- Submissions

Full Text
Integrative Journal of Conference Proceedings
Smart Museum for Nepal Cultural Heritage Information Exchange System
Sharma G1* and Gurung RC2
1Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nepal
2Islington College, Nepal
*Corresponding author: Gajendra Sharma, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, School of Engineering, Kathmandu University, Nepal
Submission: November 27, 2019;Published: January 07, 2020

Volume2 Issue1January, 2020
Abstract
Smart Museum is a study focus on Nepal Cultural Heritage information exchange system. The main objective is to provide innovative and interactive approaches which could enhance visitors experience in the museum. Its concept is based upon smart museum that is integrating digital museum contents with information exchange by using Near Field Communication (NFC) smart tags and Quick Response (QR) code. Visitors can use their smart phone to get detail information without help of anyone. The study focuses on detail research about short distance communication network that includes NFC and QR code as of RFID technologies. Back-end system is used for providing detail information of artefacts and preservation of museum in the digital format. Mobile Software Development Life Cycle (MSDLC) was chosen for the development of the application. It was used for its development criteria covered all the aspects. The study requirements were straight forward where many factories were not much changed. MSDLC was found shorter life cycle since mobile applications needs to develop in rapid due to the market competition. Most of the museums were found under-developed as per the requirements. The direct museums visited done were found also interested on the upgrading the museum services however lack of the proper management leaded to not able to do so.
Keywords: Smart museum; Cultural heritage; Information exchange system; Cultural heritage; Communication network; Nepal
Contribution/Originality
This study contributes in the existing literature on information exchange systems in smart museum that has significance in information systems development. This study uses new estimation methodology on Mobile Software Development Life Cycle (MSDLC) which was chosen for the development of the application. It was used for its development criteria covered all the aspects. This study originates new formula on information exchange system on smart museum. This study is one of very few studies which have investigated that MSDLC was found shorter life cycle since mobile applications needs to develop in rapid due to the market competition. The paper contributes the first logical analysis that direct museums visited done were found interesting on the upgrading the museum services. The paper’s primary contribution is that the complete backend new system should be web-based with interfaces saving to host within premises. Administrator and Staffs should follow Museum privacy and information providing policies. The new system should embrace client-serverbased architecture. This study documents that the research primarily performed for the study of the Nepal Museums and prototype development of the application. The development of the application is done as android mobile application as front-end application whereas back-end application for management of the digital information.
Introduction
Smart Museum is a Research and Development study focus on Nepal Cultural heritage information exchange system. Nepal is a landlocked country with rich culture, ecological diversity and traditions. In the caste system of Nepal, four main groups (Varnas) divided which are Brahmin, Kshatriya, Vaishya and Sudra. It is subdivided into thirty-six castes from four main groups where each caste has own language, tradition and culture [1]. Museum plays a vital role in the preservation and showcase of the scientific, artistic, historical or cultural interest. Museum benefit communities, tourism, education, preserving past and economic benefits [2]. The main objective of this study is to provide innovative and interactive approaches which could enhance visitors experience in the museum. It will integrate digital museum contents with contactless information exchange by using Near Field Communication (NFC) smart tags and Quick Response (QR) code. Visitors will get more information by using smart phone. The study focuses on detail research about short distance communication network that mainly includes RFID technologies which primarily focuses on the NFC and QR code. Another important part is understanding and find information about current situation of MUSEUMS in Nepal.
The main problem in Nepal about Museum is lack of the awareness about Museum and heritage preservation and also visiting Museum trend. In Japan, recently Tokyo museum exhibits Issey Miyake’s Constant innovations about fashion which have motivated on the people to visit museum [3]. In Nepal, Museum is not established with innovative but provide basic artefacts and exhibit it to the people. Museum plays a vital role in the preservation and conservation of the Nepalese culture and heritages. It helps in creating awareness and education for future generations. There are only handful museums in the Nepal and most of them are centralized in the capital city. Smart museum aids for improving visitors experience by using interactive and innovative approach. Visitors could interact with objects to get more information. Main theory behind of smart museum is as of “The Internet of Things”. The Internet of Things defines a vision in which the Internet extends into the real world embracing everyday objects. Physical items are no longer disconnected from the virtual world but can be controlled remotely and can act as physical access points to Internet services. Smart museum is new innovative and interactive learning not just looking at objects but interactive with objects in the museum. The Internet of Things (IoT) as a concept that helps in gathering information as a real time where different sensors, software, database and cameras are used and share information through use of the Internet [4]. This study includes development of the frontend and back-end application that helps to centralized management of the propriety museum information and localization. Design and coding of NFC and QR code smart tags for storing information that will redirect to server systems. The study can lead to development of the Nepal Museums. It has many scopes possibilities for real time implementation and usages. Master study is limited to certain scope due to the time and criteria factors of the master program. In the system enhancement, it includes adding more functionalities like membership of the guest, indoor map coordination, digital floor map, quiz play and events push notification and possibilities of gift sales through Internet services [5]. Beside this, Museum needs to have promotion and marketing strategies to boost number of the visitors and proper management of the galleries and sections.
Literature Review
Nepal museums
Museum plays a vital role in the preservation and conservation of the Nepalese culture and heritages. It helps in creating awareness and education for future generations. There are only handful museums in the Nepal and most of them are centralized in the capital city. In Table 1, popular museums in Nepal are shown which are located in different regions. The first museum of Nepal as the National Museum was opened to general public on February 12, 1929 AD. which is located in the Kathmandu. It includes art gallery, Buddhist art gallery and history section. King Jaya Verma oldest stone statue approximately 185 AD. can be found in the National Museum. Among museums, most famous are the National Art Gallery, the Pujari Math Museum, Chikanfa Math Museum, and the Museum of Syayambhu Bikas Mandal [6].
Table 1: Popular Museums in Nepal [6].
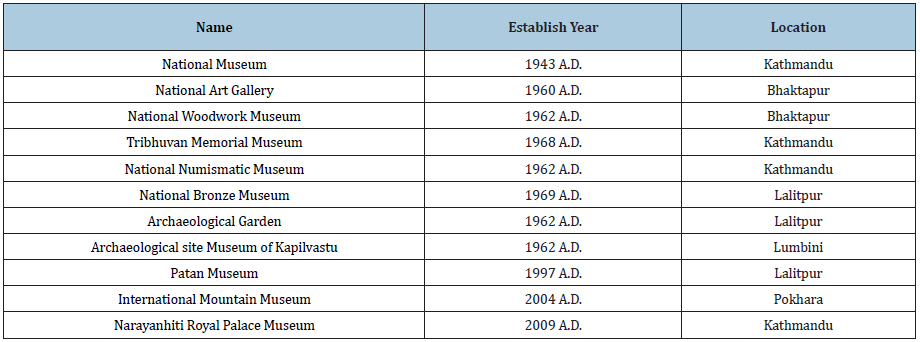
The internet of things (IoT)
IoT develop as a study of the Internet extension service to focus on the real time interaction with everyday objects. It depicts integration of the Internet, RFID, smart objects and wireless sensor networks to develop useful real time information. Not only information but also interact with the smart objects which can accept inputs as command or “Smart” objects are embedded communication and information technology which will act as intermediate devices to communicate between things, people and the Internet. As per this paper, the term “Internet of Things” was used at the work of the Auto-ID Centre at MIT in 1999 to design and propagate a cross-company RFID infrastructure. Figure 1 illustrates that IoT is not only a single component to work but combination of complementary technical technologies. It will integrate all individual system to work together. It will help in filling of gap between real world object and virtual systems. Smart Museum concept is part of the IoT in which smart objects are used for tagging information to identify the objects and visitors could get correct information from system. It will include interaction with smart objects, networks and systems.
Figure 1: IoT illustrate as Network of Networks.
Radio frequency identification (RFID)
It is evolving technology that has been used in application areas such as medical, transportation, businesses, offices and many more. It uses small transponders or as physical objects which is attached to necessary objects. RFID transceivers or readers are used to get necessary information with linked objects tagged. It is mainly used by wireless communication. RFID system is mainly used for automatic identification system such as product codes integration, physical access with proximity cards and payment mode with contact-less method.
Near field communication (NFC): NFC is subset of the RFID that uses wireless communication which operates high frequency of 13.56MHz and have close proximity distance to work. It is a shortrange wireless technology that helps mobile NFC chips inclusion devices to actively work together with other mobile devices or any passive NFC tags. As per “Introduction to NFC” paper presented by Forum Nokia, NFC is next short wireless communication network that helps users to share information with real world with touch or close together enough to share. It is defining as open-platform technology which is standardize by the NFC forum.
QR (Quick Response) code: It is another popular way of sharing information two-dimensional barcode system. Quick Response (QR) technology can be read by any smart phone over any phones with a camera and application to decode information. It can provide information such as URLs, Cards, maps location tag, and profile information [7]. In this research, NFC and QR code was used for the intermediate communication method so that not enabled NFC mobile devices also can be used for interacting with Smart Museum system. Bigger companies like PayPal, Google, Apple and Samsung have started to accept NFC technology for mode of payments.
a. Active mode: In the active mode, both devices can create own Radio Frequency field that will help in the two-way communication. Devices will need own power to generate RF field. Devices will not active during the making for data transfer.
Security context: NFC transmissions present security issues which needs to be study in depth while recognizing the technology. In the security context, NFC defines possibility of the security vulnerabilities of eavesdropping, data corruption and manipulation, interception attacks and Theft [8]. Whole confidence from side to side security matters in NFC transmissions illustrates that this is a stuff which is still reviewed presently. Attacks have at present been predictable and exposed by Collin Mulliner, “Attacking NFC Mobile Phones”, May 2008; an instance of an attack might be the try to make a phone crash by altering the content of a tag that it is working to be read by it. An attacker substitutes the content of an NFC tag and adds with the value 0xFFFFFFFF in the length field of an NDEFRecord, the devices would crash in any case. Continuous of four crashes in a row, the phone will switch off itself. Many companies are evolving new protocols to make the transmissions safer which includes payment system and digital money or wallet application.
NFC vs. Bluetooth: Although NFC and Bluetooth have nearly common features, they are complementary technologies. Both technologies are short wave or range communication, nevertheless Bluetooth has a longer range than NFC. On the other hand, it is more complex to set-up the arduous Bluetooth connection, as the existing technology involves frequent processes before transferring data i.e. configuring the Bluetooth functionality turned on, examining for new devices [9]. In the meantime, NFC technology marks the procedure very much simple by activating the transfer process by an ordinary with a touch of the mobile phones. NFC needs shorter setup time with comparison to the Bluetooth. So, a connection between two NFC devices was recognized around one tenth of a second. The data transfer rate is slower in NFC (848Kbps) while associated to Bluetooth (2.1Mbps). NFC is greatly appropriate for busy areas wherever connectivity through Bluetooth is much difficult and connections with the partner devices can be established even in switched off conditions which can be contactless smart cards. Therefore, NFC can be charity to set-up a Bluetooth connection [10].
NFC tags: An NFC tag is a passive device that can store data and can be read by an NFC-enabled device. The tags can be used within applications like smart posters and other areas in which small volumes of data can be stored and transferred towards active NFC devices. Within the smart poster, the aware area can be used by touch point for the activation of the NFC device. The stored data on the NFC tag may comprise any form of data, however common applications are for storage URLs from NFC device that may discover additional data. NFC tags are passive devices with low power. An NFC tag is consequently used when a user touches an NFC enabled device onto this tag. Consequently, a small quantity of power is occupied by the NFC tag from the reader/writer to power the tag electronics and the tag is then enabled to transferrable information to the reader/writer. Finally, the data kept in the tag memory is transferred to the NFC enabled device.
N-MARK: NFC forum is introduced by the N-Mark. It contains in a formalised ‘N’ that is considered to enable consumers with NFC phones to quickly and easily spot embedded NFC tags. The N-Mark is universal in possibility and is accessible for use in applications that are acquiescent with the NFC Forum’s NDEF description and where the tags used meet the NFC Forum Type 1/2/3/4 Tag Operation specifications. Within a year, the NFC Forum will also be presenting a second logo, the Certification Mark, which will be used to recognise devices that meet NFC Forum device provisions and have passed a determined certification process.
NFC now-a-days: The uses and applications of NFC are limitless, and many moving ideas are in development now. Currently, many cities have already tested pilot applications of NFC technology. NFC usages are properly used and following are examples of successful implementation:
A. Electronic ticketing and access to Manchester City Football
Club Stadium, in Manchester (United Kingdom), 2006.
B. Ticketing application for public transport in Berlin, 2007.
C. Payment, parking and tourism applications were
confirmed in Caen (France), 2005.
D. NFC equipped soft drink vending machines in Japan, 2006.
E. Lecture halls, laboratories and garage, payments in the
cafeterias and at vending machines in the University of Applied
Sciences campus, in Hagenberg (Austria), 2006.
NFC in the future: It is foreseen that in a span of 2 to 4 years, around twenty percent of all mobile phones be NFC-equipped, which suggests that several hundred million NFC-enabled phones and devices will be deployed worldwide by 2020, and over 700 million phones will use NFC services. NFC market was treasured at $3.2 billion in 2014 and is predictable to grow at a CAGR of 40.4% during the prediction period (2015-2020), to reach $24.0 billion by 2020. The world near field communication market has showed moderate development throughout the past few years; nevertheless, it is studied to unveil healthy growth during the forecast period.
Methodology
Today, mobile users devote 80% of mobile period in spending all types of apps. In this situation, mobile app developer focus on popularity own apps in the general public even though producing good amount of money at the same time. It is fairly challenging for the developers to grow their app hit in the app stores in the top charts [11]. Accomplishing anticipated success requires one to take detailed thoughtful of how mobile apps are developed in the proper way. Each mobile application is developed and designed for best development strategy in the mind. In this study Waterfall methodology was used. This study follows waterfall model. The waterfall model is a non-iterative, linear sequential design approach for software development, in which progress flows in one direction downwards similar to waterfall through the phases of conception, initiation, analysis, design, construction, testing, deployment and maintenance. The waterfall development model originated in the construction and manufacturing industries: highly structured physical environments in which after-the-fact changes are impossible or expensive. In the same time, it was adopted for software development, there were no recognized alternatives for knowledge-based creative work [12]
Mobile software development life cycle
Since the product to be developed is based on the Android Application, the Mobile Software Development Life Cycle (MSDLC) has also to be taken into serious consideration. A full-fledged Mobile App development requires rigorous up-front design, usability testing, QA design and finally deployment into play store or company specified terminals. The proposed MSDLC methodology is directly derived from the traditional SDLC (Waterfall).
Development
The main software development method includes requirement
analysis which produce list of the requirement for the study to
archive. There are few assumptions to be done when incurring the
study prospective that visitors will use moderated smartphone
and any services required by application are run by the users. The
Smart Museum feature includes:
a. NFC Scan: It helps visitor to scan interested artefacts to
get more information. It will connect to the Museum Wi-Fi network
to get information to display on the mobile.
b. QR Scan: It is ambitious feature that will help user to get
information about the artefacts that will connect to Museum Wi-
Fi network. Through Museum server information as per request
on the bases of the QR unique code it will get that identified code
information.
c. Museum Location: It helps visitors to get particular
location of the Museums through google map. Visitors can get
pinpoint location and also get direction help from current location.
d. Museum Information: It is the unique feature that user
can get more information of the various museums. It helps to get
information about opening of the museums and contact information.
e. Help Menu: It includes how application can be used and
help if any problem during the applications usages will encounter.
Resources Needed and Architecture
For study completion, following resources was needed Table 2.
Security of study and confidentiality
Information was maintained confidentiality by using authentication and authorization mechanism. The proprietary information of individual information was protected where visitors can get information only when scanning smart tags and it was not accessed outside the premises. Encryption mechanism such as Secure Socket layer (SSL) was used to protect communication between visitors mobile and servers.
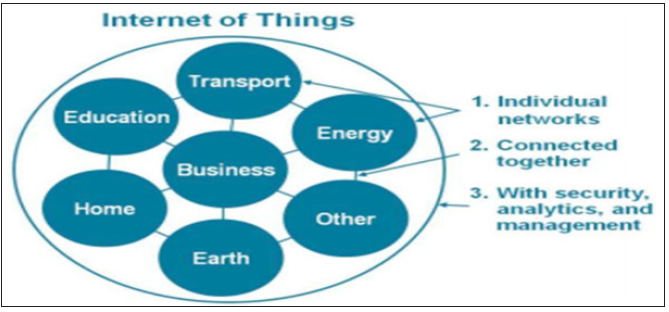
Hardware architecture diagram
In the hardware architecture, hardware required include server, Wi-Fi network, Smart Phone and NFC/QR code. As per Figure 2, in the first step, user will scan the Smart objects through mobile apps. Mobile apps get unique code from Smart Object. In the second step, it will transmit the request through Wi-Fi. As in the third step, it will request the server through URL. In the fourth step, server will transmit the information and display in the mobile application.
Table 2:

Figure 2: Hardware architecture [6].
Software / Information architecture
In the software architecture, information flow occurs from mobile user apps to server respond. Smart objects unique code that was compared with the server information stored. It uses Wi-Fi network as a network media through which user and server will interact with each other.
atabase design-relationship scheme Th
e backend-application that was developed uses database which includes different tables and bridging tables. The backendapplication includes country, address, user, user group, review, object related, member, object, category, quiz, category description, answer, answer option and question tables. Category is main table which includes record of the different section in the museum which can be art gallery, history section and so on. Likewise, object includes individual artefacts that will be tag with smart object. Quiz includes question, answer and answer option that will be used for quiz features. Members are the admin and staff with personal information.
Android app UI/UX design
Enhanced for the mobile efficiently learn the most significant design techniques that will assistance them make superior apps. App User Interface (UI) is important part for the development which includes layouts of the application. It helps in designing icons and options placement that needs to user friendly and quick access. Whereas App User experience (UX) defines how user will interact with the application. The splash screen includes picture and text that will help loading time of the application to sync. It helps mobile apps to briefly introduce mobile app and reduce wait time before application launch.
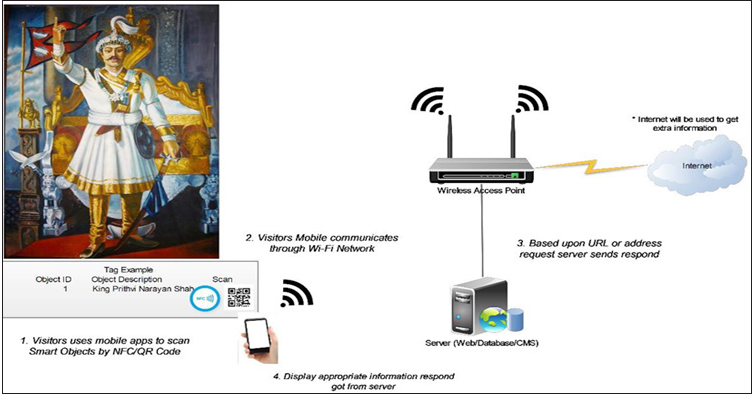
Back-end application
This application is coded on PHP and MySQL Database. Following Pictures are backend functions of the application. This page is for login that will require authentication. With proper authentication user, it will open main page of the back-end application. The page displays main page that includes option of the Cate-log, members, quiz, users and language localization. Figure 3 illustrates the museum objects that have recorded. It plays main role for the smart museum. Each artefact is recorded to the objects which include various information to display on the mobile apps. The figure highlights how we can add detail information about the objects. It includes NDEF code, QR code, Object URL, Youtube Link and images. We can add detail information of the objects that will be display on the mobile apps as a description. It creates users that for staffs management for the smart museum.
Figure 3: Museums Objects that includes artefacts based upon the categories [2].
Mobile application screenshot
The user interface is separated into functional layout activities which includes main screen, NFC Scan screen, QR Scan screen, Location screen, Museum information screen, help screen and about screen. The main layout is based upon the grid layout of the android that helps to quickly access menu by selecting each option. The layout of each section is using linear layout, relative layout and list layout.
I. Android permissions: It is set in manifest file of the android study which includes accessing location by GPS or Wi- Fi network i.e. used by museum map, Internet permission for accessing network based servers, NFC permission for any hardware available for NFC scan and camera access permission used for QR code scan.
Test Plan
a. Test plan (Table 3)
b. Test result (Table 4)
Table 3:
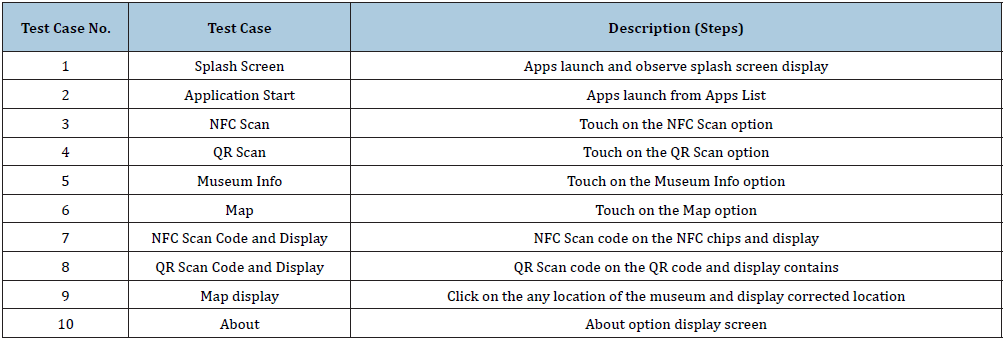
Table 4:
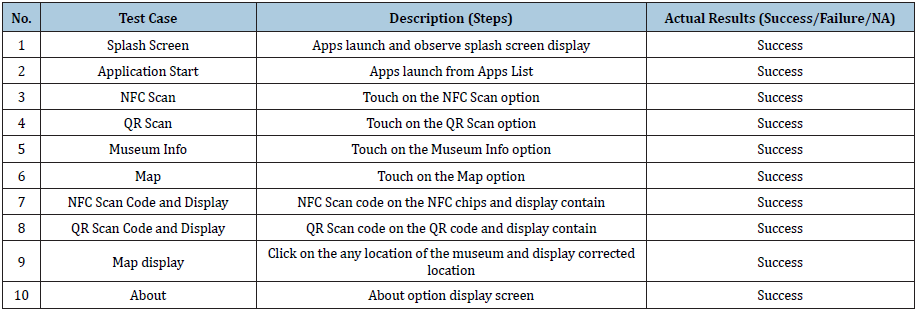
Analysis
Requirement analysis
It is to find out and capture explicit set of requirements of the Smart Museum. The collected requirements will be conveyed in the System Requirements Specification (SRS) document. In order to gather the data and requirements numerous fact-finding methods have been used. The SRS document will consist of the list of necessities characterized under Functional, Non-Functional and usability necessities. Enquiry contains renovating a problem description out of a problem domain which is an unclear set of facts, data and even misapprehensions, into a cooperative and intelligible declaration of the system’s requirements. Since it involves alteration, which always is a problematic task, mobile application takes this stage as one of the most dangerous and period overwhelming step.
Plan of action for requirements analysis: Since requirements Analysis is a critical task, the analyst has prearranged it consequently, giving adequate time and incomes to it. In this section, the same plan is put forth. The strategy consists of the major fact-finding methods contained and the set of necessities produced out of it.
Use case diagram for smart museum: Figure 4 shows Use Case Diagram for confinement of the dynamic feature of Smart Museum system. It helps in gathering system requirements which include internal and external influences. Mainly it includes administrator of the system and visitors. It is focused on the design aspect of the system (Table 5 & 6). It will assist in Museum system analysis with use cases and actors that will be involved in the system operation. Following are the main objectives for selecting Use Case:
Table 5:
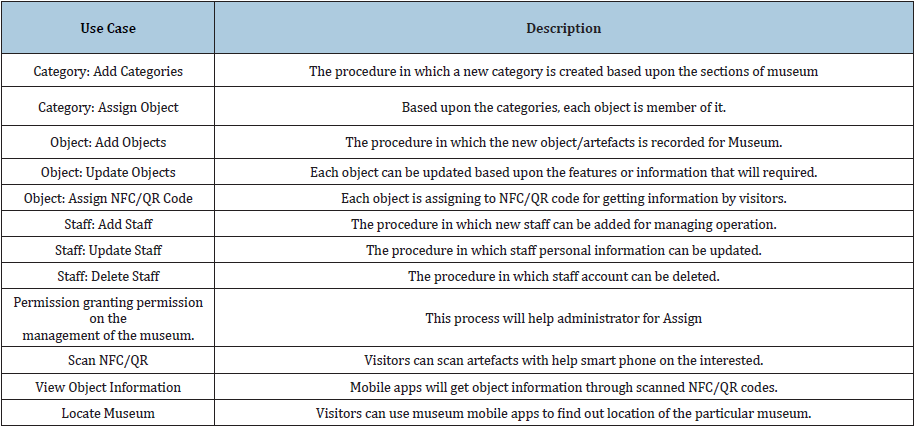
Table 6:
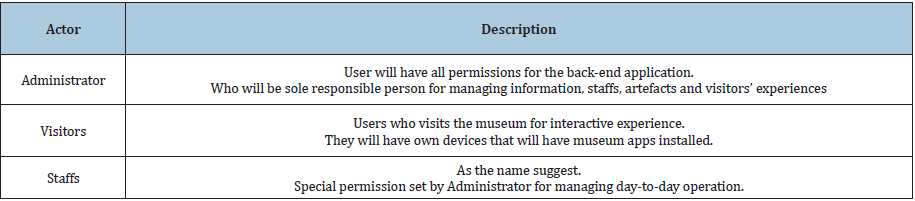
Figure 4: Use Case Diagram [7].
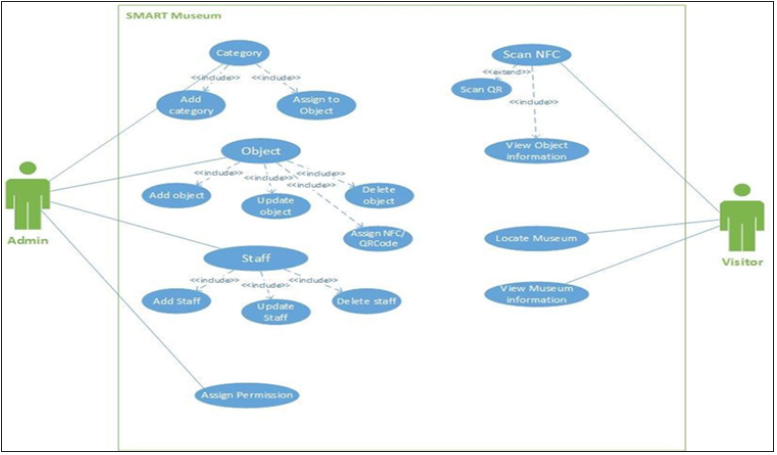
a. It will help to understand and find out requirements of
Museum System.
b. It assists in analysis of outer view of the system for
Museum System.
c. Analysis of the factors that can influence internal or
external once such as objects/artefacts, operation of museum,
human resources and visitors towards operation of the museum
system.
d. It will assist in finding out actors which are involved in the
operation of Museum System.
Requirements list table
Following Requirements List Table (Table 7) is produced so as to shorten the comprehensive outcomes of the requirements analysis.
Table 7:
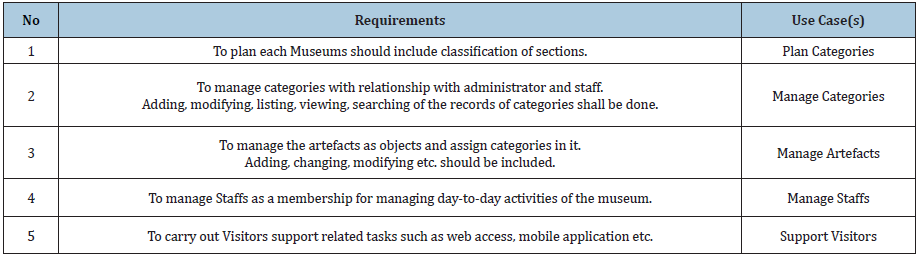
General requirements (non-functional): The complete backend new system should be web-based with interfaces saving to host within premises. Administrator and Staffs should follow Museum privacy and information providing policies. The new system should embrace client-server-based architecture. Mobile application should be used for enhancement of experience. Mobile application is proprietary and manage according to individual museums. During usages of the mobile phone in the Museum is controlled and monitored based upon the Museum police
Scientific risk analysis
Smart tags prototype: The smart tags are main significance of the study that will be used to interact with visitors and systems. It categories as a high risk since failure of the smart tags that lead to maximum impact to the study completion. Alternative will be use of the simple RFID tags system.
Museum information management system: Museum information management system aids to store information about museum objects and handle visitor request. It will be based upon web-based application. It categories as medium risk since failure will not lead to study completion and success. Alternative solution would be use of available information system from different Internet websites.
Mobile application-museum: Mobile application is critical part of the study since it will be used by visitors to get interact with smart tags and get requested information from museum information management system. It is classified as high risk failure of the mobile application that can lead to the failure of completion study. It is android based application in which support and tools are easily available.
System setup management: System setup is part of the museum information management system that will help in the hosting of the services. It is based upon the Linux system that is open source and support is also easily available. System setup management is a system engineering process for establishing and maintaining consistency of a product’s performance, functional, and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life.
Network communication: Network communication is easily setup by placing wireless access point and wired where necessary. Chance of the failure is very low as it will only need device and configuration management. It is categorizing as low risk and its severalty to the study is low as well. Communication management plays vital role for this. Communications management is the systematic planning, implementing, monitoring, and revision of all the channels of communication within an organization, and between organizations; it also includes the organization and dissemination of new communication directives connected with an organization and network.
Integration management: It plays vital role for the study where all development components must be integrating together to work properly and accomplish aim. It is categories as low risk since integration part can be done easily where mobile application will interact with smart tags and as per smart tag request will be send back to mobile to request information through network to backend server and vice-versa.
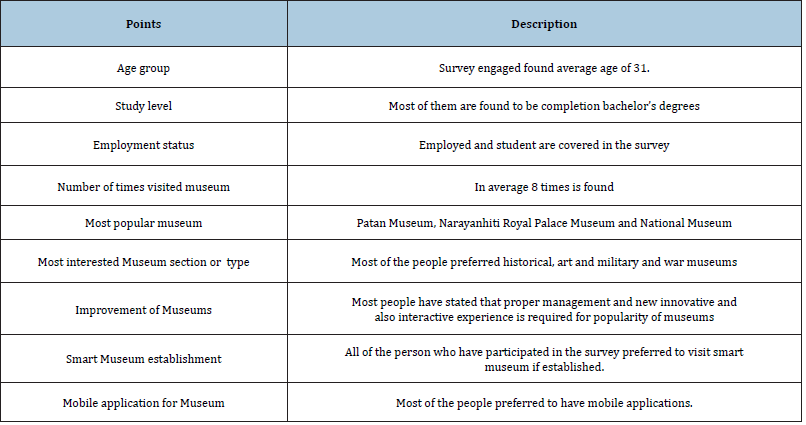
Survey questionnaire/result: The Survey was conducted into two parts which includes on-site visit to the Museum and online survey. On-site visit survey is done for analysis of the current situation of the museum. We have selected two main popular museums which is Patan Museum and International Mountain Museum. Online survey was done by using google form that is to find out how many times have visited to Museum, prefer type of the museums, interest to Smart Museum and ways to improve Museum visits. The observation of people coming into the Museum is a participant observation.
On-Site visit survey at patan museum: It is recognized and safeguard by UNSECO as International campaign for monuments of Kathmandu valley. It is well recognized museum for arts, historical and palace artefacts. Nepal is only first public museum established with concept of autonomous institution. With the help of the Austrian Government, museum have restored as original grandeur with model cultural heritage. During on-site visit, they have stated that number of the visitors per day in average is 150-200. There is a special package for student and foreigners. Also, with modern technologies, they have own websites and Internet facilities for visitors to use. New renovation is under-construction and due to constraint of the building infrastructure they could not expand as per they have planned. They said that they will also upgrade technologies integration part also if possible, in the future. International mountain museum: It is first museum that has started well-planned and infrastructure based upon the museum requirements. It is dedicated mountaineer museum that includes various valuable artefacts. During visit, we have found that they have already attracted many visitors as it resides in the Pokhara known as tourist city. They have also stated with modern tools and technologies they would like to promote museum. With concept of the smart museum, they have also started working on the building better profile in the Internet services, modern display and computer system integration for information digitization. Survey result: In this study, online survey was conducted to find out current viewpoints and understanding of the Nepal museums. Its main objective was to study on the knowledge of the smart museum.
Survey analysis: Following are the summarized result analysis of the survey results Table 8.
Contribution: This study primarily performed for the study of the Nepal Museums and prototype development of the application. The development of the application is done as android mobile application as front-end application whereas back-end application for management of the digital information. In terms of practical context, the study has developed prototype application based upon the android mobile application. Through use of it, users could get new way of experience during the visit to the museum. They will be able to get more information that was not possible on the display site. They can also get location information of various museums that was not possible without asking. It will popularize the Nepal museums with the modern mobile application. In the theoretical part, the research data of the Nepal Museums information that was not studied properly. The number of the museum in the Nepal was not found properly managed and coordinated. New technologies which included NFC and QR codes that link to the smart museum implication was studied. The new research possibility of the study is initiated for the further study in the context of the museums. In the research part, the study has shown the possibility of the study in the Nepal Museums. There are various museums that have not been well-recognized. The survey has shown that they are interested in the visit of the museums. But without proper information, they have not known about so many museums that exist in Nepal. The concept of the Museum was not properly address and not given priority as it should have.
Table 8:
Conclusion
This study focuses on Nepal Cultural Heritage information exchange system that provides innovative and interactive approaches. Smart museum formed with integrating digital museum contents with information exchange by using NFC smart tags and QR code. Visitors were to use their smart phone to get detail information without help of anyone. It was found that only handful Museum have maintained various facilities to visitors. Patan Museum and International Mountain Museum were found more preferable and frequent visit made by the people. MSDLC was preferred for the advance of the application. It was castoff for its growth standards enclosed all the features. The study necessities were straightforward where various reasons were not much changed. MSDLC was establish tinier life cycle since mobile applications essential to develop in speedy due to the market struggle. Most of the museums were found under-developed as per the requirements for smart museum. The survey result shows that many people preferred to visit the museum only if the museum primary aspect is fulfilled. In the future, if there is good museum integrated advancement of the technology definitely increases number of the visitors.
Future work
This study can lead to development of the Nepal Museums. It has many scopes possibilities for real time implementation and usages. Master study is limited to certain scope due to the time and criteria factors of the master program. In the system enhancement, it includes adding more functionalities like membership of the guest, indoor map coordination, digital floor map, quiz play and events push notification and possibilities of gift sales through Internet services. Beside this, Museum needs to have promotion and marketing strategies to boost number of the visitors and proper management of the galleries and sections. Mobile application is based upon android devices which can also be developed other mobile OS. Special membership and discount arrangement to the student and elders could be provided through mobile application.
References
- Dave R (2012) The decaying decadence of Nepal’s caste system. Nepal.
- (2015) The Manitoba museum value benefit, Manitoba, Canada.
- Yuri K (2016) Tokyo museum exhibits Issey Miyake's constant innovations. Tokyo, Japan.
- Matsuo H (2014) Introduction to the internet of things and thing speak.
- (2013) Cayan QR vs
- (2008) Cultural treasures of Nepal. tourist service centre: academic search premier. Nepal tourism board, Nepal, pp. 47-48.
- Cassavoy L (2015) QR codes: A definition.
- Geiger H (2011) NFC phones raise opportunities, privacy and security issues.
- Evans D (2011) The Internet of things how the next evolution of the internet Is changing everything.
- Liam M (2015) NFC vs Bluetooth- Its difference & distinct benefits.
- Good F (2016) Solving the 3 most common mobile app marketing challenges.
- D Benington H (1983) Production of large computer programs. Annals of the History of Computing 5(4): 350-361.
© 2020 Gajendra Sharma. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






