- Submissions

Full Text
Environmental Analysis & Ecology Studies
Sustainable Use of Nature Resources and Agriculture High-quality Production
Zhongsheng Guo1,2*
1Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Northwestern A & F University, Yangling, China
2Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Chinese Academy of Science and Ministry of Water Resources, Yangling, China
*Corresponding author:Zhongsheng Guo, Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Northwestern A & F University, Yangling, China
Submission: May 16, 2023; Published: June 16, 2023

ISSN 2578-0336 Volume11 Issue2
Abstract
Key Points
a. With the increase of population and economic development, people consume more and more plant-based food.
b. To meet increasing demand for the quantity and variety of crop production, it is better to obtain the maximum yield and benefit of plants.
c. The limit of resources utilization by plants and vegetation carrying capacity in the key period of plant resources relationship regulation must be used to realize Sustainable Use of Nature Resources and Agriculture High-quality production.
With the increase of population and economic development of a country or a region, people consume more and more plant products and services. To meet increasing demand for the quantity and variety of plant products and service, 80% of the original forest has become man-made vegetation such as farmland, man-made forest, fruit, crop and grass. A lot of exotic food plants were introduced to produce more plant products and service. As crop plants grow, the plant resources relationship may change from equilibrium state to non-equilibrium state, leading to land degradation, decline of vegetation and the decline of plant yield and quality or resources waste. To solve this problem, saskatoon berries, red plum apricot and corn planted in semi-arid region of the Loess Plateau of China were taken as examples to study the plant resources relationship and the method of Sustainable Use of Nature Resources and Agriculture High-quality production. The results show that Saskatoon berries will grow well and fruit, but red plum apricot and corn cannot grow well and fruit. To realize the sustainable utilization of resources and the crop high-quality production, the limit of resources utilization by plants and vegetation carrying capacity, especially the vegetation carrying capacity in the key period of plant resources relationship regulation has to be applied to adjust the plant resources relationship to obtain the maximum yield and benefit of plant products and realize crop high quality production. In water-limited regions, the theory of resource utilization limit by plant is the soil water resources utilization limit by plants and the carrying capacity of vegetation is soil water carrying capacity for vegetation.
Keywords:Plant production and service; High quality production; Sustainable supply; Resources utilization limit by food plant; Vegetation carrying capacity; Food security
Introduction
Plant-based human food products are more sustainable than animal-derived products [1]. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, including algae, take in light energy and turn carbon dioxide and water into energy-rich organic matter while releasing oxygen. It mainly includes two stages of light reaction and dark reaction, involving light absorption, electron transfer, photophosphorylation, carbon assimilation and other important reaction steps, which is of great significance for realizing energy conversion in nature and maintaining carbon-oxygen balance in the atmosphere. Food plants produce food and so on and provide a guarantee for people’s health, life and development because sometime food, fruits and vegetables were negatively associated with the incidence of colon cancer [2] and positively related with health. For example, Citrus fruits are important health promoting fruits rich in bioactive components like limonoids, hesperidin, naringenin and citrus pectin. The anticancer properties were correlated with antioxidant enzyme rejuvenation, signaling pathway inhibition, inflammatory mediator suppression and cell cycle arrest [3]. Citrus Fruits (CFs) containing flavanones exerted their antioxidant activity mainly by directly scavenging free radicals and enhancing the defense ability of cells [4]. Grains and cereals are primary energy resources for human beings. Certain grains and cereals showed protective effects against colon cancer cells. Millet is an important cereal food and exhibits multiple biological activities, including immunomodulatory and antioxidant activities. A novel protein extracted from foxtail millet bran displayed anti-carcinogenic characteristics [5]. In addition, millet brand derived bound polyphenols showed anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-induced HT-29 colon cancer cells via ROS/miR-149/ Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway, indicating that the polyphenols might inhibit the initiation and progression of colorectal cancer [6].
With the increase of population and economic development of a country or a region, people consume more and more plant-based food, there is an increasing demand for the quantity and variety of plant-based food production, but original forest ecosystem products and services cannot meet the need of demand for the quantity and variety of plant-based food production, most of the original forest has become food plants, farmland, man-made forest and grass [7]. A lot of exotic food plants were introduced to produce food and meet the needs of the people. Because exotic food plant changes the plant resources relationship and the weather change with year and month in a year, which will cause vegetation decline or resources waste, which is not good for sustainable use of nature resources and high-quality produce of food plant. To solve these problems, we study the plant resources relationship and search the method for sustainable use of nature resources and high-quality production of plant products and service.
Method and Material
Study site
The study site located in the Shanghuang Eco-experimental Station, which belong to the semi-arid region of the Loess Plateau, in the Eastern 20Km from Guyana County, China (Figure 1). The area was in a hilly loess region with an elevation range of 1,534 to 1,824m and slope gradients of about 8˚ and the slope gradients below the valley shoulder line is more than 25˚. The main soil type is Hangman soil (Calcaric Cambisol, FAO 1988) that is developed from loess and is susceptible to soil and water losses, which are serious in this region. The rainfall is unevenly distributed in the year with a mean annual precipitation of 416mm, and rainfall from June to September accounts for 64.7% of the total annual precipitation. The coefficient of variation of precipitation among the years from 1983 to 2001 was 23.8% and rainfall amounts ranged from 259.9mm in 1991 to 634.7mm in 1984, with a median rainfall amount of 434mm (Figure 2& 3). Mean solar radiation is 5, 342MJm2; annual average temperature is 7.0 ˚C. Plant growing period is 152 days. Groundwater level is more than 60 meters [7]. Low temperature, frost and drought are the main disaster weather which influence sustainable produce of red plum apricot. Since red plum apricot introduced in 1988 from Shaanxi province to the Shanghuang Eco-experimental Station (Figure 1 & 4).
Figure 1:The Location of Shanghuang eco-experiment station in China.
Figure 2:The change of average monthly precipitation with month in a year in the Shanghuang Eco-experimental Station.
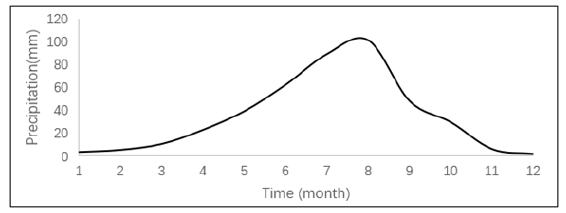
Figure 3:Change of precipitation with year in the Shanghuang Eco-experimental Station.
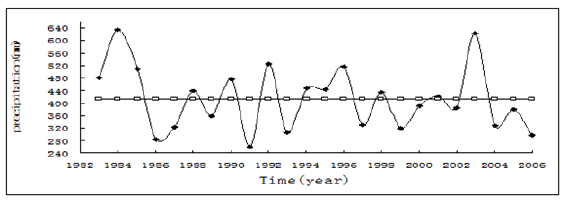
Figure 4:Saskatoon berries grow well in the Shanghuang Eco-experimental Station.

The precipitation is less, and the seasonal and interannual variations of precipitation are larger, soil dry often happens in the dry years, which will cause soil degradation, vegetation decline and corn failure or waste of soil water resources because planting density is smaller than soil water carrying capacity for vegetation in wet years. Amelanchier alnifolia Nutt (common names: Saskatoon berry) is a pome fruit-bearing shrub native to the North American prairies [8]. First, it is transferred to plant in Liaoning, China in 1997and then be introduced to plant in Guyana, China in 2008 because Saskatoon berries fruit are good sources of many bioactive phenolic components, such as flavanols, anthocyanins, procyanidins and phenolic acids. As much as 382mg/100g based on fresh weight of anthocyanins, Anthocyanin- and flavonoid-rich foods have been demonstrated to have a beneficial protective function in combating certain cancers, inflammation and cardiovascular diseases, type II diabetes, obesity, and age-related macular degeneration (Figure 4). Red plum apricot tree is a small tree and grows well. The shape of red plum apricot fruit is about round and looks beautiful (Figure 2). The fruit weight of red plum apricot per single fruit weight is about 40-56g. The apricot is rich in juice, soluble solids content (14.3%), potassium (410.8mg per 100g), selenium and Vc (8.3mg per 100g) (Gang et al, 2011). The potassium content of red plum apricot is higher than that of apple (Malus domedtia), pear (Pyrus), peach (Amygdalus persica) and grape (Vitis vinifera) (Figure 5).
Figure 5:The shape of red plum Apricot in the Shanghuang Eco-experimental Station.

Corn is a native to Central and South America and now It is now grown all over the world. Corn contains rich vitamin, which are five times more vitamin for rice, wheat, which has the highest percentage of the content of vitamin A, everyone hundred grams 63 micrograms of content, and the researchers point out that vitamin A is very beneficial to people’s eyes. A nutritional factor, corn, with its powerful antioxidant to protect vision effect, and absorb harmful to the eyes of the useless components. Corn prevents obesity and constipation. Corn contains rich plant cellulose is not easy to be absorbed by the body, it can stimulate gastrointestinal peristalsis, promote fecal excretion. Corn can restrict the absorption of excessive sugar in the body, inhibit the increase of blood sugar in the body after dinner; Fiber can also inhibit fat absorption. Corn can help people prevent obesity, but also can help people lose weight, to achieve the effect of beauty and thin body. One of the nutrients in corn is niacin, which plays an important role in the metabolism of fat and sugar and helps us maintain a healthy digestive system and healthy skin. Corn can prevent heart disease and cancer in the corn in addition to contain carbohydrates, carotene these common elements, it also contains vitamins and riboflavin, and nutritional factors contained in the corn, absorbed by the body and then transformed into has anti-cancer effects of vitamin, corn and rich plant fiber, it can make effective discharge carcinogens and other poisons, it also has the effect of stimulating the brain to enhance one’s brain power and memory. In addition, selenium and magnesium contained in corn also have good anti-cancer effects. They can accelerate the decomposition of peroxides in the body, which can inhibit the growth and division of cancer cells, so that cancer cells are inhibited, and can also promote the discharge of waste in the body, which is also good for cancer prevention (Figure 6) the soil water and plant growth was investigate.
Figure 6:Corn plant will wilt in critical period of plant water relationship regulation in the Shanghuang Ecoexperimental Station in 2021

Result and Discussion
Resources use limit by plants
Nature Resources is limit to plant and the resources plant use also is limit. The Resources use limit by plants include the space Resources use limit by plants in soil water and nutrient enough regions, soil water Resources use limit by plants in water limited regions and soil nutrient Resources use limit by plants in soil nutrient limited regions [9]. One of the indicators to express the harmony degree of plant resources relationship is the resources use limit by plants. The plant resources relationship is the dynamics relationship. Plant growth changes greatly with the supply of resources as plants grow. There is an equilibrium point. At the equilibrium point, the supply of resources is equal to the demand of resources plant grow. The supply of resources is more than the demand of plant growth resources in resources rich period or years. According to the amplitude of the plant resources relationship, edible plants can be divided into two types: native plants and exotic plants. Because goods and services that native plant production cannot meet the peoples need, so most of old-growth vegetation was changed into man-made vegetation, edible plan belongs to exotic plants.
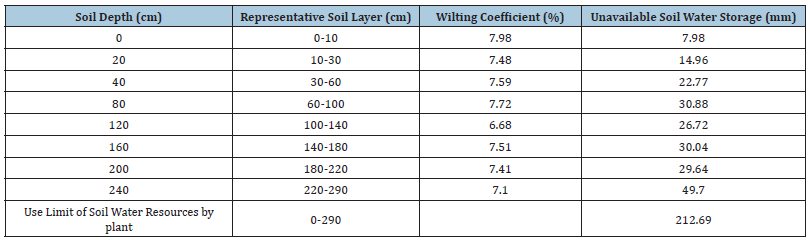
Exotic plants are those plants they are introduced from other places whether intentionally or introduced not intentionally. The intentional is often called introduction but introduced not intentionally called invasive species. Because some exotic plants have good ability to adapt themselves to the local environment, these plants do not need to regulate edible plant and resources relationship, such as Amelanchier alnifolia Nutt planted in the semiarid loess hilly region of China. Red plum apricot and corn all is not native to the semiarid loess hilly region of China. After being introducing to the semiarid loess hilly region of China, the Amelanchier alnifolia plant grow fast and well and fast bear fruit. But Corn in the semiarid loess hilly region of China (Guyuan, China) cannot adapt themselves to the dry environment. In the study site, corn should be sowed in April and mature in September. The plant resources relationship should be regulated according to resources use limit by plant and vegetation carry capacity. For example, the resources use limit by plants in the Shanghuang Eco-experimental Station is soil water resources use limit by plant because the station belongs to water-limited regions. The soil water resources use limit by plant is soil water storage in the maximum infiltration depth when the soil moisture content of all layers within the maximum infiltration depth range is equal to the withering coefficient [10- 13]. The Use Limit of Soil Water Resources by red plum apricot see Table 1. When soil water resources in the maximum infiltration depth is equal to soil water resources use limit by plant. The plant water relationship enters the key period of plant water relationship regulation and should consider be regulated [12,13].
Table 1:The use limit of soil water resources by red plum apricot.
Vegetation carrying capacity
Carrying capacity of land for Vegetation is a measure of whether a plant community is using land resources sustainably and healthy growth. Nature Resources is limit to plant and the resources plant use also is limit. Another indicator to express the harmony degree of plant resources relationship is vegetation carrying capacity, which decides the quantity of plant resources relationship regulation. Vegetation carrying capacity is the ability of land resources to support vegetation, which can be defined as the maximum density (relative index) or population number (absolute index) of an indicator plant that land resources can support normal plant growth in a plant community. Because land resources can be divided into four types of vegetation carrying capacity according to the influence of land resources on plant growth, vegetation carrying capacity includes spatial vegetation carrying capacity, soil water vegetation carrying capacity, soil nutrient vegetation carrying capacity and temperature vegetation carrying capacity. Spatial vegetation carrying capacity is the ability of spatial resources to support vegetation in the soil water and soil nutrient rich regions. Soil water carrying capacity for vegetation is the ability of soil water resources to support vegetation in the water limited region. Soil water resources are the water stored in the soil, especially in root zone and the critical period of plant water relationship regulation. Soil water vegetation carrying capacity is the plant density when soil water supply is equal to soil water consumption in each period, especially the key period of plant resources relationship regulation. Soil nutrient carrying capacity is limited by soil nutrient resources, and soil water carrying capacity is limited by soil water resources. Soil nutrient carrying capacity can be divided further into soil N carrying capacity, which is driven by soil N storage or resources, soil Phosphorus (P) carrying capacity, which is driven by soil P storage or resources, and soil Potassium (K) carrying capacity, which is driven by soil K storage or resources [9]. Temperature vegetation carrying capacity is the ability of temperature resources to support vegetation.
Vegetation Carrying Capacity is the maximum density (relative index) or population size (absolute index) of an indicator plant in a plant community when the soil water consumption equal soil water supply in the root zone soil over a given time scale, especially critical period of plant-water relationship regulation and minimum death days because they decide the maximum yield and beneficial effect. minimum death days in which the relationship between soil water and plant growth decided plant growth condition during whole season and the maximal produce and service of a plant ecosystem in water-limited regions. The plant resources relation must be regulated on vegetation carrying capacity. For example, the plant water plan relation has to be regulated on the soil water vegetation carrying capacity in the site because the station belong to water limited regions, otherwise, soil water drought would cause soil degradation, vegetation decline, or crop failure in water resources rich year or waste in water resources rich years [11, 14-18]
Soil water vegetation carrying capacity is limited in water shortage area, which is called soil water carrying capacity for vegetation [14]. It is the ability of soil water resources to support the vegetation [7, 11-16, 18-20] or irrigation was used to add water to meet the need of plant water in water limited regions if there are water resources to make corn grow well in dry year to obtain maximum yield and beneficial result. Soil water vegetation carrying capacity is the maximum quantity or plant density soil water resources per unit area can maintain healthy growth of indicator plants at a given period and site condition [15] and can be estimated by soil water-lant density model [11,12], expressed by the number (absolute index) or density (relative index) of indicator plant in the plant community. Soil water carrying capacity for vegetation (SWCC), changing with plant species (vegetation type), time and location, is the theoretical basis for determining indicators and criteria for high quality and sustainable management of forest vegetation [11,12].
The critical period of plant water relationship regulation
Edible plant and resources relationship can be divided into two kinds, one is the dynamic balance or harmony relationship such as native plants in original vegetation. Because the plant resources relationship is developed based on long-term evolution and plants have certain self-regulation ability and can self-regulate the relationship with nature. Even if the ecological environment changes to some extent within the limit of plant use resources during the season growth of plants, especially in the critical period of plant water relationship regulation if the available resources do not exceed the limit of the use of resources by plants, or the plants can adjust themselves to adapt to the changes, the plants will blossom and bear fruit. This kind of plant resource relationship cannot be regulated. Another is not balance or harmony relationship such as most of exotic plants, the plant resources relationship must be regulated. The critical period of plant water relationship regulation is the most important period in plant growing season because it decides the maximum yield and benefit food plant, which range from the starting time soil water resources in the maximum infiltration depth equal soil water resources use limit by plant [21] to the failure time to regulate plant water relationship on soil water vegetation carrying capacity. The soil water resources in the critical period of plant water relation regulation are the soil water resources in the root zone at the starting time of the critical period of plant water relation regulation plus soil water supply from precipitation through canopy in the critical period of plant water relation regulation [12,13].
High quality production of plants
In order to realize the sustainable utilization of resources and obtain maximum yield of food plant to realize high quality production of food plant and high quality and sustainable development of social economy, it is time to adjust plant resources relationship regulation on the limit of resources utilization by plant and the vegetation carrying capacity to obtain the maximum yield and benefit of food plant and meet sustainable supply of plant-based foods in market , when the resources lack duration is more than the critical period of plant resources relationship regulation and the preserve plant density in the critical period of plant resources relationship regulation is more than vegetation carrying capacity, the plant resources relationship regulation must be adjusted. The soil water vegetation carrying capacity in the critical period of plant water relation regulation, which is the ability of soil water resources in the critical period of plant water relation regulation to support vegetation. The reducing amount of plant is equal to preserve density minus soil water vegetation carry capacity denoted by the number or density of a population of indicative plants. For example, the station belongs to the semi-arid Loess Hilly region, which belong to the water-limited regions, the limit theory of resource utilization by plant is the soil water resources utilization limit by plant and the carrying capacity of vegetation is soil water vegetation carrying capacity because soil water mainly come from precipitation and underwater is deep and there is not irrigation condition.
According to three years study of red plum apricot from 2017 to 2021 in the station, the factors influencing the high quality production of red plum apricot is the low temperature and frost happened in the early spring from the last ten days of March to the middle ten days of April, which influences the development of flowers, pollination and young fruit of red plum apricot, hearteating insects influences the young fruit of red plum apricot when the young fruit of red plum apricot grows to 0.8~1.0 cm in diameter on the around May 20, and soil dry. When the soil water resources in the maximum infiltration depth are reduced to soil water Resources use limit by red plum apricot, the plant water relationship should be considered regulated. When the leaf amount is more than the suitable leaf amount when present density is equal to soil water vegetation carrying capacity in the critical period of plant water relationship regulation, showing that soil water severely influences plant growth. At this time, plant resources relation has to be regulated on the suitable amount of leaves, which is the amount of leaves when the present density is equal to the soil water carrying capacity of red plum apricot because plant water relation generally should be regulated by pruning some branch and leave quantity instead of cutting some plant and then regulate the fruit and leave relation because the power of leave to produce carbohydrate is limit.
Discussion
Because the indicate plant in original vegetation is constructive species, which is native to the local region because for a long time they have developed a good relationship with the local nature, plant resources relationship is very harmony and plant grow well and bear fruit but the goods and service cannot meet people’s need, so a lot of original vegetation has been changed into nonnative plantation such as Saskatoon berries in the semiarid region, China, they grow and develop well, suitable for local climate, easy to develop. But another plant such as corn and red plum apricot are not suited to the local climate and need to regulate plant resource relationships. So, to carry out sustainable use of natural resources and Agriculture high quality production, we have to use the natural resources in sustainable way. If there are plants that are overusing natural resources because the plant density exceeds the vegetation capacity or underuse natural resources, the plant resources relation should be regulated by the natural resources use limit by plants increases and vegetation carrying capacity, especially the vegetation carrying capacity in the critical period of plant resources relation regulation if the available resources decrease to the limit of resource utilization by plant, which is the function of plant species and location [11,12].
If available natural resources are smaller than the natural resources use limit by plants, the plant resources relationship enters the critical period of plant resources relation regulation and the ending time of the critical period of plant resources relation regulation is the ineffective time of plant resources relation regulation. The vegetation carrying capacity is the ability of nature resources to carry vegetation, which changes with plant species, time and location [11-13,22]. If the plant density is more than the vegetation carrying capacity in the critical period of plant resources relation regulation and the preserve density is more than the plant resources relationship should be regulated, otherwise the further increase of natural resources used by plant will lead to the decline of vegetation and the decline of grain yield and quality [7, 11- 16,19,22].
Conclusion
The role of dietary nutritional factors (13%) is greater than that of medical factors (8%), second only to genetic factors (15%). According to the WHO Global Nutrition Report (2018 edition), 20% of deaths are related to dietary nutritional imbalance and dietary nutritional factors have become the primary risk factors for global morbidity and mortality [23-28]. For the health of the people and food security, we must make high-quality production and sustainable development of social economy. Sustainable use of nature resources and the high-quality production of food plants must be carried out and the limit of resource utilization by plants and vegetation carrying capacity. The limit of resource utilization by plants and vegetation carrying capacity is the soil water resources utilization limit by plant and the soil water vegetation carrying capacity in water-limited regions. The limit of resource utilization by plants and vegetation carrying capacity should be used to prevent soil degradation, vegetation decline and Agriculture failure or resources waste to obtain maximum yield to carry out sustainable use of natural resources and Agriculture high quality production [29-32].
Acknowledgement
This project was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Project No: 42077079,41271539, 41071193) and Study on high quality sustainable development of soil and water conservation (A2180021002). We thank two anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions.
References
- Wehrmaker RM, Draijer N, Bosch G, Goot AJvd (2021) Evaluation of plant-based recipes meeting nutritional requirements for dog food: the effect of fractionation and ingredient constraints. Animal Feed Science and Technology 290: 115345.
- Leenders M, Siersema PD, Overvad K, Tjønneland A, Olsen A, et al. (2015) Subtypes of fruit and vegetables, variety in consumption and risk of colon and rectal cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. International Journal of Cancer 137(11): 2705-2714.
- Kaur J, Kaur G (2015) An insight into the role of citrus bioactives in modulation of colon cancer. Journal of Functional Foods 13: 239-261.
- Singh B, Singh JP, Kaur A, Singh N (2020) Phenolic composition, antioxidant potential and health benefits of citrus peel. Food Research International 132: 109114.
- Shan S, Li Z, Guo S, Li Z, Shi T, et al. (2014) A millet bran-derived peroxidase inhibits cell migration by antagonizing STAT3-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human colon cancer. Journal of Functional Foods 10: 444-455.
- Shi J, Shan S, Li H, Song G, Li Z (2017) Anti-inflammatory effects of millet bran derived-bound polyphenols in LPS-induced HT-29 cell via ROS/miR-149/Akt/NFkappa B signaling pathway. Oncotarget 8: 74582-74594.
- Guo Z, Shao M (2013) Impact of afforestation density on soil and water conservation of the semiarid loess plateau. J Soil Water Conserv 68(5): 401-410.
- Moyo M, Aremu AO, Staden JV (2018) Deciphering the growth pattern and phytohormonal content in Saskatoon berry (Amelanchier alnifolia) in response to in vitro cytokinin application. New Biotechnology 42: 85-94.
- Guo Z (2019) Rice carrying capacity and sustainable produce of rice in resources-limited regions. Int J Agric Sc Food Technol 5(1): 054-057.
- Guo Z, Shao M (2010) Effect of artificial Caragana korshinskii forest on soil water in the semiarid area of loess hilly region. Chin Forest SCI 46(12): 1-7.
- Guo Z (2014) Theory and practice on soil water carrying capacity for vegetation, pp. 45-100.
- Guo ZS (2021) Soil water carrying capacity for vegetation. Land Degradation & Development 32(14): 1-11.
- Guo ZS (2021) Soil hydrology process and sustainable use of soil water resources in desert regions. Water.
- Guo Z, Shao M, Zhang Y, Wu Q (2002) An layer-dividing approach to the soil water in forest land, Proceedings of Soil Physics and Ecological Environmental Construction, Shanxi Science and Technology Press, Xiaan, China, pp. 74-79.
- Guo Z, Shao M (2003) Vegetation carrying capacity of soil water and soil desiccation in artificial forestry and grassland in the semiarid regions of loess plateau. Chin. J ECOL 23: 1640-1647.
- Guo Z, Shao M (2004) Mathematical model for determining vegetation carrying capacity of soil water. J Hydr 35(10): 95-99.
- Guo Z (2020) Estimating method of maximum infiltration depth and soil water supply. Scientific Reports 10: 9726.
- Guo Z (2009) Limit of vegetation rehabilitation for soil and water conservation in semi-arid region of Loess Plateau. Chin J Science Soil Water Conserv 7: 49-54.
- Guo Z (2010) Soil water resource use limit in semi-arid loess hilly area. Chin J App Eco 21(12): 3029-3035.
- Guo Z (2011) A review of soil water carrying capacity for vegetation in water-limited regions. Chinese Journal of Forest Science 47(5): 140-144.
- Guo Z, Li Y (2009) Initiation stage to regulate the caragana growth and soil water in the semiarid area of loess hilly region, China. J Ecol 29: 5721-5723.
- Guo Z (2023) Forest restoration, resources sustainable use and high-quality sustainable management. Glob J Ecol 8(1): 007-010.
- Abbo S, Gopher A (2020) Plant domestication in the neolithic near east: The humans-plants liaison. Quaternary Science Reviews 242: 106412.
- Budagovski AI (1986) Soil water resources and available water supply of the vegetation cover. Water Resources 12(4): 317-325.
- Guo JY, Li X, Browning JD, Rottinghaus GE, Lubahn DB, et al. (2004) Dietary soy isoflavones and estrone protect ovariectomized ER alpha KO and wild-type mice from carcinogen-induced colon cancer. Journal of Nutrition 134(1): 179-182.
- Guo Z, Zhang W (2016) Impact of initial planting density on soil water resource use limit by plants. Geoinfor Geostat: An Overview 4: 1.
- Iriarte J, Elliott S, Maezumi SY, Alves D, Gonda R, et al (2020) The origins of Amazonian landscapes: Plant cultivation, domestication and the spread of food production in tropical South America. Quaternary Science Reviews 248: 106582.
- Ko Y, Jeong J, Choi Y, Ryu C (2013) Soy soluble polysaccharide induces apoptosis in HCT-116 human colon cancer cells via reactive oxygen species generation. Molecular Medicine Reports 8(6): 1767-1772.
- Sheflin AM, Borresen EC, Kirkwood JS, Boot CM, Whitney AK, et al. (2017) Dietary supplementation with rice bran or navy bean alters gut bacterial metabolism in colorectal cancer survivors. Mol Nutr Food Res 61(1).
- Signorelli P, Fabiani C, Brizzolari A, Paroni R, Casas J, et al. (2015) Natural grape extracts regulate colon cancer cells malignancy. Nutrition and Cancer-An International Journal 67(3): 494-503.
- Sung H, Lim Y, Choi Y (2006) Soy isoflavones do not alter the effects of fructooligosaccharide on the intestinal ecosystem of colon-cancer model rats. Food Science and Biotechnology 15(6): 931-936.
- Yu H, He W (2021) Plant invaders outperform congeneric natives on amino acids. Basic and Applied Ecology 54: 75-84.
© 2023 © Zhongsheng Guo. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






