- Submissions
Full Text
Global Journal of Endocrinological Metabolism
Apelin and Sirtuin 1 Dysregulation induce Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders in Chronic Disease
Ian James Martins1*
Edith Cowan University, Australia
*Corresponding author: Ian J Martins, School of Medical Sciences, Edith Cowan University Western Australia
Submission: September 11, 2017; Published: October 02, 2017

ISSN: 2637-8019Volume1 Issue1
Abstract
Interests in chronic diseases have increased globally with the global death related to the increased chronic disease rate [1] with the most prevalent chronic disease such as cardiovascular disease linked to the metabolic syndrome and non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The role of the peptide apelin to the global obesity and diabetes epidemic has become of concern with relevance to its role in ischemic heart failure [2-4], treatment for obesity/diabetes [5-7], neuroendocrine function [3,8], glucose/energy metabolism [5], kidney disease [1,3,9] and NAFLD [10]. Analysis of plasma apelin levels and their regulation by nutrigenomic diets, exercise, drugs, lifestyle changes has become critical to prevent and reverse various chronic diseases that are linked to cardiovascular disease and NAFLD.
Apelin is a peptide and present in a number of tissues such as the GItract, stomach, heart, brain and adipose tissue [1]. The apelin receptor is a G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) and referred to as the APJ receptor and present in various tissues and in neurons of the hypothalamus [3]. The peptide apelin originates from preproapelin and apelins are a family of peptides and a substrate for angiotens in converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), a carboxy peptidase in the renin– angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAS) responsible for conversions of apelin and angiotensin II [11-13]. Apelin its regulation of the ACE2 and the RAS provide links between hypertension and cardiovascular disease [11-13]. Apelin-13 peptides are potent regulators of cardiovascular function [12] with longer peptides such as apelin-36 more effective in inhibiting HIV infection by blocking the HIV coreceptor APJ [14]. Apelin is involved with the kidney [1,3,9] and water balance with apelin found as a complex with vasopression (co-localization) and the apelin- APJ signaling inhibits the secretion of arginine vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone).
Sirtuin 1 (Sirt 1) is a nuclear receptor that is now important to insulin secretion with relevance to lipid/glucose/energy metabolism [15], insulin resistance [16], cardiovascular disease [17-20], kidney disease [21] and NAFLD [22]. The effects of stress interfere with apelin-Sirt 1 interactions [23] that are essential forthe prevention of insulin resistance and mental disorders in diabetes. The pathways for apelin-Sirt 1 interactions and nitric oxide (NO) homeostasis have become of major interest to global endocrinology and metabolism with NO now referred to as the hormone [24] that is involved with the early induction of autoimmune disease [25-27] that is connected to various chronic diseases and neuro degeneration (Figure 1).
Figure 1:
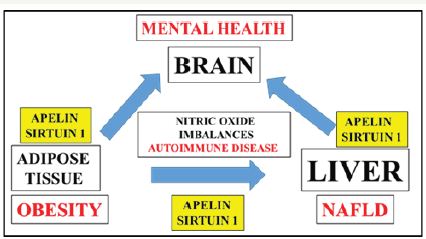
Apelin and Sirt 1 levels are of critical importance to NO imbalances connected to cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disease and the induction of global chronic diseases. Plasma apelin and Sirt 1 levels require analysis to assist with evaluation of early NO imbalances with relevance to autoimmune and endocrine/ metabolic disorders connected various organ diseases.
Apelin and Sirt 1 are both vasodilators with their role in NO balance imbalances associated with cardiovascular disease [28- 30]. In the heart the effects of apelin and its receptor are involved in vasodilation with protection of the heart from uncontrolled contractility and cardiac hypertrophy. NO imbalance is now critical to autoimmune disease [25-27] with defective apelin-Sirt 1 interactions now of primary relevance to endocrine and metabolic disorders that involve adipose tissue disease, NAFLD and neuro degeneration (Figure 1). Plasma levels of apelin and Sirt 1 require analysis [27] to indicate relevance of early chronic disease detection to prevent irreversible immunologic endocrine disease [31,32] that is connected to the global chronic disease epidemic.
Keywords: Apelin; Sirtuin 1; NAFLD; Chronic disease; Cardiovascular disease; Nitric oxide; Hormone; Autoimmune disease
Conclusion
Diet and nutrition have become important to stabilize the global chronic disease epidemic. Excess calorie consumption inactivates the calorie sensitive gene Sirt 1 relevant to apelin dysregulation that is connected to NO balance, cardiovascular disease and NAFLD. Sirt 1 repression induces autoimmune disease and has become of primary concern to apelin dysregulation in endocrinology/ metabolism with relevance to irreversible global chronic disease.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by grants from Edith Cowan University, the McCusker Alzheimer’s Research Foundation and the National Health and Medical Research Council.
References
- Martins IJ (2015) Nutritional diets accelerate amyloid beta metabolism and prevent the induction of chronic diseases and Alzheimer’s disease. Photon ebooks. The Journal for Endocrinology and Metabolism, Imprint: Photon: Peer Reviewed Indexed International Journal.
- Yu XH, Tang ZB, Liu LJ, Qian H, Tang SL, et al. (2014) Apelin and its receptor APJ in cardiovascular diseases. Clin Chim Acta 428: 1-8.
- Carroll OAM, Lolait SJ, Harris LE, Pope GR (2013) The apelin receptor APJ: journey from an orphan to a multifaceted regulator of homeostasis. J Endocrinol 219: R13-R35.
- Zeng H, He X, Hou X, Li L, Chen JX (2014) Apelin gene therapy increases myocardial vascular density and ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy via upregulation of sirtuin 3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306: H585-H597.
- Bertrand C, Valet P, Castan-Laurell I (2015) Apelin and energy metabolism. Front Physiol 6: 115.
- Higuchi K, Masaki T, Gotoh K, Chiba S, Katsuragi I, et al. (2007) Apelin, an APJ receptor ligand, regulates body adiposity and favors the messenger ribonucleic acid expression of uncoupling proteins in mice. Endocrinology 148(6): 2690-2697.
- Castan-Laurell I, Dray C, Knauf C, Kunduzova O, Valet P,et al. (2012) Apelin, a promising target for type 2 diabetes treatment? Trends Endocrinol Metab 23(5): 234-41.
- Newson MJ, Roberts EM, Pope GR, Lolait SJ, O Carroll AM, et al. (2009) The effects of apelin on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis neuro endocrine function are mediated through corticotrophin-releasing factor- and vasopressin-dependent mechanisms. J Endocrinol 202(1): 123-129.
- Coskun Yavuz Y, Sevinc C, Deniz MS, Yavuz S, Altunoren O, et al. (2015) The Role of Apelin 13 in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. Iran J Kidney Dis 9(5): 369-373.
- Montazerifar F, Bakhshipour AR, Karajibani M, Torki Z, Dahsipour AR, et al. (2017) Serum omentin-1, vaspin, and apelin levels and central obesity in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Res Med Sci 22: 70.
- Kalea AZ, Batlle D (2010) Apelin and ACE2 in cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 11(3): 273-282.
- Wang W, McKinnie SM, Farhan M, Paul M, McDonald T, et al. (2016) Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Metabolizes and Partially Inactivates Pyr-Apelin-13 and Apelin-17: Physiological Effects in the Cardiovascular System.Hypertension 68(2): 365-377.
- Siddiquee K, Hampton J, McAnally D, May L, Smith L, et al. (2013) The apelin receptor inhibits the angiotensin II type 1 receptor via allosteric trans-inhibition. Br J Pharmacol 168(5): 1104-1117.
- Zou MX, Liu HY, Haraguchi Y, Soda Y, Tatemoto K, et al. (2000) Apelin peptides block the entry of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). FEBS Lett 473: 15-18.
- Ye X, Li M, Hou T, Gao T, Zhu W-G, et al. (2017) Sirtuins in glucose and lipid metabolism. Oncotarget. 8(1): 1845-1859.
- Martins IJ (2015) Over nutrition Determines LPS Regulation of Mycotoxin Induced Neurotoxicity in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16(12): 29554–29573.
- Matsushima S, Sadoshima J (2015) The role of sirtuins in cardiac disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 309(9): H1375-H1389.
- Onofrio DN, Servillo L, Balestrieri ML (2017) SIRT1 and SIRT6 Signaling Pathways in Cardiovascular Disease Protection. Antioxid Redox Signal.
- Li Y, Ni J, Guo R, Li W (2016) In Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Type 2 Diabetes, SIRT1 Expression in Circulating Mononuclear Cells Is Associated with Levels of Inflammatory Cytokines but Not with Coronary Lesions. Biomed Res Int. 2016: 8734827.
- Chong ZZ, Wang S, Shang YC, Maiese K (2012) Targeting cardiovascular disease with novel SIRT1 pathways. Future Cardiol. 8(1): 89-100.
- Guan Y, Hao CM (2016) SIRT1 and Kidney Function. Kidney Dis (Basel) 1: 258-265.
- Ding RB, Bao J, Deng CX (2017) Emerging roles of SIRT1 in fatty liver diseases. Int J Biol Sci 13: 852-867.
- Martins IJ (2017) Apelinergic System Defects with Relevance to Mental Disorders in Diabetes. World J Psychiatry Ment Health Res 1: 1001.
- Ghasemi A, Zahediasl S (2011) Is nitric oxide a hormone? Iran Biomed J 15(3): 59-65.
- Martins IJ (2017) Regulation of Core Body Temperature and the Immune System Determines Species Longevity. Curr Updates Gerontol 1: 6.1
- Martins IJ (2017) Defective Inter play between Adipose Tissue and Immune System Induces Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Updates Nutr Disorders Ther 1: 31.
- Martins IJ (2017) The Future of Biomarkers Tests and Genomic Medicine in Global Organ Disease. Arch Infect Dis Ther 1: 1-6.
- Mattagajasingh I, Kim CS, Naqvi A, Yamamori T, Hoffman TA, et al. (2007) SIRT1 promotes endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation by activating endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(37): 14855-14860.
- Japp AG, Cruden NL, Barnes G, van Gemeren N, Mathews J, et al. (2010) Acute cardiovascular effects of apelin in humans: potential role in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 121(16): 1818-1827.
- Maguire JJ, Kleinz MJ, Pitkin SL, Davenport AP (2009) [Pyr1]apelin-13 identified as the predominant apelin isoform in the human heart: vasoactive mechanisms and inotropic action in disease. Hypertension 54(3): 598-604.
- Anderson MS (2008) Update in Endocrine Autoimmunity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(10): 3663–3670.
- Michels AW, Eisenbarth GS (2010) Immunologic Endocrine Disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125(2 Suppl 2): S226–S237.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






