- Submissions

Full Text
Cohesive Journal of Microbiology & Infectious Disease
Report of 2 Cases of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
Hu Zhi Min* and Jin Qiu Sheng
Department of Endoscopic, China
*Corresponding author: Hu Zhi Min, Department of Endoscopic, China
Submission: August 16, 2021; Published: September 21, 2021

ISSN 2578-0190 Volume5 issues4
Purpose
To review the clinical data of two patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) and to review the literature so as to improve the understanding of the disease and reduce misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis [1-6].
Method
Collecting and collating the medical history data, laboratory examinations, imaging examinations, bronchoscopic findings, histopathological findings of the two patients, and comparing the latest diagnostic criteria of allergic bronchial aspergillosis and reviewing the literature.
Result
The clinical symptoms of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis were easily confused with asthma, tuberculosis and lung cancer. The imaging manifestations are varied, the early lung shadow is migratory, and the middle and late stages of “central bronchiectasis” have more characteristic changes. Bronchoscopic mucus embolism is common (Figure 1-3). Eosinophils in peripheral blood increased. The necessary conditions for diagnosis included two items: the increase of serum speci_ C IgE (sIgE) level (>0.35 kUA/L) or the positive rate of Aspergillus fumigatus skin test, and 7 the increase of serum total IgE level (>1000U/mL). It is usually difficult to obtain positive results from etiology [6-10].
Figure 1:The chest CT of a 49-year-old male: The proximal bronchus of both lungs showed columnar or cystic dilatation, and the distal part was normal. The bronchiectasis of both lungs showed centripetal distribution.
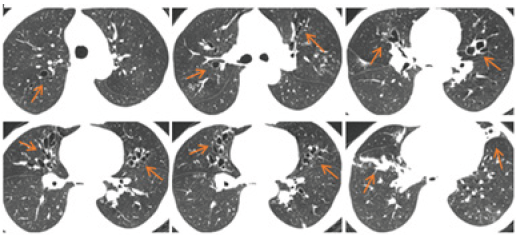
Figure 2: The 49-year-old male a-f: Necrotic mucus embolus was found in the lingual bronchus, left lower dorsal bronchus and right lower inner anterior basal segment bronchus. Removal of mucus thrombus with cryoprobe and biopsy forceps . g: Removal of mucus suppository by cryotherapy h: Under light microscope, mucus with eosinophils infiltration was found, and there were scattered fungal hyphae with parallel wall and transverse septum. Pathological diagnosis: mucus embolus formation with fungal infection, considered the possibility of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA-CB).

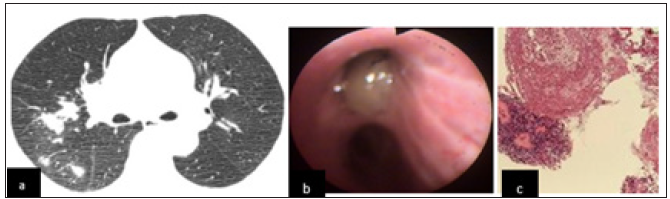
Figure 3: A 56-year-old female cough for half a year. (a). Multiple nodules and patchy shadows were found in the upper lobe of the right lung. Halo sign was found around some lesions, and interlobar pleura was thickened; (b). Under the bronchoscope, a large amount of thick purulent secretion was found in the right upper bronchusc: Microscopically, the main lesion was coagulative necrosis, with obvious thickening of lamina propria basement membrane and eosinophil infiltration (ABPA-Sa).
Conclusion
The diagnostic criteria of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis are constantly improved and revised. Medical workers need to improve their understanding of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and reduce misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis [10- 13].
References
- Agarwal R, Chakrabarti A, Shah A (2013) Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: review of literature and proposal of new diagnostic and classification criteria. Clin Exp Allergy 43(8): 850-873.
- Zhou Z, Chunsong Y (2017) Research progress of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Journal of Practical Clinical Medicine 18 (10): 103-107.
- Asthma Group (2017) Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of allergic bronchial pulmonary aspergillus. Chinese Journal of Medical Sciences 97(34): 2650-2656.
- Greenberger PA, Bush RK, Demain JG (2014) Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2(6): 703-708.
- Han L, Zheng H, He Quanli (2016) Chinese Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care 15(3): 294-297.
- Hu Hong, Zhang Li, She Danyang (2012) Clinical characteristics of seven cases of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Chinese Journal of Tuberculosis and Respiratory 35: 37-41.
- Xu Yang, LIU Kaixiong, Qu Jieming (2018) Case analysis based on expert Consensus on diagnosis and treatment of allergic bronchial pulmonary Aspergillus in 2017 edition. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University 38 (10): 1191-1196.
- Group of Infectious Diseases (2007) Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary mycosis. Chin J Tuberculosis & Respiratory 30(11): 821-834.
- Chen J, Cui XF (2015) Clinical significance of serum CEA in evaluating the therapeutic effect of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Global Chinese Medicine 11(8): 261-262.
- Xu L, Cai BQ, Xu KF (2007) Analysis of 23 cases of allergic bronchial pulmonary aspergillosis. Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine 46(3): 208-212.
- Gao Wei, Su Xin, Shi Yi (2013) Clinical characteristics and misdiagnosis analysis of 16 cases of ABPA. Journal of Clinical Pulmonary Medicine 18(10): 1798-1799.
- Li R, Xu J, Sun YC (2011) Clinical analysis of 11 cases of allergic bronchial pulmonary aspergillosis. Chinese Journal of Asthma 5(6): 423-428.
- Patternson, Strek ME (2010) Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 7(3): 237-244.
© 2021,Hu Zhi Min. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






