- Submissions

Full Text
Evolutions in Mechanical Engineering
Electromagnetoelastic Actuator for Nanomechanics and Nanotechnology
Afonin SM*
National Research University of Electronic Technology, MIET, Russia
*Corresponding author:Afonin Sergey Mikhailovich, National Research University of Electronic Technology, MIET, 124498, Moscow, Russia
Submission: April 06, 2021;Published: June 3, 2021

ISSN 2640-9690 Volume3 Issue4
Abstract
The characteristics of an electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology are received. The structural diagram of an electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology is obtained. The structural diagram of an electromagnetoelastic actuator has a difference in the visibility of energy conversion from Cady and Mason electrical equivalent circuits of a piezo vibrator. The matrix transfer function of an electromagnetoelastic actuator is obtained.
Keywords: Electromagnetoelastic actuator; Characteristics; Structural diagram; Piezo actuator; Deformation; Matrix transfer function; Nanomechanics and nanotechnology
Introduction
An electromagnetoelastic actuators in the form of piezo actuators or magnetostriction actuators are used in nanomechanics and nanotechnology for nanomanipulators, laser systems, nano pumps, scanning microscopy [1-5]. The piezo actuator is used for nano displacements in photolithography, microsurgical operations, optical-mechanical devices, adaptive optics systems and adaptive telescopes, fiber-optic systems [6-15]. The electromagnetoelasticity equation and the differential equation are solved to obtain the structural model of an electromagnetoelastic actuator. The structural diagram of an electromagnetoelastic actuator has a difference for from Cady and Mason electrical equivalent circuits of a piezo vibrator in the visibility of energy conversion. The structural diagram of an electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology is obtained by applying the theory of electromagnetoelasticity [4-12].
Characteristics of Electromagnetoelastic Actuator
The structural diagram of an electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology is changed from Cady and Mason electrical equivalent circuits [4-8]. The equation of electromagnetoelasticity [1-15] has the form of the equation of the reverse effect for the actuator
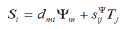
where 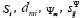 and Tj are the relative deformation, the module, the control
parameter or the intensity of field, the elastic compliance, and the mechanical intensity.
Let us consider in static regime the characteristics of an electromagnetoelastic actuator
for nanomechanics and nanotechnology. The mechanical characteristic [4-39] of an
electromagnetoelastic actuator has the form
and Tj are the relative deformation, the module, the control
parameter or the intensity of field, the elastic compliance, and the mechanical intensity.
Let us consider in static regime the characteristics of an electromagnetoelastic actuator
for nanomechanics and nanotechnology. The mechanical characteristic [4-39] of an
electromagnetoelastic actuator has the form
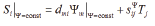
The regulation characteristic [4-39] an electromagnetoelastic actuator has the form
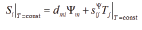
The mechanical characteristic of an electromagnetoelastic actuator has the form
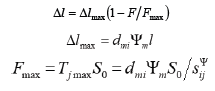
where index max is used for the maximum value of parameter. For the transverse piezoelectric effect the maximum values of parameters of the piezo actuator for nanobiotechnology have the form
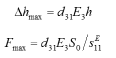
For the transverse piezo actuator for nanomechanics and
nanotechnology at 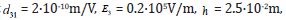
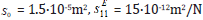 its parameters are found Δhmax = 100nm and Fmax = 4N.
its parameters are found Δhmax = 100nm and Fmax = 4N.
At elastic load the regulation characteristic of an electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology is obtained in the form
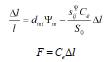
The equation of the displacement of an electromagnetoelastic actuator at elastic load has the form
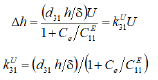
For the transverse piezo actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology the equation of the displacement at elastic load has the form
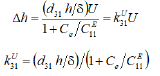
where 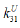 is the transfer coefficient.
is the transfer coefficient.
Therefore, at 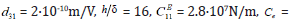 0.4∙107N/m, U = 200V, its parameters are found
0.4∙107N/m, U = 200V, its parameters are found 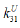 = 2.8nm/V and
steady-state displacement Δh = 560nm. Theoretical and practical
parameters are coincidences with an error of 10%.
= 2.8nm/V and
steady-state displacement Δh = 560nm. Theoretical and practical
parameters are coincidences with an error of 10%.
Let us consider in dynamic regime the characteristics of an electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology. The differential equation of an electromagnetoelastic actuator has the form [4-32]
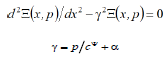
where Ξ(x, p) is the transform of Laplace for displacement; p , γ , cΨ , α are the operator of transform, the coefficient of wave propagation, the speed of sound, the coefficient of attenuation
The decision of the differential equation of an electromagnetoelastic actuator has the form
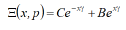
where C , B are the coefficients
The coefficients C , B have the form
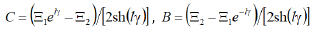
where 1(p) Ξ , 2 (p) Ξ are the transforms of Laplace displacement of faces 1 and 2 for an electromagnetoelastic actuator.
The system of the equations for the forces on faces of an electromagnetoelastic actuator is found [10-38]
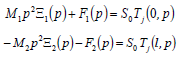
where M1 , M2 , F1(p), F2 (p) , Tj (0 , p) , Tj (l , p), S0 are the masses of the load, the transforms of Laplace the forces and the stress on faces 1 and 2, the area of an actuator.
The system of the equations the transforms of Laplace the stresses acting on faces of an electromagnetoelastic actuator has the form
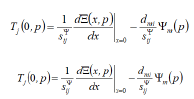
The system of equations for the structural diagram on Figure 1 and model of an electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology has the form
Figure 1:Structural diagram of electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology.
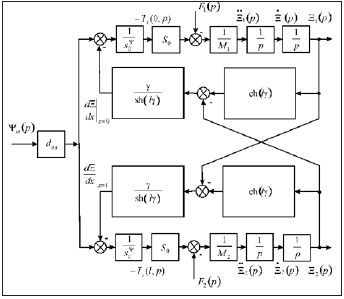
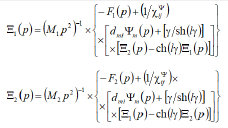
where 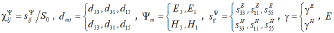 is
the intensity of electric field, H is the intensity of magnetic field.
is
the intensity of electric field, H is the intensity of magnetic field.
The matrix equation for an electromagnetoelastic actuator with matrix transfer function has the form
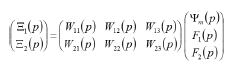
Therefore, at the inertial load the steady-state displacements , of an electromagnetoelastic actuator have the form
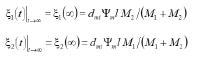
For the mechatronics control systems with an electromagnetoelastic actuator its characteristics are found.
Conclusion
In work the characteristics of an electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology are received. The structural diagram of an electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics and nanotechnology is obtained. The structural diagram of an electromagnetoelastic actuator has a difference from Cady and Mason electrical equivalent circuits of a piezo vibrator in the visibility of energy conversion. The structural diagram of an electromagnetoelastic actuator is found from its electromagnetoelasticity and differential equations. The matrix transfer function of an electromagnetoelastic actuator is received.
References
- Schultz J, Ueda J, Asada H (2017) Cellular actuators. (1st edn), Butterworth-Heinemann Publishers, Oxford, UK, p. 382.
- Afonin SM (2006) Absolute stability conditions for a system controlling the deformation of an electro magnetoelastic transducer. Doklady Mathematics 74(3): 943-948.
- Uchino K (1997) Piezoelectric actuator and ultrasonic motors. Kluwer Academic Publisher, Boston, MA, USA, p. 347.
- Afonin SM (2005) Generalized parametric structural model of a compound electro magnetoelastic transducer. Doklady Physics 50(2): 77-82.
- Afonin SM (2008) Structural parametric model of a piezoelectric nano displacement transducer. Doklady Physics 53(3): 137-143.
- Afonin SM (2006) Solution of the wave equation for the control of an electro magnetoelastic transducer. Doklady Mathematics 73(2): 307-313.
- Cady WG (1946) Piezoelectricity: an introduction to the theory and applications of electromechanical phenomena in crystals. (1 st edn) McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, USA, p. 806.
- Mason W (1964) Physical acoustics: principles and methods. (1st edn), Academic Press, New York, USA, p. 515.
- Zwillinger D (1989) Handbook of differential equations. (3rd edn), Academic Press, Boston, USA, p. 673.
- Afonin SM (2006) A generalized structural-parametric model of an electro magnetoelastic converter for nano- and micrometric movement control systems: III Transformation parametric structural circuits of an electro magnetoelastic converter for nano- and micrometric movement control systems. Journal of Computer and Systems Sciences International 45(2): 317-325.
- Afonin SM (2016) Decision wave equation and block diagram of electro magnetoelastic actuator nano- and micro displacement for communications systems. International Journal of Information and Communication Sciences 1(2): 22-29.
- Afonin SM (2015) Structural-parametric model and transfer functions of electro elastic actuator for nano- and microdisplacement. Chapter 9 in Piezoelectrics and Nanomaterials: Fundamentals, Developments and Applications. In: Parinov IA (Ed.), Nova Science, New York, USA, p. 225-242.
- Afonin SM (2017) A structural-parametric model of electro elastic actuator for nano- and micro displacement of mechatronic system. Chapter 8 in Advances in Nanotechnology. In: Bartul Z & Trenor J, Volume 19, Nova Science, New York, USA, p. 259-284.
- Afonin SM (2018) Electro magnetoelastic nano- and microactuators for mechatronic systems. Russian Engineering Research 38(12): 938-944.
- Afonin SM (2012) Nano- and micro-scale piezomotors. Russian Engineering Research 32(7-8): 519-522.
- Afonin SM (2007) Elastic compliances and mechanical and adjusting characteristics of composite piezoelectric transducers. Mechanics of Solids 42(1): 43-49.
- Afonin SM (2014) Stability of strain control systems of nano-and micro displacement piezo transducers. Mechanics of Solids 49(2): 196-207.
- Afonin SM (2017) Structural-parametric model electro magnetoelastic actuator nano displacement for mechatronics. International Journal of Physics 5(1): 9-15.
- Afonin SM (2019) Structural-parametric model multilayer electro magnetoelastic actuator for nanomechatronics. International Journal of Physics 7(2): 50-57.
- Afonin SM (2017) Structural-parametric model of piezoactuator nano- and micro displacement for nanoscience. AASCIT Journal of Nanoscience 3(3): 12-18.
- Afonin SM (2016) Solution wave equation and parametric structural schematic diagrams of electro magnetoelastic actuators nano- and micro displacement. International Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 3(4): 31-38.
- Afonin SM (2018) Structural-parametric model of electro magnetoelastic actuator for nano mechanics. Actuators 7(1): 1-9.
- Afonin SM (2019) Structural-parametric model and diagram of a multilayer electro magnetoelastic actuator for nano mechanics. Actuators 8(3): 1-14.
- Afonin SM (2016) Structural-parametric models and transfer functions of electro magnetoelastic actuators nano- and micro displacement for mechatronic systems. International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mathematics 2(2): 52-59.
- Afonin SM (2018) Structural-parametric model of electro elastic actuator for nanotechnology and biotechnology. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutics 5(1): 8-12.
- Afonin SM (2010) Design static and dynamic characteristics of a piezoelectric nano micro transducers. Mechanics of Solids 45(1): 123-132.
- Afonin SM (2018) Electro magnetoelastic actuator for nano mechanics. Global Journal of Research in Engineering: A Mechanical and Mechanics Engineering 18(2): 19-23.
- Afonin SM (2018) Multilayer electro magnetoelastic actuator for robotics systems of nanotechnology. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference EI Con Rus p. 1698-1701.
- Afonin SM (2018) A block diagram of electro magnetoelastic actuator nano displacement for communications systems. Transactions on Networks and Communications 6(3): 1-9.
- Afonin SM (2019) Decision matrix equation and block diagram of multilayer electro magnetoelastic actuator micro and nano displacement for communications systems. Transactions on Networks and Communications 7(3): 11-21.
- Afonin SM (2020) Condition absolute stability control system of electro magnetoelastic actuator for communication equipment. Transactions on Networks and Communications 8(1): 8-15.
- Afonin SM (2020) A Block diagram of electro magnetoelastic actuator for control systems in nanoscience and nanotechnology, Transactions on Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence 8(4): 23-33.
- Afonin SM (2020) Optimal control of a multilayer electro elastic engine with a longitudinal piezo effect for nanomechatronics systems. Applied System Innovation 3(4): 1-7.
- Afonin SM (2020) Structural scheme actuator for nano research. COJ Reviews and Research 2(5): 1-3.
- Afonin SM (2018) Structural-parametric model electro elastic actuator nano- and micro displacement of mechatronics systems for nanotechnology and ecology research. MOJ Ecology and Environmental Sciences 3(5): 306-309.
- Afonin SM (2019) Condition absolute stability of control system with electro elastic actuator for nano bioengineering and microsurgery. Surgery & Case Studies Open Access Journal 3(3): 307-309.
- Afonin SM (2020) Multilayer engine for microsurgery and nano biomedicine. Surgery & Case Studies Open Access Journal 4(4): 423-425.
- Afonin SM (2020) Condition absolute stability of control system electro magnetoelastic actuator nano displacement for nano research in sciences. Novel Research in Sciences 5(1): 1-4.
- Nalwa HS (2004) Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. 25 Volumes, Los Angeles: American Scientific Publishers, USA.
© 2021 Afonin SM. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






