- Submissions

Full Text
Cohesive Journal of Microbiology & Infectious Disease
Implementation of Quality Risk Management for Manufacturing of a Non-Sterile Pharmaceutical Product- Case study
Ahmed Assem*
MBA, Tabuk pharmaceuticals, Saudi Arabia
*Corresponding author: Ahmed Assem, MBA, Tabuk pharmaceuticals, Saudi Arabia
Submission: January 16, 2018;Published: April 06, 2018

ISSN: 2578-0190 Volume1 Issue3
Abstract
This article will address a model for implementation of quality risk management for the manufacturing of a non-sterile product through a real case. The risk addressed in the article is the microbiological contamination and the procedure followed was Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) mainly. It can be used by pharmaceutical scientist to evaluate the possible causes of microbiological contamination of their products and will show how to evaluate the risks and describe a monitoring plan based on the associated risks
Keywords: Pharmaceutical microbiology; Quality risk management; Pharmaceutical manufacturing; Microbial contamination
Introduction
The holder of a manufacturing authorisation must manufacture medicinal products so as to ensure that they are fit for their intended use, comply with the requirements of the Marketing Authorisation and do not place patients at risk due to inadequate safety, quality or efficacy [1]. As Per ICH Q9, Quality Risk Management, “Risk management is the systematic application of quality management policies, procedures, and practices to the tasks of assessing, controlling, communicating and reviewing risk [2].
To protect patients in terms of quality, safety and efficacy of medicines, international medicines regulatory authorities (MRAs) are recommending pharmaceutical manufacturers to adopt a riskbased approach to the life-cycle of a pharmaceutical product [3]. The quality risk management system should ensure that [4]. The evaluation of the risk to quality is based on scientific knowledge, experience with the process and ultimately links to the protection of the patient; the level of effort, formality and documentation of the quality risk management process is commensurate with the level of risk.
Procedure
The following procedure will be used to perform the risk assessment (the risk addressed is the microbial contamination of a non-sterile product).
- First step is to develop a process flow chart to fully describe the manufacturing process
- Second step is to form a project team
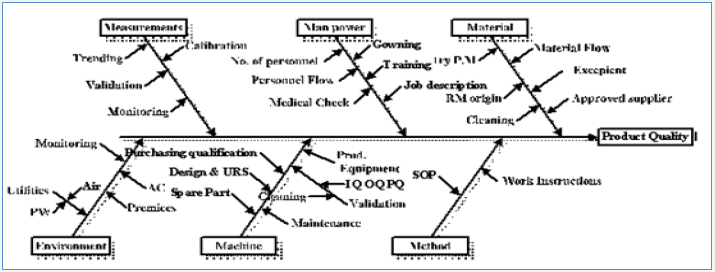
- A Cause & Effect (Fishbone) diagram will be prepared by the team (using the process flow chart) to evaluate the possible causes of microbial contamination.
- FMEA will be developed by the team (using the prepared Cause & Effect diagram) to evaluate the risk associated with different factors (Raw materials, Packaging materials, Utilities, etc.)
- Pareto diagram will be used to highlight the most critical factors that may lead to microbial contamination of the product (using the developed FMEA)
- Finally, a monitoring plan will be developed to insure that all the identified high risk factors are monitored frequently to insure the risk (microbial contamination risk) is controlled
The team should be composed of to reflect all function that could have a decision influence on quality or compliance
The team will include product-specific knowledge and expertise The team will include:- The Quality Director
- The Microbiology manager
- The production manager
- The engineering manager
- The validation manager
Figure 1:
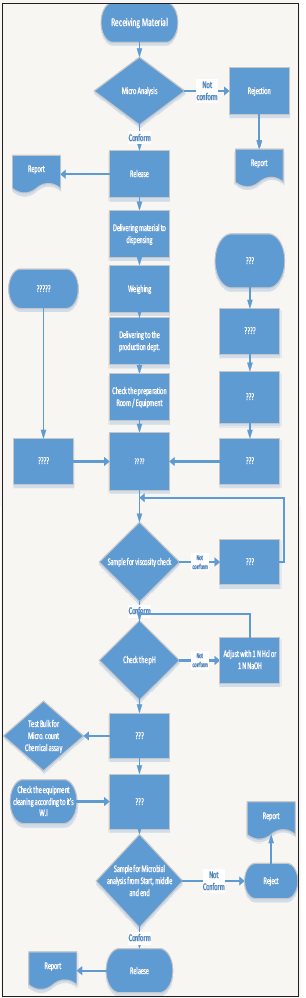
The team will include:
- Conduct a hazard analysis
- Identify potential hazards
- Identify hazards which should be controlled
- Recommend controls and critical limit
- Devise procedures for monitoring and verification
- Recommend appropriate corrective action where deviations occur
One of the most common used methods is Fish –bone diagram which summaries all critical influencing variables on the product quality [6,7]; (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Cause & Effect Diagram.
Determining the risk ranking (using Pareto chart)
Vilfredo Pareto was an Italian economist who lived from 1848to 1923. His study of the wealth distribution in the Italian economy yielded a key finding that 80% of the land was owned by 20% of the population. Since then, his discovery what we call the Pareto principle has been found to hold true in many other situations. For problem solvers, the simple Pareto principle provides a powerful root cause analysis (RCA) tool to separate the vital few factors from the trivial many determining risk ranking for Raw materials & Primary Packaging materials using the Pareto Chart.
Risk assessment using FMEA [8,9]Risk ranking policy
(Table 1-7)
Table 1: The Product.
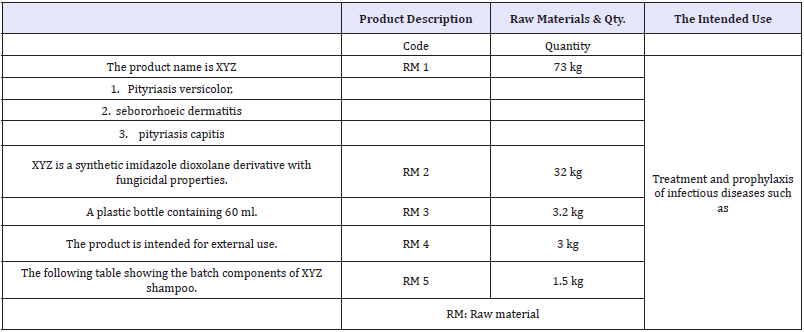
Table 2: The following table showing scoring policy.
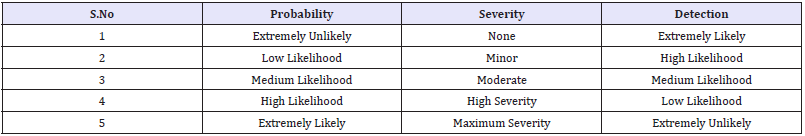
Table 3: The following table showing Ranking policy.
Table 4: Risk Assessment for Raw Materials & Packaging Material.
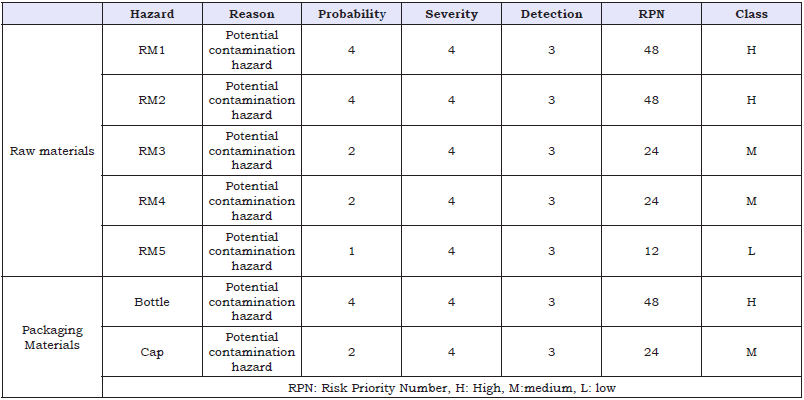
Table 5: Risk Assessment of different processes.

Table 6: Risk Assessment of different Utilities, Equipments and machines.
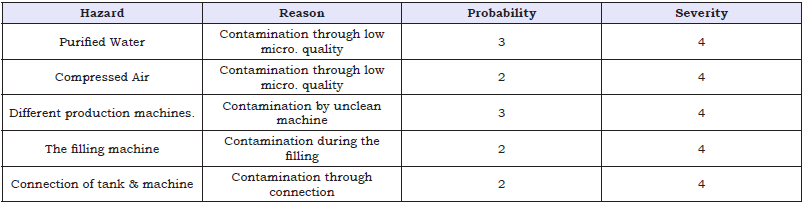
Table 7: Risk Assessment of different premises.

Determining the risk ranking (using Pareto chart)
Figure 3: Determining Risk Ranking for different Processes using the Pareto Chart.

Vilfredo Pareto was an Italian economist who lived from 1848 to 1923. His study of the wealth distribution in the Italian economy yielded a key finding that 80% of the land was owned by 20% of the population. Since then, his discovery what we call the Pareto principle has been found to hold true in many other situations. For problem solvers, the simple Pareto principle provides a powerful root cause analysis (RCA) tool to separate the vital few factors from the trivial many [10]. Determining Risk Ranking for Raw materials & Primary Packaging materials using the Pareto Chart [11,12]; (Figure 3).
Conclusion
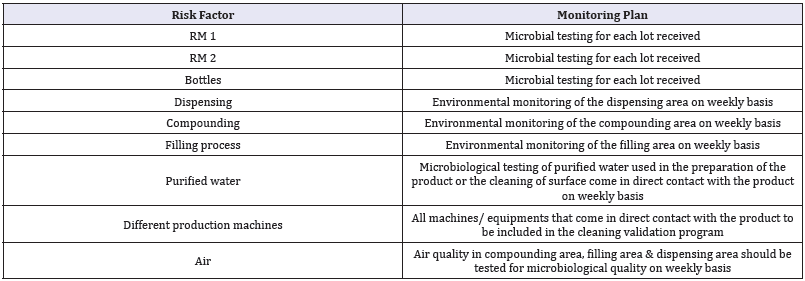
Using the QRM the following monitoring plan was developed which can be considered an effective monitoring plan. The developed plan is highly effective as it will monitor the most critical factors that may cause microbial contamination in a non-sterile product and it found to be a cost effective plan as it will eliminate monitoring the factors that will not affect the product quality (Table 8).
Table 8:
References
- Eudra Lex (2010) EC guidelines to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) for human and veterinary medicinal products chapter 1 pharmaceutical quality system; European Commission.
- Quality Guideline (2005) Q9: quality risk management; international conference on harmonization.
- Good manufacturing practices (2014) WHO guidelines on quality risk management. In: WHO expert committee on specifications for pharmaceutical preparations. Forty-seventh report. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
- L Viornery (2010) Quality Risk Management, Implementation of ICH Q9 in the pharmaceutical field an example of methodology from PIC/S, PIC/S.
- ASQ Flow Chart Template.
- ASQ Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram.
- ASQ Fishbone diagram template.
- ASQ Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA).
- (2003) Guidelines for Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) for Medical Devices, Dyadem Press.
- Bhalla, Aditya (2009) Don’t misuse the pareto principle. ASQ six sigma forum magazine 3: 15-18.
- ASQ Pareto Chart.
- ASQ Pareto Chart Template.
© 2018 Ahmed Assem. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






