- Submissions

Full Text
Environmental Analysis & Ecology Studies
Climatic Trend and Variability Over Indonesia Maritime Area for Period 1990-2016
Paulus AW*
Indonesia
*Corresponding author: Paulus AW, Indonesia
Submission: August 13, 2018;Published: June 3, 2019

ISSN 2578-0336 Volume5 Issue5
Abstract
The processing of cassava tuber into finished products such as gari generates large wastes water. The effluents are known to contain cyanide and acidic pH in addition to other chemical characteristics such as heavy metals, chemical oxygen demand among others. The effluents have toxicological impacts on the receiving ecosystem (Soil and Surface Water) as well as some of its associated fauna and flora. During degradation processes by the indigenous microbes in the soil the effluents emits odour that are offensive to human. This study reviews recycling options of cassava mill effluents through bioenergy production. The study found that cassava mill effluents have demonstrated positive potentials for biogas, biohydrogen, bioethanol, bioelectricity using varying technologies. During bioenergy production, the characteristics of the raw effluents is improved upon in some of the parameters such as chemical oxygen demand, total solid, pH etc probably due to the activities of some microorganisms. As such there is the need for research to focus on other possible utilization of the sludge generated such as bio-fertilizer production as an option for reuse.
keywordsBioenergy; Biotechnology; Cassava wastewater; Environmental contamination; Reuse; Toxicology
Introduction
Maritime Continent area of Indonesia lies in the tropical region between two oceans (Indian and Pacific Oceans) and two continents (Asia and Australia). As the tropical maritime continent area; most of the time humid maritime continent air mass always prevails to give some rainfall during the dry season period (June-September) and more rainfall during rainy season period (December-March) previously before the year of 1990. Such that this climate situation encouraged the agricultural activities for the country region and last 1990 the UN system for Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) presented the award for the developing country succeeding in the National Food Security itself. Starting 1991; for the first time the country for the whole country area were occurring less of rainfall or drought with largest area and longest in time comparing with climate situation for the last 30 years.
This drought continued up to the end of decade 1991-2000; because of these conditions the National Food Security Program destroyed that it was due to the climatic variation from the global scale. Where the global phenomena of the El Nino episode were very active with increasing temperature of sea surface over the wider area the Eastern Pacific Ocean. The long and frequent El Nino episode might cause the impact of the climatic variation in term of the long episode of drought. The drought might disturb agribusiness production starting local up to national level. Based upon the observational tools found that global climate variability of the El Nino episode (longer on record of 1991-1994); quickly developed and highest on record of Sea Surface Anomaly in Pacific Ocean of ENSO episode 1997-1998 and changes in the pattern of ENSO episode 2002-2003.
These occurrences would encourage the developing of the weather and climate variations starting global up to regional/local scales [1]. Impact of the global scale in term of changing pattern the global circulation including regional circulation of Asia-Australia Monsoonal wind system. The regional wind system affects into the national/local monsoonal wind system of the maritime continent of Indonesia. One of the results from the observational of this study is the longer period of the easterly monsoonal wind system than westerly monsoonal wind system. Because these wind system-controlled weather and climate in this region. Some unusual and strange weather and climate pattern observed. This unusual pattern would report in this paper. The objective of the present study is to report and present some of the results from the manual observation and analyses of the unusual and strange occurrences of the weather and climate over the maritime continent of Indonesia.
The Data and Method
For many decades; climatologist has examined how the climate especially Earth’s surface temperature changed before 19th century. The Earth’s surface temperature has fluctuated naturally over hundreds of millions of years. These past changes suspected from several sources which drive the past climate system up to present time. One important drive would be coming from the solar radiation in term of sunspots number which fluctuates every average year of 11.5 years [2]. One sunspot number variability from no sunspot number the toward maxima up to returning back to the none sunspot number cloud be considered as one cycle; where the current year of 2017 is under cycle number 24 for the period 2010- 2021. Complete sunspot cycle can be presented in the next Figure 1 as follows [3].
Figure 1:Sunspot cycle was arranged by NASA with cycle number in above every cycle [3].
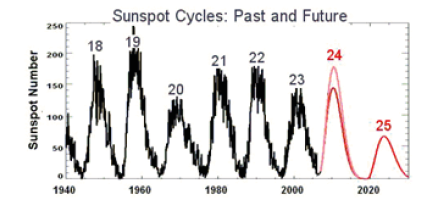
Figure 2:Impact El Nino 1997 on the global environment.
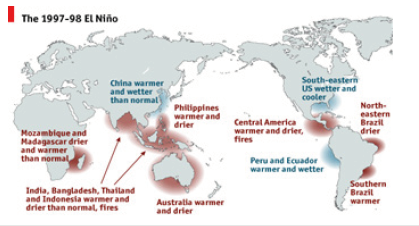
Table 1:Period global climatic phenomenon of El Nino activities and its impact to Indonesia.
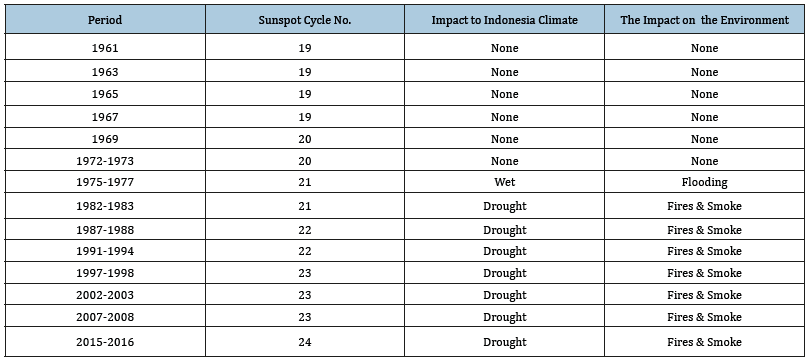
From the sunspot cycles; it can expand into relation with global climatic variation especially with global atmospheric phenomenon such as El Nino activities. As it defined warming period of the sea surface temperature over equatorial east Pacific Ocean [4]; it should have relation with warming earth’s surface coincide with the higher frequency of the sunspot number. The global impact of the El Nino 1997 phenomenon can be presented in Figure 2 as follows. Based upon the investigation in Meteorological and Geophysical Agency of Indonesia; it was noted some official record of El Nino activities as follows (Table 1)
From this table shows that there was relation the trend on the climatic impact to the environment that:
A. Most the sunspot cycles number starting number 18 up to 23 had maximum more than 150 sunspot number/month in the peak of the sunspot cycle.
B. High sunspot cycles number 19 generated more frequent El Nino.
C. Sunspot cycle no 21-23 generated El Nino with wide impact to the global.
From this point of the global phenomenon of El Nino impact initially started last 1982 in term of wildfire and smoke/haze only over the small area over Borneo and this impact might continue last 1987. Then the impact to the environment might be wider area than before in 1991 and widest area arose from the impact last 1997 to cover from East Papua island up to Sumatera on the West; from Indonesia in the South up to Thailand and Philippines areas in the North. Detail of the study would be discussed in the next discussion.
The Discussion
Based upon the observational record from operational basis weather and climate analyses and information; several unusual/ strange in weather and climate could be reported as follows:
A. Dry Season period longer from the normal (1961-1990) and shorter period of the wet season especially during long warming episode (1991-1994); strong warming episode (1997-1998) and recent development starting 2000 up to present time.
B. From general view found that the dry season having relation with the easterly wind system and the wet season with westerly wind system of the most maritime continent area especially over most southern hemisphere region. It observed that regular period of the monsoonal wind was varied (westerly monsoonal wind system period to become shorter and longer easterly monsoonal wind system conversely).
C. Total number of the annual rainfall especially the area having two different seasons namely dry or less rainfall and wet or more rainfall; with having trend variability in term of decreasing number the total rainfall starting 1997 up to 2016 on the selective area over Indonesia Maritime Continent.
D. Decreasing number of the annual rainfall observed having relation with the easterly wind system such that the support downward vertical air motion mechanism; then it supports the development of inversion layer. These developing layers generated the air pollution of haze/smoke when there was source of fires. The experiencing area of haze was over shifting wind area of Sumatra and Borneo Islands; based upon the experience the smoke/haze spreading up over adjoining countries such as Malaysia; Singapore; Brunei Darussalam starting last 1991 during the dry season or easterly monsoonal wind period. To illustrate the wildfires and smoke/haze pollution can be presented in Figure 3.
Figure 3:Description wildfires and transboundary smoke/haze.

E. During the wet or westerly monsoonal wind was having trend shorter period than normal; it generated some extreme features of the weather phenomena in term of storms of wind; rainfall and thunder. One unusual tropical cyclone developed closely with the equator and several tropical depressions also generated during Northeast Monsoonal wind system over the South China Sea starting 1996 up to present time.
F. The climate variability was observed especially coming from convective cloud system. Previously the formed in the transition period of either from wet-dry or dry-wet seasons. Current feature showed that they can be developed in all season yearly and they increased during the wet season; they might interact with the environmental degradation and give impact to the increasing number and area disasters of the landslide; flashflood; flood during wet season and hot day; drought; fires and haze during the dry season.
G. The long-wet season might arise starting 2010 up to the present time of 2017. There are several global significant weather and climate events with the reverse of El Nino phenomenon of La Nina might exist to replace El Nino activities which had mostly affected Indonesia long drought episode during dry season since last 1991-2007.
Based upon the method and data coming from the operational basis of the weather and observation over the maritime continent of Indonesia; it showed the variability of the weather and climate starting the year of 1991 up to present time. The extreme weather pattern was observed when the tropical cyclone crossing near equator line of latitude 0 degrees (Tropical Cyclone Vamei; December 2001) and the Tropical Cyclone Kirrily generated last April 2009 from Arafura Sea of Eastern Indonesia. This tropical cyclone moves northward approaching the equator; it might be unusual tropical cyclone generated over low latitude. The convective cloud formation was pronounced as part of the variability of climate. The fires; smoke or haze more easily develop yearly either during dry or wet seasons. These phenomena were no correlation with the Asian Brown Cloud (ABC), but they are the similar type of condition with the haze of Indonesia (Figure 3).
Based upon the operational basis from current condition beginning 2004; some features of the unusual pattern in weather and climate observed starting January 2004. Where lacking the tropical cyclone generated over South Indian Ocean; it was due to the high pressure over this area. This features almost the same condition with a year before of last January 2003 with unusual easterly wind prevailed. It meant during the two years; extensive of the easterly wind system had blown over most of the maritime continent area of Indonesia as part of the climatic variation. Summarizing of this paper that seasonal namely long dry season and the short-wet season would be climate variability over the maritime continent of Indonesia; compared with the normal from each season. Such that this variability would give impact to the increasing number of the disasters either during wet and or dry condition.
Summary
The interesting observational studies would like to present the climatic pattern in term of the variability of the seasonal pattern yearly of the rainfall. Where the seasonal rainfall pattern would have relation with seasonal wind system over Indonesia Maritime Continent. In another word; the monsoonal wind system over Maritime Continent varies with respect to the time especially in the period of 1991-2005; could it be part of the global/regional climatic change? The unusual weather pattern of the tropical storm formation would be in the lowest latitude (1-3 degrees) in the last December 2001; it was followed some tropical cyclones track closer to the low latitude of Indonesia area during period January- February 2002 and April 2009 causing triple amount of monthly rainfall over capital city of Indonesia for each month. And then this unusual tropical storm track continued until the end period of last April 2002. The El Nino episode of 2002-2003 would identify as the unusual global phenomenon; it was due to the formation in advance of the normal formation. Where the normal episode would be approaching the middle of each consecutive year with weak in intensity and longer than the normal episode. This condition might cause none tropical storm formation over Northern Australia or Southern Indonesia Maritime Continent area. The La Nina episode starting 2010 up to 2016 seem to replace the El Nino episode starting 1991-2007; it might replace the dry condition into wet condition. Such that presently wettest disaster of flooding; landslide and flash flood would be replaced drought disaster with impact to the environment in term burning plantation including forestry and some agriculture production over Indonesia Maritime Continent area. It could be the climatic trend in the next climatic period at about next few decadal of time of the year.
References
- (1977-2016) Some notes from the operational experienced meteorologist, Bureau Meteorology and Geophysics of Indonesia.
- (1998-2002) Some report from CLIVAR meetings.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar cycle
- http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/ninonina.html
© 2019 Paulus AW. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






