- Submissions

Full Text
Biodiversity Online J
Increasing the Importance of ESG Management and Defense Industry
Jaeho Jung*
Korea Institute of Science & Technology Information, Republic of Korea
*Corresponding author:Jaeho Jung, Postdoctoral Researcher (Ph. D), Korea Institute of Science & Technology Information, Republic of Korea
Submission: June 25, 2023; Published: July 13, 2023

ISSN 2637-7082Volume3 Issue5
Opinion
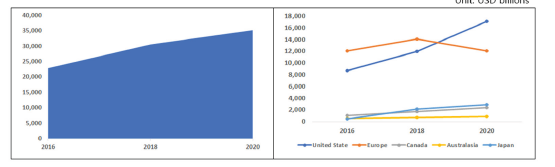
ESG management emphasizes the importance of sustainable management as a core value and emphasizes performance in terms of the environment, society, and governance. Recently, companies are strongly required to implement ESG management by investors and key stakeholders. Compliance with ESG values has affected overall management performance such as investment, credit and financing [1]. In this situation, I briefly look at the recent changes in the size of global ESG investment. In particular, I will look at why ESG is important to defense companies. Finally, I opinions what needs to be developed for ESG management. As of 2020, the total ESG investment assets are estimated to be about $35 trillion, an increase of more than 10 trillion won from about 22 trillion won in 2016. The annual average investment growth rate is also increasing steeply to about 11.5%. By country, investment in the United States increased significantly from about $8.7 trillion in 2016 to about $17.1 trillion in 2020. The annual average investment growth rate is 18.3%. Meanwhile, Europe showed the largest ESG investment at $12 trillion in 2016, but it is estimated to be at a similar level in 2020. Meanwhile, as an Asian country, Japan has invested $2.8 trillion in 2020, showing a high annual investment growth rate of 56.9% compared to 2016. In other words, it can be seen that the size of ESG investment is rapidly increasing worldwide (Figure 1). However, In Europe, it is estimated that some of the existing investment products have been excluded from statistics due to the recent change in the definition of ESG investment [2].
Figure 1:Global sustainable investing assets. total investing assets and major region investing assets.
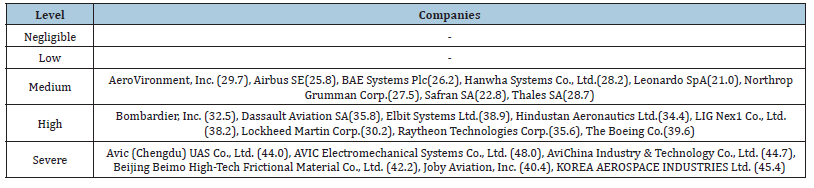
In particular, in the case of the defense industry, which produces weapons that kill lives, ESG risks are highlighted in terms of financing. This is because financial institutions are reluctant to invest or lend in the defense industry as they are likely to receive negative results in ESG management evaluation just by the fact that they have defense portfolios. State-run financial institutions, which should be supported, are also in a difficult situation. Recently, state-run banks have been speeding up climate finance by reducing financial support for coal power exports, and this passive loan attitude is likely to spread to the defense industry in the future. Such a blind spot in ESG management is also called the so-called “sin industry” such as weapons, cigarettes, alcohol, and gambling [3]. In fact, most of the major defense companies are evaluated to have medium high and severe ESG risks (Table 1). Consistency of the ESG evaluation system is needed in order to expand ESG management value in the future and make a practical contribution to sustainable management of companies. Currently, there is virtually no ESG evaluation standard that is recognized for public trust worldwide. ESG evaluation of companies is not only crowded with institutions that have applied their own evaluation criteria, but also has limitations in terms of reliability of evaluation due to the low consistency and objectivity of the evaluation system [3]. In particular, when comparing the results of the FTSE ESG index (ESG evaluation index prepared by Financial Time Stock Exchange Russell, a UK stock index and related data service provider, divides the environment, society, and governance into 300 detailed items to conduct ESG evaluation) and the MSCI ESG index (As an ESG index published by Morgan Stanley Capital International in the United States, it is an evaluation system that evaluates 10 areas and 35 key issues and gives 7 grades), which are representative ESG evaluation indicators, no clear correlation is observed. In other words, ESG institutions in each country or around the world will need to prepare more unified ESG evaluation indicators so that companies can respond to ESG risks and pursue sustainable management [4,5].
Table 1:ESG risk rating in defense & aerospace.
References
- Sim S, Kim MJ, Jung J (2022a) Global competitive evaluation of south korean defense industry and its challenges.
- Hwang and LEE (2021) Implications from trends in liability investment and investment restrictions by major overseas pension funds and asset management companies.
- KIET (2022b) ESG Risks and countermeasures in the defense industry.
- Global Sustainable Investment Alliance (2021) Global sustainable investment review 2020.
- Sustain Analytics.
© 2023 Jaeho Jung. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






