- Submissions

Full Text
Gerontology & Geriatrics Studies
Can VR Help in Vestibular Rehabilitation?
Nachiket Nayagaonkar*, Arundhati Guha Thakurta and Indresh Verma
NMIMS-School of Design, Mumbai, India
*Corresponding author:Nachiket Nayagaonkar, NMIMS-School of Design,Mumbai, India
Submission: August 29, 2022; Published: January 12, 2023

ISSN 2578-0093Volume8 Issue2
Summary
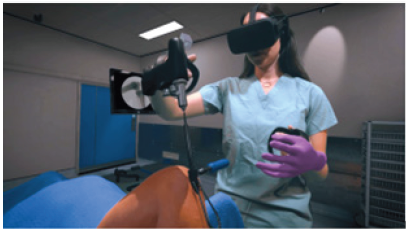
Vestibular dysfunctions are the disturbances in the balance system of the body. These disorders are acutely present in the body. These disorders are treated with rehabilitation therapy. This is known as vestibular rehabilitation. The main aim of the white paper is to find how Virtual reality can be used in this rehabilitation therapy. Medical science is slowly adapting Virtual reality for training as well as medical purposes. Since virtual reality is regarded as the future, it is predicted that it will be used across various fields serving different purposes. It is very interesting to look at the future of virtual reality being used in mainstream medicine (Figure 1).
Figure 1:Virtual reality by using rehabilitation therapy.
Keywords: Environment; Technology; Healthcare system; Vestibular system; Labyrinthitis
Abbreviations:VR: Virtual Reality; BPPV: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual reality is the technology used to create simulated environments. These environments provide immersive experiences. It replaces the flat screen with an immersive and interactive experience with virtual worlds. These worlds can be explored in 360 degrees. It is not being designed to build an alternative reality but a real life-like reality. It uses a host of technologies to achieve this goal. It has both entertainment and serious uses. Technology is becoming cheaper and more widespread. We can expect to see many more innovative uses for technology in the future and perhaps a fundamental way in which we communicate and work thanks to the possibilities of virtual reality. The devices that bridge the gap between real and virtual worlds are called VR headsets. These headsets enable users to explore simulated environments [1]
VR in Healthcare System
VR simulation technologies have long been used in medical education and training. Major virtual reality companies are creating products that combine 360-degree video and 3D interactive content to create the best learning programs for physicians and students. This technology enables them to practice complex, life-saving procedures in a risk-free environment, improve their skills, and receive usability feedback while doing so. Virtual reality is now making inroads into nursing. VR is used as a powerful diagnostic tool, assisting doctors and physicians in making accurate diagnoses. This is done in conjunction with other methods, such as MRI/ CT scans, and eliminates the need for any invasive techniques, providing the patient with a pain-free experience. Exposure therapy is a common treatment method for various types of mental illness [2]. VR is gradually changing the way exposure therapy is delivered to mentally ill patients by providing a low-cost, flexible, and low-risk treatment option. VR also aids in the treatment of anxiety and panic attacks by providing new ways to keep the body relaxed and calm. For a long time, physicians have used cognitive distraction methods to treat various types of pain. VR gives these distraction methods a new face by offering a variety of interactive games. These games are played in a simulated environment and include a variety of interactive features. While some apps offer therapeutic virtual reality for burn victims, there are also significantly advanced measures that allow for effective limb pain management. Furthermore, VR can be used with or without clinical care settings as a drug-free pain management alternative. Virtual reality in surgery has been around for a while and has grown in popularity among the medical community. The surgery is carried out by a robotic device that is guided by a human surgeon. This method shortens the recovery time and lowers the risk of surgical complications. VR is important in tele-surgery, which is performed by a surgeon on a patient in another location. The force feedback feature assists the surgeon in measuring the amount of pressure that must be applied while performing a delicate procedure such as dentistry, etc.
What is a Vestibular System?
The vestibular system is a sensory system that provides information to our brain about motion, head position, and spatial orientation; it also participates in motor functions that allow us to maintain balance, stabilize our head and body during movement, and maintain posture. As a result, the vestibular system is critical for normal movement and balance. Vestibular sensations begin in the inner ear, in the vestibular labyrinth, which is a series of interconnected chambers that connect to the cochlea. The semicircular canals are the most visible parts of the vestibular labyrinth. These are made up of three tubes that are roughly at right angles to one another and are each located in a plane in which the head can rotate. Each canal in this design can detect one of the succeeding head movements: nodding up and down, shaking sideways, or tilting left and right. These rotational acceleration movements of the head around an axis can be contrasted with linear acceleration, which involves forward or backward movement [3].
What are Vestibular Disorders?
A vestibular disorder can occur when a disease or injury damages the vestibular system. The most common symptoms are dizziness and difficulty balancing, but you may also experience hearing and vision issues.
Some of the most common vestibular disorders: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV): The most common cause of positional vertigo, which is a sudden sensation of spinning or swaying. Labyrinthitis: Also known as an inner ear infection. It occurs when a delicate structure deep within your ear known as a labyrinth becomes inflamed. Not only will your balance and hearing be affected, but you may also experience ear pain, pressure, pus or fluid coming from your ear, nausea, and a high fever. Vestibular neuritis is caused by a viral infection elsewhere in your body, such as chickenpox or measles, and affects the nerve that sends sound and balance information from your inner ear to your brain. The most common symptoms are dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and difficulty walking [4]. Meniere’s disease is characterized by sudden attacks of vertigo, tinnitus (a ringing, buzzing, or roaring sound in the ears), hearing loss, and a sensation of fullness in the affected ear. This could be caused by an excess of fluid in the inner ear as a result of a virus, allergy, or autoimmune reaction. Hearing loss worsens over time and, in some cases, becomes permanent [5].
What is Vestibular Rehabilitation?
Vestibular rehabilitation is an exercise-based program which promotes vestibular compensation and provides replacement of sensory input and habituation of the motion or situation that causes dizziness, which enhances postural and movement stability, reduces fall risk, and improves associated anxiety and depression. For most people, the deficiency caused by vestibular diseases is permanent because the amount of recovery is very small. But, due to compensation, the brain learns to use other senses and the symptoms can be reduced. This occurs naturally, but for someone the symptoms don’t reduce and for such patients, virtual reality can help in recovery by boosting compensation. Patients with dizziness, imbalance, vertigo, Meniere’s syndrome, Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), neck-related dizziness, and migraines are usually referred for vestibular rehabilitation therapy. Patients who have had a stroke or brain injury, or who frequently fall, are also applicable. Vestibular rehabilitation therapy is frequently the only treatment required. Sometimes it is part of the pre- and post-surgery treatment plan. Most patients’ balance and dizziness problems improve or disappear completely if they continue to practice the exercises they learned [6].
Virtual Reality for Vestibular Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation exercises often just become a part of routine or to-do-list, more like a daily chore. It is important to make these exercises into an experience or a challenge that the patients would be excited and motivated to take up. This can be done through moving these exercises to the virtual realm [7]. Virtual reality turns these rehabilitation into a gamified experience which makes the rehabilitation process more exciting and motivating for the patient. Virtual reality has gained widespread acceptance as a therapeutic tool for neurological patients, involving real-time simulation and interactions between sensory, motor, and cognitive channels. Since virtual reality involves real-life-like stimulations, it allows healthcare professionals to provide a wide variety of stimuli, with greater accuracy than traditional vestibular therapy. Virtual reality allows continuous habituation exercises and environment manipulation which disrupts or perturbs the balance, forcing the patient to figure out balance recovery strategies. This is done while avoiding any threat to the patient. While using virtual reality for vestibular rehabilitation, it provides constant feedback on progress. The progress tracking achieved with virtual reality is a feature which is unavailable in traditional rehabilitation methods. Following vestibular exercises, many people experience temporary dizziness, nausea, and queasiness. When VR is used for vestibular rehabilitation, this is not the case. Vestibular rehabilitation with virtual reality does not cause dizziness, nausea, or queasiness; the only thing to be concerned about is cyber sickness, which lasts no more than a day. The primary goal of VR is to promote compensation through a problem-solving approach. This feat is accomplished by tailoring different exercises to the needs of each individual. Instead of a real therapist, the software’s built-in artificial intelligence can provide detailed guidance and support. This makes the rehabilitation process less expensive and more flexible in terms of time [8].
Conclusion
Virtual reality definitely has the potential to be used for vestibular rehabilitation therapies. But a major drawback is cyber-sickness. More research is required to tackle this problem. But besides this, VR can make the whole process of rehabilitation much more exciting, which can help the patient’s brain to learn to compensate by using other senses and recover fast. Vestibular rehabilitation is an expensive therapy and hence, virtual reality can help reduce costs. Also, the therapy can be customized as it is designed as per each patient and constant progress mapping is available. So, virtual reality is ready to take over the traditional methods of vestibular rehabilitation.
References
- Tonelo C (2020) Virtual reality therapy for vestibular rehabilitation.
- Virtual reality applications in healthcare.
- Know your brain: Vestibular system.
- Booth S (2021) What are vestibular disorders.
- Dougherty J, Carney M, Emmady P (2022) Vestibular dysfunction.
- Song J (2019) Virtual reality for vestibular rehabilitation.
- Garcia A, Gananca M, Cusin S, Tomaz A, Gananca F, et al. (2013) Vestibular rehabilitation with virtual reality in Ménière's disease. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology 79(3): 366-374.
- Vestibular rehabilitation.
© 2023 Nachiket Nayagaonkar. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






