- Submissions

Full Text
COJ Nursing & Healthcare
Emotional Intelligence and Decision-making Styles among Nurse Managers
Fatma Rushdy Mohamed1* and Eman Ahamed Mohamed2
1Professor of Nursing Administration, Faculty of Nursing, Egypt
2Lecturer of Nursing Administration, Faculty of Nursing, Egypt
*Corresponding author: Fatma Rushdy Mohamed, Professor of Nursing Administration, Faculty of Nursing, Egypt
Submission: April 19, 2020;Published: March 06, 2020

ISSN: 2577-2007Volume6 Issue1
Abstract
Background: Emotional intelligence plays a significant role in many aspects of leaders. It is important to make effective decisions in day to day life in an organization.
Aims: Assess emotional intelligence and decision-making styles among Nurse Managers and explore relationship between emotional intelligence, decision-making styles, and personal characteristics of Nurse Managers at Assiut University Hospitals.
Subject and method: The study was carried out at the main Assiut Univversity Hospital (no= 58), The Pediatric Health Hospital (no=12) and The El-Rajhy Assiut Hospital (no=20) nurse mangers. Self–administered questionnaire sheet which consisted of three parts: Personal characteristics data, Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire, and Decision-making styles Questionnaire.
Result: Showed that, there was high Level of Nurse Managers emotional intelligence (66.7%) at Pediatric Health Hospital than at Main Assiut University Hospital & El Rajhy Assiut Hospital (63.8% & 60.0%) respectively, the high mean scores were in participative style of decision-making in all Assiut University Hospitals,.
Conclusion: There was high Level of Nurse Managers emotional intelligence at Pediatric Health Hospital than at Main Assiut University Hospital & El Rajhy Assiut Hospital, the high mean scores were in participative decision-making style in all Assiut University Hospitals, a positive significant correlation between age and emotional intelligence. Nurse Managers' emotional intelligence had significant relationships with Bachelor qualification and years of experience. While, there was a negative correlation between authoritative decision-making style and emotional intelligence, and negative correlation among delegative decision-making style and nurse managers who are married, had a bachelor’s degree of Nursing, and administrative years of experience.
Keywords: Emotional intelligence; Decision-making styles; Nurse managers
Introduction
Today's organizations that face with complex and changing internal and external environments, decision makers should have various skills and abilities to make decisions in order to deal with these extreme situations. Managers need to evaluate their current skills and develop more creative approaches. According to Diggins, (2004) the best administrators need to possess Emotional Intelligence (EI) to make good decisions based on a blend of self-management, relationship skills and awareness of their behavior's effects on others in the organization. He argued that EI plays a greater role than "Traditional Intelligence" in determining leaders and organizations' success and concluded that EI helps people to be more aware of their interpersonal style. Recognize and manage the impact of emotions on their thoughts and behavior and understanding how well they manage relationships and how to improve [1-6]
Every person and organization share the goal of improving the quality of decision-making, and the manipulation of emotional intelligence skills can assist in the attainment of that goal. Decision makers who are self-aware and can accurately and honestly assess their strengths in comparison to others in the organization have the pros of leveraging the attributes of others in the decision-making process [3]. Emotions play vital role in decision-making. Emotions allocate worth to objects, assist in the understanding the ways to get those objects, and provide motivation in doing so. The importance of emotions in decision-making is apparent from the fact that most of the times decision-making itself is an emotional process [5].
Emotional Intelligence as a very important personal trait has an inevitable role in doing all managerial activities in appropriate ways; especially, in changing environments that relying on cognitive intelligent is not effective enough to make correct decisions and to be adaptive with unknowns for different managers. Emotional Intelligence defined as an integration of emotional, personal and social abilities and skills that impact an individual's ability to cope effectively with environmental demands and stressors [7-10]. Emotional Intelligence is the combination of abilities, competencies and skills that represent a collection of knowledge meant for coping with life effectively. Emotional intelligence represented a significant role in many aspects of managers. It is valuable to make effective decisions in day to day life in an organization. Strong emotions help leaders to make effective decisions. All health organizations require decision-making and all decisions have both cognitive and emotional components. A decision maker’s emotional treatment ability depends on previous experience, current emotional capacity and the emotional investment an individual is willing to make in the decision’s outcome [11].
Managers, usually, see decision-making as their central job because they must constantly choose what to be done, who is to do it, when, where and occasionally even how it will be done. We can say that managers face with situations (chances or threats) that have to make decisions in doing all their activities; therefore, decision-making is of great importance in all managerial activities and organizational processes [7]. Decision-making is one of the most important life skills for everyone. Making an effective decision is not easy and it is one of the main challenges for every administrator and leader. Decision-making is an essential leadership skill which will move forward individuals and teams to success. People make many good decisions which cause them to succeed but they make many bad decisions which cause them to fail. If they understand and learn about the different kinds of choices which are available to them, their lives would be more satisfying and particularly more effective in the workplace [1,11].
Vroom & Yetton’s [12] Theory of decision-making styles - Autocratic decision-making styles in which the decision-maker usually collects specific information from his/her team, then makes a final decision based on the specific information he/she has received [12]. They do not tell the team or other people involved that their input is to be used to make the decision. Consultative decision-making style in which the decision-maker shares and explains his/her ideas to the team to collect some different ideas, suggestions from them and then makes a decision. Group decision-making style, in which the decision maker always shares his /her ideas, asks for suggestions and brainstorms together in a group to find a solution to the problem. He/she brings the problem or cause to their team and discusses different ideas or suggestions to make a decision. The decision-maker believes that his/her role is to facilitate and guide the team to reach their goals and make final decisions together. The final decision will be the result of everyone agreeing and being satisfied with the decision.
Significance of the Study
It is interesting that up to this moment, nationally there is no study has been found to link the concept of EI and decisionmaking styles. Therefore, the topic of emotional intelligence of nurse managers is required for better decisions become extremely important. There are two main objectives in this study. First, as it would be extremely valuable to assess the emotional intelligence and decision-making styles of nurse managers at Assiut University Hospitals. Secondly, this study explores the relationship between emotional intelligence and decision-making styles. We propose that as nurse managers with high emotional intelligence are more sensitive to make a good decision according to the circumstances of the situation.
Aim of the Study
A. Assess emotional intelligence and decision-making styles among Nurse Managers at Assiut University Hospitals.
B. Explore relationship between emotional intelligence, decision-making styles, and personal characteristics of Nurse Managers at Assiut University Hospitals.
Research Question
What is the relationship between emotional intelligence, decision-making styles, and personal characteristics of Nurse Managers at Assiut University Hospitals?
Subject and Method
Study design
A descriptive correlational design was used in the present study.
Setting
The study was carried out at Assiut University Hospitals namely: The main Assiut Univversity Hospital, The Pediatric Health Hospital and The El-Rajhy Assiut Hospital.
Subject
The subject includes all nurses working in aforementioned settings with a total number of 90 nurse mangers which classified into (no= 58) in the main Hospital and (no=12) in the Pediatric Health Hospital and (no=20) in the El-Rajhy Assiut Hospital.
Data collection tools
Self-administered questionnaire sheet which consist of three tools.
Personal characteristics data: It was designed to collect personal data about study participants: name of the hospital, age, gender, marital status, educational qualification, years of experience, and administrative years of experience.
Emotional intelligence questionnaire: The Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire was adopted from Mohamed & Yousef [8]. It consisted of seventeen items which used to determine nurse managers emotional intelligence level [8].
Scoring system: The used scoring system is (1 = most of the time, 3 = often of the time, 5 = sometimes, 7 = rarely, and 9 = never). The levels of Emotional Intelligence are classified into the following: from 50 to less than 70 is a very low level of Emotional Intelligence, 70- less than 85 is a low Emotional Intelligence, 85 to less than 115 is a mild level of Emotional Intelligence, 115 to less than 130 is a High level of Emotional Intelligence, 130 to 150 is a Genius Emotional Intelligence.
Decision- making styles questionnaire: It developed by Clark [2] and updated it in December 2007, it is consisted of 30 statements [2]. Ten of them reflect authoritative style, 10 items reflect participative style, and 10 items reflect delegative decision-making style. Responses were measured on 5 points Likert scale ranged from (5) always true to (1) never true.
Pilot study
The pilot study served to test the feasibility of the study tools, the clarity and practicability of the data collection tool. It was carried out on 20 nurse managers from different inpatient departments at Main Assiut University Hospital. The nurse mangers in the pilot study were excluded from the total sample. Data collected from the pilot study were reviewed and used in making the necessary modifications prior to the finalization of the data collection tool.
Fieldwork
An official permission was obtained from the hospital’s directors, the nursing service directors, and the head of each department before embarking on the study. After the finalization of the study tools, the actual data collection was started in January 2019 and ended in March 2019. The researchers met with the eligible nurse managers, explained to them the aims of the study, and asked for their oral consent to participate. Those who agreed to participate were given the tool and asked to fill it out and return it anonymously in the same setting or at most the next day. The researchers were available for any clarifications.
Ethical considerations
All the related principles of ethics in research were followed. The study protocol was approved by the pertinent authority. Nurse Managers' consent to participate was obtained after informing them about their rights to participate, refuse, or withdraw at any time. Total confidentiality of any obtained information was ensured. The study maneuver could not entail any harmful effects on participants.
Statistical analysis
Data coded, entry and statistical analysis were done by using SPSS 19.0 statistical software package. Data were presented using descriptive statistics. Pearson correlation analysis was used for assessment of the inter-relationships among quantitative variables, and Spearman rank correlation for ranked ones. Statistical significance was considered at p-value <0.05.
Result
Table 1 Illustrated that, the highest percentages of Nurse Managers had bachelor’s degree of Nursing Sciences in Main Assiut University Hospital and El Rajhy Assiut Hospital (82.7% & 75.0%) respectively, while they had master’s degree in the Pediatric Health Hospital (66.7%). The majority were females (90.0%) , aged less than 35 years old, had less than 5 years of experience, and had administrative years of experience (75.0%) at El Rajhy Assiut Hospital , while All Nurse Managers of Pediatric Health Hospital were married (100.0%), aged between 25 -< 35 years old ( 66.7%).
Table 1: Personal characteristics of the nurse managers at Assuit University Hospitals (n=90).
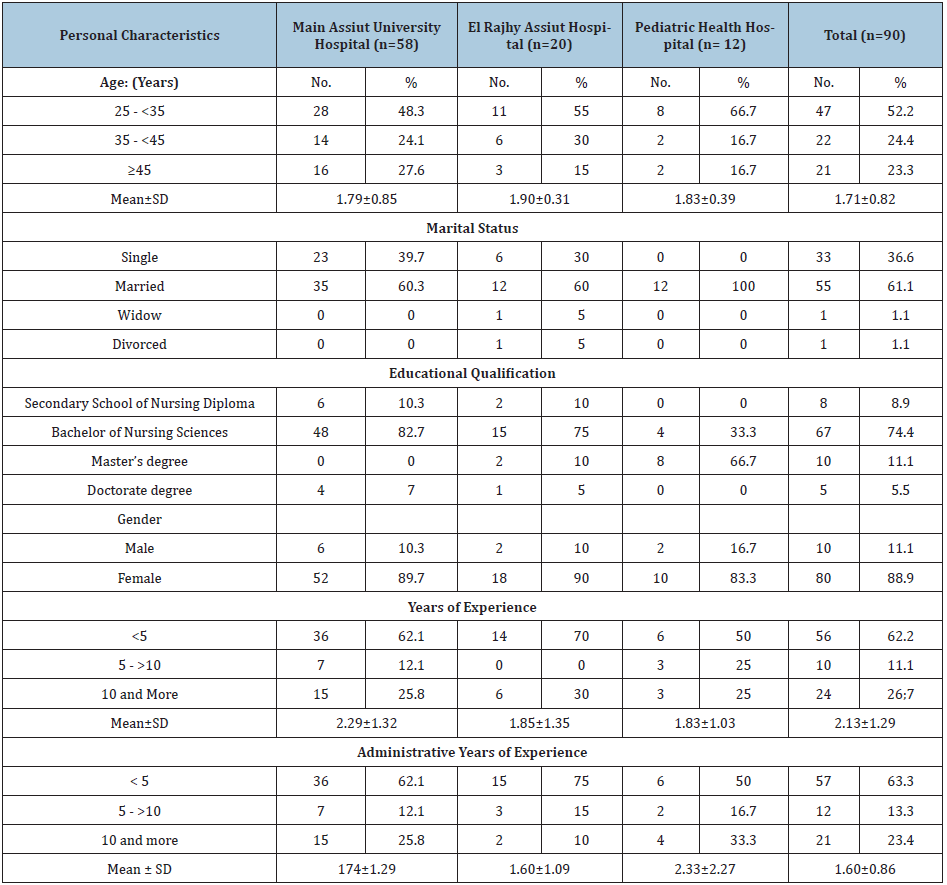
Table 2 Shows that, there was high level of Nurse Managers emotional intelligence (66.7%) for Pediatric Health Hospital than at Main Assiut University Hospital & El Rajhy Assiut Hospital (63.8% & 60.0%) respectively.
Table 2: Distribution of emotional intelligence levels among the studied nurse managers at Assuit University Hospitals (n=90).
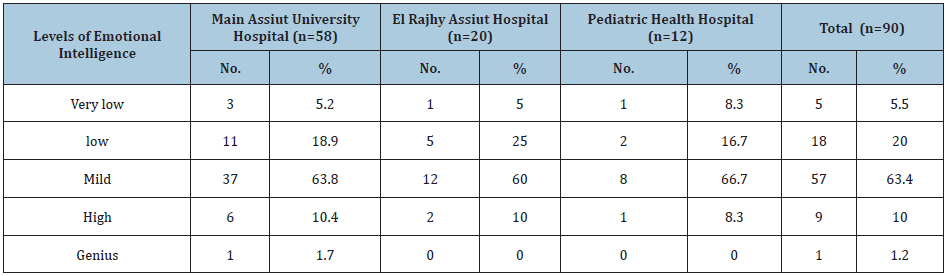
Table 3 Explores that the high mean scores were in participative style of decision-making in all Assiut University Hospitals (40.65±5.40; 39.62±4.36 & 38.25±6.06) respectively.
Table 3: Mean scores of decision-making styles among studied nurse managers at Assuit University Hospitals (n=90).
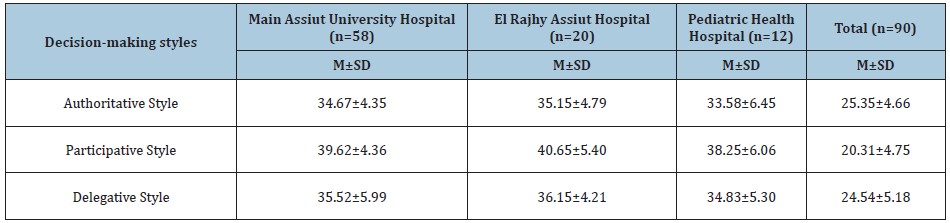
Table 4 Reveals a positive significant correlation between age and emotional Intelligence (0.238*). Nurse Managers' emotional intelligence had significant relationships with Bachelor qualification and years of experience (0.229* & 0.256*) respectively. While, there was a negative correlation between authoritative style of decision-making and emotional intelligence (-0.022), and negative correlation among delegative style, and nurse managers are married, had a bachelor’s degree of Nursing, and administrative years of experience (-0.080; -0.043& -0.023) respectively.
Table 4: Correlation between the scores of emotional intelligence, decision-making styles and nurse managers personal characteristics.
(#) Pearson correlation coefficient (*) Statistically significant at p<0.05.
Discussion
Management decision-making is an important part of organizational behavior. However, managers’ decision-making styles and decisions made by them are mainly affected by their perceptions. Emotional intelligence seems to be one of the factors that affect management decision-making styles, which has been emphasized greatly by many scholars and has created significant developments in the field of organizational behavior management theories [9].
The emotional intelligence skill of social awareness and its core competencies of empathy, service orientation and organizational awareness of decision-makers are to judge the impact of not only their decisions but also the manner in which those decisions are made [11].
The current study was conducted with the aims to assess emotional intelligence and decision-making styles and explore the relationship between emotional intelligence and decision-making styles among Nurse Managers at Assiut University Hospitals.
The results of the present study as shown in (Table 1) revealed that eighty percent of the studied Bachelor degree of Nursing Sciences in Main Assiut University Hospital while sixty percent of the studied Master degree in the Pediatric Health Hospital .The majority were females at El Rajhy Assiut Hospital , while All Nurse Managers of Pediatric Health Hospital were married.
The findings of the present study clarified that the highest percentages of the Nurse Managers emotional intelligence were in Pediatric Health Hospital (Table 2). This may be due to most of them had master’s degree of Nursing Science. This finding was in accordance with finding of Goleman, (2005) who argued that emotional intelligence was the strongest indicator of human success. Our emotions play a much greater role in thought, decision-making and individual success. Also, Conrad, (2007) concluded that leaders who had high levels of emotional intelligence exhibited better decision-making, higher levels of social responsibility and displayed better interpersonal relationships.
Ongoing of the present study findings in (Table 3) clarified that highest mean scores were in participative style of decision-making. This finding was in accordance with Sharan [10] who concluded that emotionally intelligent employees utilize participation in decision-making opportunities to achieve their objectives as well as organizational objectives [10]. Also, in accordance to Sumathy et al. [11] who concluded that the transformational leader’s decision-making highly leveraged by participation whereas transactional leader’s decision-making was enhanced by felt accountability [11].
The results of the present study as shown in (Table 4) declared that a positive significant correlation between age and emotional intelligence. This may be due to when increase the age the manager will be able to well-developed emotional skills are satisfied and efficient in their life as they possess intellectual habits which turn them into productive and competent people. Also, (Table 4) shown that there were Nurse Managers' emotional intelligence had significant relationships with bachelor’s degree qualification and years of experience. This finding was in accordance with James & Arnold [4] who concluded that the emotions people expect to experience or have experienced as a result of their decisions are important determinants of their current and future behaviors [4].
Also, there was a negative correlation between authoritative style of decision-making and emotional intelligence, and negative correlation among delegative style, and nurse managers are married, had a bachelor’s degree of Nursing, and administrative years of experience (Table 4). These findings were in accordance with Nowzari [9] who found that there is a negative relationship between managers’ emotional intelligence and rational and avoidant decision-making styles and a positive significant relationship between managers’ emotional intelligence and intuitive decision-making style [9]. Besides, emotional intelligence was found to predict rational, intuitive, and avoidant decision-making styles. This finding was consistent with study results conducted by Sumathy et al. [11] which found a significant relationship between emotional intelligence and decision-making.
Conclusion
There was high Level of Nurse Managers emotional intelligence at Pediatric Health Hospital than at Main Assiut University Hospital & El Rajhy Assiut Hospital, the high mean scores were in participative decision-making style in all Assiut University Hospitals, a positive significant correlation between age and emotional intelligence. Nurse Managers’ emotional intelligence had significant relationships with Bachelor qualification and years of experience. While, there was a negative correlation between authoritative decision-making style and emotional intelligence, and negative correlation among delegative decision-making style and nurse managers who are married, had a bachelor’s degree of Nursing, and administrative years of experience.
References
- Beri N (2013) Job satisfaction among primary school teachers in relation to decision making styles of their heads. Educationia Confab Journal. Lovely Professional University, Punjab, India. pp. 2320-009.
- Clark D (1998) Originating a movement. Cicely Saunders and the Development of St. Christopher’s Hospic. Mortality 3(1): 43-63.
- Hess J (2011) Enhancing decisions and decision-making processes through the application of emotional intelligence skills. Management Decision 49(5): 710-721.
- James D, Arnold C (2011) Enhancing decisions and decision‐making processes through the application of emotional intelligence skills. Emerald Group Publishing Limited, UK.
- Khan E, Riaz M, Batool N, Riaz M (2016) Emotional intelligence as a predictor of decision-making styles among university students. J Appl Environ Biol Sci 6(4S): 93-99.
- Maree J, Finestone M (2007) The impact of emotional intelligence on human modeling therapy given to a youth with bipolar disorder. International J Adolescence and Youth 13: 175-194.
- Moghadam A, Tehrani M, Amin F (2011) Study of the relationship between Emotional Intelligence (EI) and management decision making styles. World Applied Sciences Journal 12(7): 1017-1025.
- Mohamed F, Yousef H (2014) Emotional intelligence and conflict management styles among nurse manager at assiut university hospitals. Journal of Education and Practice 5(5): 160-165.
- Nowzari V (2015) Relationship between emotional intelligence and decision-making styles among managers at sports organizations in fars province. Indian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Life Sciences 5(S2): 1302-1310.
- Sharan K (2009) A study on employee participation in decision making. Unitar E J 5(1): 20-38.
- Sumathy L, Madhavi C, Felix A (2015) Influence of emotional intelligence on decision making by leaders. American International Journal of Social Science 4(1):
- Vroom V, Yetton P (2013) Vroom yetton contingency model. Slide Share, New York, USA.
© 2020 Fatma Rushdy Mohamed. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






