- Submissions

Full Text
COJ Technical & Scientific Research
On the Possibility of Gravity Control by Magnetic Field
Yoshinari Minami*
Advanced Science-Technology Research Organization, Japan
*Corresponding author: Yoshinari Minami, Advanced Science-Technology Research Organization, Japan
Submission: November 19, 2018;Published: November 26, 2018

Volume1 Issue3 November 2018
Relationship between the Essence of Gravity and Magnetic Field
As is well known in General Relativity, gravity is generated by a curved space. The curvature of space and the size of curved space region determine the gravitational acceleration. Curvature of space is formed in a concentric sphere state around the celestial body by the mass of celestial body like the Earth.
Minami derived the equation of curvature of space induced by magnetic field in 1988 [1]. It was found that this equation was accordance with the equation that Levi-Civita considered (i.e., the static magnetic field creates scalar curvature) by Minami in 1995 [2].
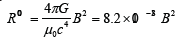
where 
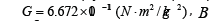 is a magnetic field with Tesla and R00 is a major component of
spatial curvature (1/m2 ).
is a magnetic field with Tesla and R00 is a major component of
spatial curvature (1/m2 ).
The major component of curvature of space R00 can be produced by not only mass density but also magnetic field B (see APPENDIX A: Curvature Control by Magnetic Field). Above equation indicates that the major component of spatial curvature can be controlled by magnetic field.
The curvature of flat space R00 is zero (strictly speaking, only
20 independent components of Riemann curvature tensor Rpijk are
zero), then the gravitational acceleration becomes zero. A curved
space is generated not only by mass density but also by magnetic
field or electric field. In case that the intensities of the magnetic
field B and the electric field E are equal, the value of 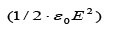 is about seventeen figures smaller than the value of
is about seventeen figures smaller than the value of 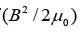 . As
a consequence, the electric field only negligibly contributes to the
spatial curvature as compared with the magnetic field. Accordingly,
it is effective that the space can be curved by magnetic field. Since
the region of curved space produces the field of acceleration, the
massive body existing in this acceleration field (i.e. curved space
region), is moved in accordance with Newton’s second law.
. As
a consequence, the electric field only negligibly contributes to the
spatial curvature as compared with the magnetic field. Accordingly,
it is effective that the space can be curved by magnetic field. Since
the region of curved space produces the field of acceleration, the
massive body existing in this acceleration field (i.e. curved space
region), is moved in accordance with Newton’s second law.
Ultimately, it can be said that the magnetic field can be made equivalent to the gravitational field by the action of curving the space [3-6].
Appendix A: Curvature Control by Magnetic Field
Let us consider the electromagnetic energy tensor Mij . In this case, the solution of metric tensor gij is found by
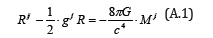
Eq (A.1) determines the structure of space due to the electromagnetic energy.
Here, if we multiply both sides of Eq (A.1) by gij , we obtain
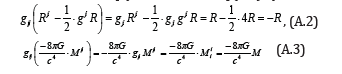
The following equation is derived from Eqs.(A.2) and (A.3)
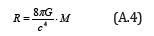
Substituting Eq.(A.4) into Eq.(A.1), we obtain
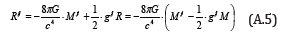
Using antisymmetric tensor ij f which denotes the magnitude of electromagnetic field, the electromagnetic energy tensor Mij is represented as follows;
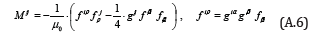
Therefore, for M, we have
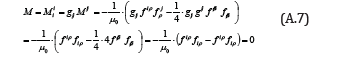
Accordingly, substitutingM = 0 into Eq.(A.5), we get
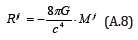
Although Ricci tensor Rij has 10 independent components, the major component is the case of i = j = 0 , i.e., R00 . Therefore, Eq.(A.8) becomes
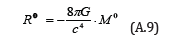
On the other hand, 6 components of antisymmetric tensor fij = − fji are given by electric field E and magnetic field B from the relation to Maxwell’s field equations
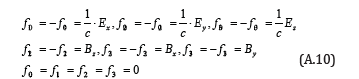
Substituting Eq.(A.10) into Eq.(A.6), we get
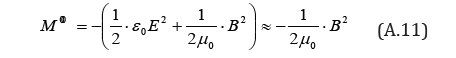
Finally, from Eqs.(A.9) and (A.11), we obtain
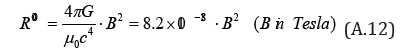
where 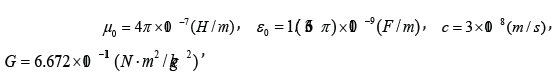
B is a magnetic field in Tesla and R00 is a major component of spatial curvature(1/m2 ) .
References
- Minami Y (1988) “Space Strain Propulsion System”, 16th International Symposium on Space Technology and Science (16th ISTS), 1: 125-136.
- Pauli W (1981) Theory of Relativity. Dover Publications, New York, USA.
- Minami Y (2014) A Journey to the Stars-By Means of Space Drive Propulsion and Time-Hole Navigation. LAMBERT Academic Publishing, Germany.
- Minami Y (2015) Space Propulsion Physics toward Galaxy Exploration. J Aeronaut Aerospace Eng 4(2): 149.
- Minami Y (2015) Continuum Mechanics of Space Seen from the Aspect of General Relativity-An Interpretation of the Gravity Mechanism. Journal of Earth Science and Engineering 5: 188-202.
- Williams C, Minami Y (2015) Advances in General Relativity Research. Nova Science Publishers, USA.
© 2018 Yoshinari Minami. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






