica (Amala) is an Immunity Enhancer and Anti-Obesity Agent: Prefect Fruit for Corona Era
Shallini Singh*
QSAR & Cheminformatics Laboratory, Department of Chemistry, India
*Corresponding author:Shallini Singh, QSAR & Cheminformatics Laboratory, Department of Chemistry, Bareilly College, Bareilly, India
Submission:November 08, 2021;Published: November 12, 2021

ISSN 2578-0263Volume5 Issue4
Opinion
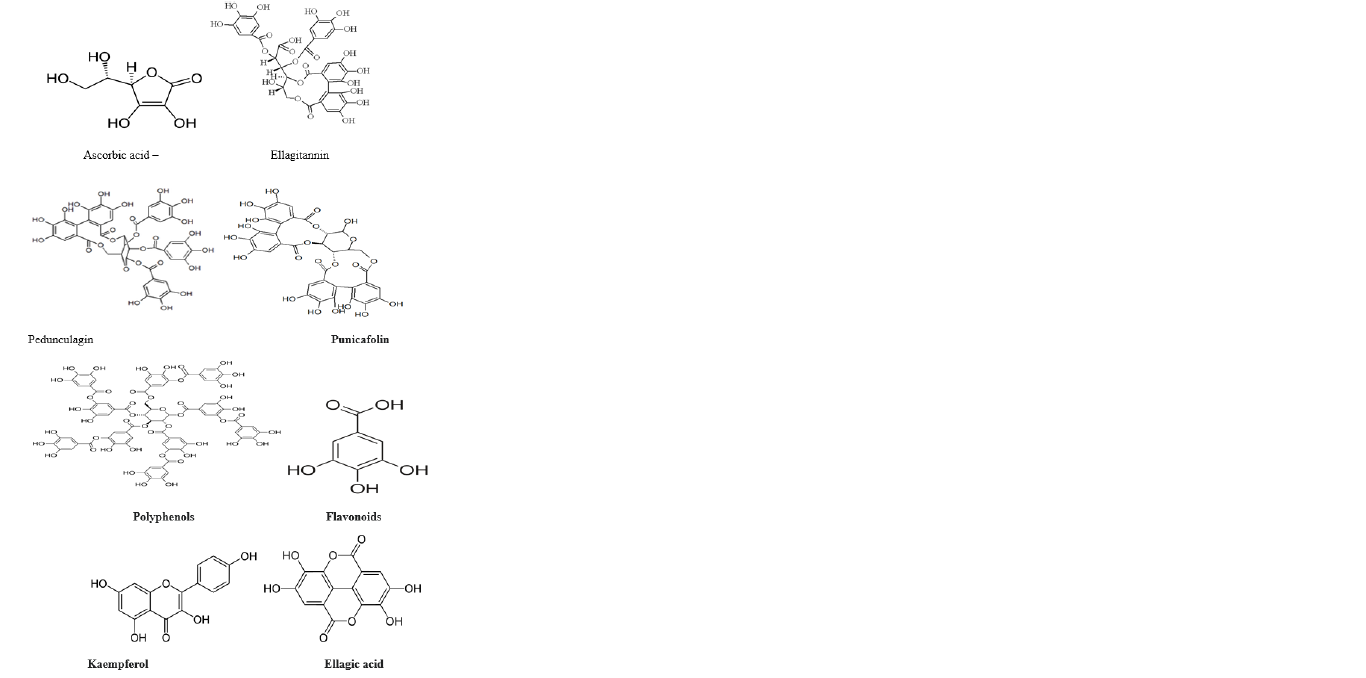
The Indian society has been reverent to nature since ancient times. We bow before mother nature like a God. We worship the sun which lights us up and illuminates the world and drives away all the darkness. We wake up in the morning, touch the earth because we get so much from it, necessary to support life. We worship Tulsi and Peepal because these give us oxygen for 24 hours and are also used in several Ayurvedic medicines. Phyllanthus embilica or Embelica officinalis, commonly known as Indian gooseberry or Amla has a superior therapeutic value in indigenous medicinal system, Ayurveda (Figure 1). The extracts from various parts of Embelica officinalis, especially fruit, contain various phytoconstituents like polyphenols (gallic acid, ellagic acid), different tannins, minerals, vitamins amino acids, fixed oils and flavonoids like rutin and quercetin. The extract or the powder of the fruit has curative effect against a variety of ailments like inflammation, cancer, osteoporosis, neurological disorders, hypertension and many others. These actions are attributed to either regulation of various molecular pathways involved in several pathophysiology or antioxidant property which prevents the damage of cellular compartments from oxidative stress. Amla keeps digestive system on right track and induces appetite. It strengthens the digestive system by converting calories in food stuffs into energy which has a direct bearing on obesity. The ingredients of Amla fight symptoms of fatty liver and high cholesterol and help reduce unwanted fat. Since ancient times, Amla (which is known as nectar fruit in India), is worshiped in India and it is said that 90% of the diseases of the body are cured by eating Amla in any of the forms viz. Morabba, Amla Candy, Chutney, Pickle etc. It is the main constituent of the general Ayurvedic tonic, Chyavanprash, a valued product of several Ayurvedic pharmacies. It is an important source of Vitamin C. Hence, its consumption in any form, stated above, mitigates risk of cold and cough and acts as an immunity booster. Given this benefit as a boon to man, the tree of Amla is regarded as sacred tree in India and is worshipped in our society since ancient times. Kartik Mahatmya and Vrit Kaunudi order the worship of this tree. Covid- 19 pandemic, vitamin C was the subject of more FDA warning letters than any other quack treatment for Covid-19 These fruits contain high amounts of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) [1]. Their bitter taste is attributed to high density of ellagitannins, [2] such as emblicanin A (37%), emblicanin B (33%), punigluconin (12%), and pedunculagin (14%) [3]. Amla also contains punicafolin and phyllanemblinin A, phyllanemblinin other polyphenols, such as flavonoids, kaempferol, ellagic acid and gallic acid (Figure 2).
Figure 1:Indian gooseberry: Amla.

Figure 2:Chemical structures of Ascorbic acid, Ellagitannin, Pedunculagin, Punicafolin, Polyphenols, Flavonoids, Kaempferol, Ellagic Acid.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an essential nutritional supplement for animals and human beings. Vitamin C activity in animals is observed due to several vitamins that come under the category of vitamin C. Some dietary supplements also encompass Ascorbate salts such as sodium ascorbate and calcium ascorbate. Vitamin C is made from simple sugars by nature. Many enzymatic reactions in animals and human beings occur with vitamin C as cofactor. Healing and repair of injured body parts and a variety of essential biological functions are mediated by those enzymatic reactions. In humans, vitamin C is a necessity for collagen synthesis and impairment of synthesis of this protein leads to scurvy. The symptoms of scurvy suffered by the 18th century sailors viz. loose teeth, sores and blisters were caused by their inability to synthesize collagen [3].
Ellagic acid
Ellagic acid is a polyphenol and a micronutrient found in many fruits and vegetables. Some foods contain a more complex version called ellagitannin which is converted to ellagic acid in the body. Ellagic acid is known for its antioxidant properties, meaning thereby that it removes toxins from the body and protects against harmful free radicals. Ellagitannins belong to a class of hydrolvazable tannins, and are esters of hexahydroxydiphenoic acid and monosaccharide, generally glucose. Ellagitannins are hydrolyzed in the digestive tract slowly releasing the ellagic acid molecule. Their chemical structure determines physical and chemical properties and the propensity of biological activity Kaempferol: (3,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) It is a natural flavanol, a class of flavonoids, found in many fruits and vegetables. This biologically active compound exhibits many pharmacological activities like antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, and anticancer activities.
References
- Tarwadi K, Agte V (2007) Antioxidant and micronutrient potential of common fruits available in the Indian subcontinent. Int J Food Sci Nutr 58(5): 341-349.
- Dharmananda S (2003) Emblic myrobalans (Amla). Institute of Traditional Medicine, Canada.
- Bhattacharya A, Chatterji A, Ghosal S, Bhattacharya SK (1999) Antioxidant activity of active tannoid principles of Emblica officinalis (amla): Indian J Exp Biol 37(7): 676-680.
© 2021 Shallini Singh. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






