- Submissions

Full Text
Investigations in Gynecology Research & Womens Health
A Study on Sildenafil Citrate in the Treatment of IUGR & Oligohydramnios
Jayati Nath*, Sarita Chaube, Neha Rani and Pahula Verma
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, India
*Corresponding author: Jayati Nath, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, India
Submission: October 10, 2020;Published: April 21, 2021

ISSN: 2577-2015 Volume4 Issue2
Abstract
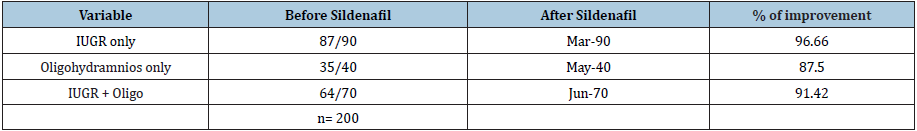
Intra Uterine Growth Restriction is a challenge to clinicians all over the world because no definitive treatment is available, and many empirical therapies are tried for treating the same. The present study was a multi-centric hospital based prospective observational study conducted in three tertiary care centers in Northern India on 200 patients with late onset IUGR and oligohydramnios. Sildenafil citrate 25mg 8 hourly was given till delivery. All the outcomes were noted and analyzed. After sildenafil therapy, 87 out 0f 90 patients with only IUGR, 35 out of 40 cases of oligohydramnios only and 64 out of 70 patients with IUGR & oligohydramnios both had marked improvement & 14 cases showed no improvement. From this study we concluded that adding sildenafil citrate in the treatment of IUGR and oligohydramnios can be a beneficial option.
Keywords: Intrauterine growth restriction; Oligohydramnios; Sildenafil citrate; Placental insufficiency
Abbreviations
IUGR: Intrauterine Growth Restriction; FGR: Fetal Growth Restriction; AC: Abdominal Circumference; AFI: Amniotic Fluid Index; BPP: Biophysical Profile; EFW: Estimated Fetal Weight; MCA: Middle Cerebral Artery; NST: Non-Stress Test; NICU: Neonatal Intensive Care Unit; USG: Ultrasonography
Introduction
Intrauterine Growth Restriction, also called Fetal Growth Restriction, still an enigmatic clinical entity with not many treatment options, is basically because of underlying placental insufficiency which often associated with oligohydramnios, which causes major perinatal morbidity and mortality [1,2]. In developing countries like ours, IUGR poses a big burden on the healthcare sector-accounting for approximately 50 percent of stillbirths & 10 percent of perinatal mortality [1-4]. It is also seen that the survival rate of very remote from term, severely growth restricted babies (< 28 weeks of gestation) is quite dismal [1,5,6]. The main underlying osteopathological process of IUGR is placental insufficiency, attributed to failure of adequate invasion by the placental trophoblasts & transform the spiral arterioles in the maternal placental vasculature in early pregnancy [1,7,8]. Sildenafil citrate, a type 5 Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor (PDE5) is a potent vasodilator which dilates the myometrial arterioles in women with pregnancies complicated with IUGR [1,9]. It also enhances the availability of amino acids important in the conception and fetal growth & thus can have positive impact on pregnancy with fetal growth restriction. In many studies with sildenafil in IUGR, the results have been encouraging as evidenced by better fetal abdominal circumference (AC), increased liquor volume and better Doppler changes with associated decreased NICU admissions and improvement in perinatal outcomes [1,10-12]. The present study was therefore embarked upon simultaneously in 3 different tertiary care centers of North India (2 in Haryana & 1 in UP) to evaluate the effectiveness of sildenafil citrate in treatment of early & late onset IUGR and oligohydramnios.
Materials & Methods
a) Study type: Multi-centric, hospital based, prospective, observational study.
b) Study population: Antenatal patients with IUGR (early & late onset) & Oligohydramnios
c) Study sample size: 200
d) Study period: October 2019 to September 2020
e) Study duration: One year
Inclusion criteria
a) Pregnant women with period of gestation 27-36 weeks with IUGR (early/late onset)
b) Ac and/or EFW<10th centile with/without Doppler changes
c) AFI < 5cm
Exclusion Criteria:
a) Patients with fetal congenital anomalies/ congenital infections
b) Known case of medical disorders eg chronic renal / cardiac diseases
All such antenatal patients fulfilling the inclusion & exclusion criteria were enrolled in the study with proper informed written consent & were given sildenafil citrate 25mg 8 hourlies till delivery with USG & Doppler color flow studies two weekly. All these patients were assessed regularly for weight gain, blood pressure, complete blood count, serum uric acid & creatinine, Liver function tests, albumin. Fetal assessment was done by Doppler USG, AFI, BPPevery two weeks & biweekly NST. Any side effects like headaches, indigestion, palpitations, facial skin flushing, photophobia, visual disturbance, hearing impairment were noted. In Doppler color flow studies, Uterine & Umbilical arteries, Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA), Ductus Venosus (DV) were studied for changes before & after administration of sildenafil citrate.
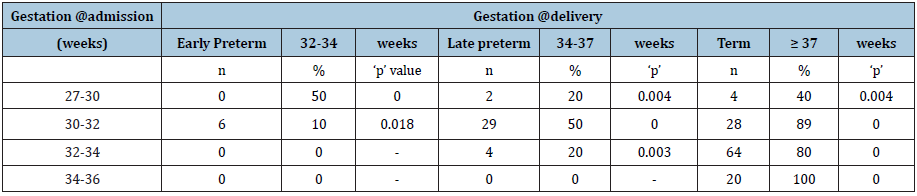
Amniotic Fluid volume (AFI) & Abdominal Circumference (AC) were assessed 2 weeklies to monitor fetal growth. At delivery, mode and gestation at delivery, birth weight, APGAR score, liquor color (meconium) & NICU admission & duration of stay was noted (Table 1).
Table 1:The demographic and general characteristics of groups.
Statistical analysis
All the relevant data were entered into MS Excel-2007 & analyzed using SPSS version 20.0 software. Interpretation of the data was done with the help of Chi- square test (ꭓ2 test) & period student ‘t’ test to compare continuous variables. A ‘p’ value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant (Table 2);[13].
Table 2: Result with sildenafil citrate.
Results & Observations
Discussion
No specific full proof therapy is available for pregnancy with
severe early-onset IUGR. There are 2 ways of going about once the
diagnosis is made-(a) Expectant management including maternal
lifestyle modification & fetomaternal surveillance & (b) Termination
of pregnancy. In our study we observed significant improvement
in the fetal outcome in terms of gestational age at delivery, birth
weight, APGAR Score with sildenafil citrate treatment. Premlatha
et al. [14] in their study from Karnataka, found similar results with
2 stillbirths, with improved perinatal outcomes and reduced NICU
admissions. Von Daldeszen (Canada) reported mean gestational
age at delivery at 25+ 6 weeks in the control group as opposite to
27+6 weeks in the sildenafil group with increased AC growth (OR
12.9; 95 % CI) [1,9].
A study from Chhattisgarh showed improved Ac in 70%
of treated group with sildenafil citrate [1,15]. Panda et al. [15]
reported marked improvement in the doppler blood flow indices
and better pregnancy outcomes with sildenafil citrate [1,16].
Ferreira et al. [17] from Canada used 20mg sildenafil citrate in
severe IUGR pregnancies at average 25+3 weeks gestation until
delivery, with average weight gain at birth by 249 grams (558gm
versus 807 grams) [1,17].
Conclusion
From our study we have gathered empirical evidence that sildenafil citrate which causes vasodilatation of the myometrial arteries in IUGR, increases utero-placental blood flow and potentiates fetal growth, can offer a promising therapeutic intervention in pregnancies complicated with early onset severe IUGR and oligohydramnios.
References
- Joshi P (2019) Role of sildenafil in Fetal Growth Restriction from N, India. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol 8: 165-168.
- Sharma MS, Sharma D (2014) Intrauterine growth retardation-A Review article. J Neonatal Biol 3(135): 167-897.
- Froen JF, Gardosi JO, Thurmann A, Francis A, Pedersen BS (2004) Restricted fetal growth in sudden intrauterine unexplained death. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 83(9): 801-807.
- Richardus JH, Graafmans WC, Vanhorick SPV, Mackenbach JP (2003) Differences in perinatal mortality and suboptimal care between 10 European regions. BJOG 110(2): 97-105.
- Peterson SG, Wong SF, Urs P, Gray PH, Gardener GJ (2009) Early onset, severe FGR with absent or reversed end-diastolic flow velocity waveform in the umbilical artery: perinatal and long-term outcomes. Aust NZ Obstet Gynecol 49(1): 45-51.
- Bilardo CM, Wolf H, Stigter RH, Ville Y, Baez E, et al. (2014) Relationship between monitoring parameters and perinatal outcome in severe, early intrauterine growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 23(2): 119-125.
- Olofsson P, Laurini RN, Marsál K (2003) A high uterine artery pulsatility index reflects a defective development of placental bed spiral arteries in hypertension and FGR. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 49(3): 161-168.
- Sagol S, Sağol O, Özdemir N (2002) Placental villus vascularizatio and its relation to umbilical artery Doppler flow in IUGR. Prenat Diagn 22(5): 398-403.
- Von D, Dwinnell S, Magee LA, Carleton BC, Gruslin A, et al. (2011) Sildenafil citrate therapy for severe early‐onset intrauterine growth restriction. BJOG Int J Obstet Gynecol 118(5): 624-628.
- Dastjerdi MV, Hosseini S, Bayani L (2012) Sildenafil citrate and uteroplacental perfusion in FGR. J Res Med Sci 17(7): 632-636.
- Dunn L, Greer R, Flenady V, Kumar S (2017) Sildenafil in pregnancy: A systematic review of maternal tolerance and obstetric and perinatal outcomes. Fet Diagnos Ther 41(2): 81-88.
- Miller SL, Loose JM, Jenkin G, Wallace EM (2009) The effects of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) on uterine blood flow and wellbeing in the intrauterine growth-restricted fetus. Am J Obstet Gynecol 200(1): 102el-102e7.
- Maged M, Wageh A, Shams M, Elmetwally A (2018) Use of sildenafil citrate in cases of IUGR; a prospective trial. Taiwanese J Obstet Gynecol 57(4): 483-486.
- Premlatha HL, Raghupathi KMS, Srinivas DNB, Kanth VL (2016) Study of effect of sildenafil citrate in pregnant women with IUGR. Int J Reprod obstet Gynecol 5(9): 3094-3097.
- Singh A, Daharwal A, Kujur A, Awasthi P (2017) Effect of sildenafil citrate on IUGR. Int J Reprod Contracept Gynecol 6(5): 1806-1809.
- Panda S, Das A, Nowroz MH (2014) Sildenafil citrate in FGR. J Reprod Infertil 15(3): 168-169.
- Ferreira E (2016) Sildenafil use during pregnancy for severe IUGR :A case series and review of literature. J Obstet Gynecol 38(5): 486-488.
© 2021 Jayati Nath. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






