- Submissions

Full Text
COJ Technical & Scientific Research
Uncertainity in Occupational Safety and Health Education
Dr. Halil Ibrahim Erdim*
PhD-Occupational Safety and Health- Selinus University, Italy
*Corresponding author: Dr. Halil Ibrahim Erdim, PhD-Occupational Safety and Health- Selinus University, Italy
Submission: August 05, 2021; Published: August 31, 2021

Volume3 Issue4August, 2021
Opinion
Nearly 200 years passed after the industrial revolution to reach the Occupational Safety
and Health Law in the United Kingdom. Other countries followed the UK. Nowadays OHS
training is required by law in most countries. In the beginning, the training of employees
had been provided by trained people. They used to be called “Trainers of trainees”. Different
countries had different institutions. For example, OSHA requires employers to provide training
to workers who face hazards on the job. OSHA create training materials, distribute training
grants to nonprofit organizations, and provide training through authorized education centers.
There are different types of education centers.
a) Governmental Institutions
b) Private education centers
c) Organizations of standards (OHSAS 18001, ISO 45001 etc)
d) International organizations
e) ILO
In the last 15 years, universities provided OSH programs and started to educate people to
be OSH professionals. In the middle ages, there were occupational guilds. When an employee
worked enough to be his own master, he should take some exams. After he proves that he had
learned enough, he was authorized to establish his own business. The examiners were his
master and other experts of the sector. After training institutions and universities started to
educate professionals, the guild system was left. The occupational safety and health education
and training are similar to the occupational guild system. There are experts approved by
institutions, organizations, private education centers. Some of these are local organizations
while there are international institutions. These institutions certificate the participants,
while some of them provide diplomas. In the beginning, these certificates and diplomas were
helpful to distinguish the professionals. Now universities educating people as a technician,
engineer (bachelor), master and even Ph.D. degree on occupational safety and health. A Ph.D.
degree means 8-10 years of education. In some countries, there are short courses of about
200 hours. After completing the course and taking a successful exam, a participant is accepted
as an OSH expert or OSH Professional. It is very important to improve human resources on
different topics, but if it is human life, we have to think very carefully. We need to compare a
short course with 2 or 4 years of education.
A. The short courses allow the participants to get a diploma in a very short time, with
spending a small amount of money and effort. This means, most people may prefer this
kind of opportunity.
B. People living in developing or undeveloped countries,
which can not afford long term and expensive education will
prefer this kind of education
C. OSH aims are to protect the workers, manage hazards,
minimize workplace accidents and occupational diseases.
D. To protect human life, we need to prefer the best-educated
people.
Table 1: Comparison of the education programme provided by a university and small course.

Which one is better educated? A university student or a short
course participant? The table below, will help us to compare the
options (Table 1). Since there are a lot of organizations giving
certificates or diplomas, it is necessary to improve hierarchies for
occupational safety and health education and training. Regarding
OSH education and training, there are 4 different categories:
A. Employees training
B. Training of trainers
C. Academic education
D. Expertise courses
Employee’s training can be provided by licensed OSH
professionals while universities may be authorized for the
training of trainers and academic education (technician, safety
engineer-bachelor, MS and Ph.D.). The small courses (eg: asbestos,
offshore exploration/production, fire safety, process safety, etc)
may be provided by private education centers or governmental
institutions. ILO may organize occupational safety and health
courses or workshops, but it is a shame of the whole world that
ILO collects money from the participants. ILO must try to improve
the OSH applications. These activities must be free and globally. The
conclusion, universities should be the dominant element of OSH
education and others should be auxiliary institutions for training.
You can find the details in the chart below (Figure 1).
Figure 1: OSH training and education.
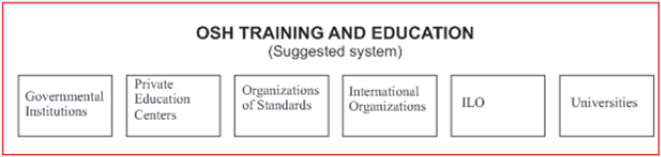
Governmental institutions
May organize free seminars, workshops, and similar activities. No need for any exam for a person who has completed university education. Governmental Institutions may license the experts for special situations (Erection of scaffolds, tower winch, asbestos, process engineer, etc).
Private education centers
May organize small courses and certificate the experts for critical jobs such as Erection of scaffolds, tower winch, asbestos, process engineer, etc.
Organizations of standards
May organize employee training and certificate the people who participated in auditing/ inspecting training.
International organizations
May organize small courses and certificate the successful participants. They should not be allowed to give the diploma.
ILO
This is a sub-organization of the United Nations. How can we allow ILO to organize courses and collect money? There are millions of people who cannot access satisfactory OSH courses and we lose more than 2.5 million people every year due to workplace accidents and occupational diseases?
Universities
Universities should be the dominant institutions in occupational education. They should be the only organizations that can give diplomas on OSH.
© 2021 Dr. Halil Ibrahim Erdim. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






