- Submissions

Full Text
Aspects in Mining & Mineral Science
Insights into Impact of Coal Mining and Burning on Air Pollution
Mohd Yusuf1*, Varun Kumar Sharma1, Sukhvinder Pal1 and Wasim Khan2
1Department of Natural and Applied Sciences, School of Science and Technology, The Glocal University, India
2Department of Petroleum Engineering, School of Science and Technology, The Glocal University, India
*Corresponding author: Mohd Yusuf, Department of Natural and Applied Sciences, School of Science and Technology, The Glocal University, Mirzapur Pole, Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh- 247121, India
Submission: June 30, 2022;Published: July 08, 2022

ISSN 2578-0255Volume9 Issue4
Opinion
Day-by-day the demand for new technological advancements have been revolutionized so far. In the 21th century has brought enormous emerging scientific developments in the way of organizing and circulating our economies, lives and lifestyle with several beneficial products from various industries, processing and manufacturing units. As the cliff of development rose higher, human civilization set new records of technology. These expansions of science and technology boosted not only the quality of our lives but also led to manifold many certain as well as uncertain glitches over the environment. Coal is an important and most frequently abundant fuel source which has been utilized for energy production and supply. Surface coal mining has increased globally during the past 30 years. World Coal Association (WCA) stated about coal as, the coal is an important fossil fuel and is critically essential for our civilization pertaining its use to provide the required electricity at a very affordable cost and in the extraction of several metals and alloys. Particularly, coal industries and associated sectors have been a popular source of economies both in advanced as well as emerging countries. The extensive utilization of coal is assumed to increase by approximately 62% over the two decades [1]. However, producing and using coal affects the environment. Concerning air pollution via the dispersion of certain gases as well as particulate matters by the activities of coal mining raises some environmental challenges [2,3]. However, the government’s repeated certain regulations and assertions globally for the sustainable mining extraction and development of rural and tribal communities living near the vicinity of mining areas, have not been converted into implementable solutions so that pollution can be controlled to a significant extent [4-6]. In general, the combustion of coal operated via an exothermic chemical reaction of oxygen with atomic carbon, hydrogen and sulphur, also known as a fusion of oxygen (Figure 1). Air pollution from coal-fired power plants is linked to asthma, cancer, heart and lung ailments, neurological problems, acid rain, global warming, and other severe environmental and public health impacts [2-5].
Figure 1:Airborne pollutants by the action of coal mining and burning/consumption.
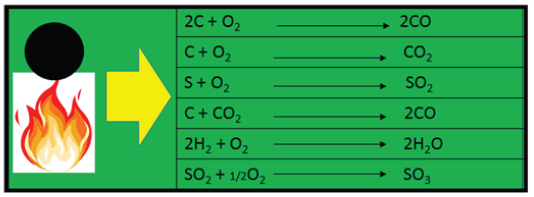
The coal mining and process of its burning leads to the emission of hazardous airborne pollutants and heavy metals into the environment where they cause severe health-related issues to the ecological entities including, mercury, carbon oxides, sulphur oxides, nitrogen oxides, particulate matters (ash etc.) associated with several respiratory-related concerns (Figure 2). Generally, out of many of coal’s environmental influences, global warming is the most irreversible as well as long-persistent concern. In this process the emissions of heat-trapping gases, primarily from human activities, that rise into the atmosphere and act like a blanket, roasting the earth’s outer surface. Various reports recommend that the increase in population triggers a massive burden on natural resources like food, water, and energy [7], more is the demand and supply of resources from natural origin, are the chief reason for the global warming process [4-6]. There are certain gaseous emissions which create a global threat to climate change and by global warming phenomenon (Figure 3). In other words, the rising global temperature poses a great threat to the environment and ecosystems due to abrupt changes in the climate [8]. Fossil fuels are still the largest source to meet the global energy demand contributing to about 85% of the world’s energy generation. The fossil fuels are formed over millions of years under the earth’s crust, but due to high energy demands, like oil, gas, and coal, are oppressed and mined much fast resulting in sooner exhaustion. Improving the energy efficiency of buildings, vehicles, industrial processes, appliances, and equipment is the most immediate and cost-effective way to reduce energy use and cut emissions.
Figure 2:Airborne pollutants associated with coal mining and its combustion suspended that make direct air pollution.
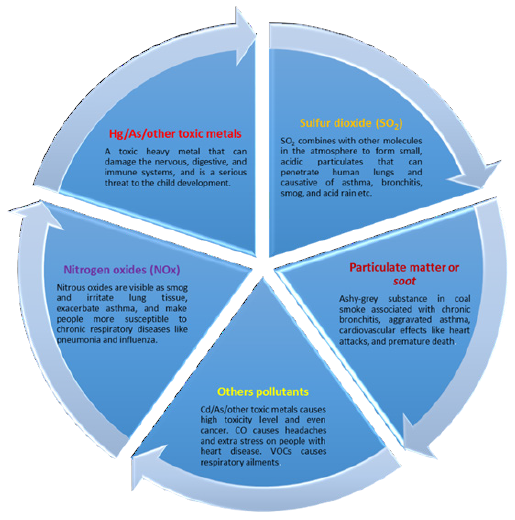
Figure 3: Prime emissions of coal combustion causes global warming.

In summary, the uncontrolled and less regulated extraction of fossil fuels such as oils/gas/coal at such extreme rates builds the accumulation and disturbance in the atmosphere, particularly, natural C & N-cycles. Several options exist to transition away from a fossil fuel economy. It is also possible for carbon emitted by the fossil fuel sector to be collected and injected back into the earth through a process called Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS). Orienting cities and towns around public transit, walking, or biking, instead of using private vehicles, also reduces energy demand. Currently, the world’s leading scientists recommended strongly to use of innovative alternatives to the conventional sources to get renewable energy [9,10], for example, hydropower, solar energy, biomass, wind, geothermal etc. in addition, nuclear energy is another zero-carbon substitute, but from the point of cost, it is expensive and leaves behind long-lasting radioactive waste that is dangerous, over-Burdon to transporting as well as storage. In addition, naturally occurring methane that is produced via the biochemical decomposition of organic matters either in landfills or others, needs to be trapped to generate alternative options for heat and energy usage and storage. Hence it is urgently needed to minimize the toxic substance emissions by using implementing effective mitigation strategies under solid regulations of regulatory bodies.
References
- http://www.worldcoal.org
- Gautam S, Patra AK, Sahu SP, Hitch M (2018) Particulate matter pollution in opencast coal mining areas: A threat to human health and environment. International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment 32(2): 75-92.
- Liu T, Xie Y, Su S, Wang L, Song Y, et al. (2022) Synergistic removal effects of ultralow emission air pollution control devices on trace elements in a coal-fired power plant. Energy & Fuels 36(5): 2474-2487.
- Mondal R, Mistri B (2022) Changing pattern of land use land cover due to Sonepur–Bazari open cast coal mine and its impact on surrounding area, West Bengal, India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing 10: 1-5.
- Yusuf M, Khan SA, Abul W, Sharma M (2021) Current and future prospects of dye confiscation potential of inorganic-based materials: A mini review. Asian Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology & Environmental Sciences 23(1): 89-95.
- Yusuf M (2021) Cellulose-based nanomaterials for water pollutant remediation. Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications pp. 213-228.
- Yusuf M, Shabbir M, Mohammad F (2017) Natural colorants: Historical, processing and sustainable prospects. Natural Products and Bioprospecting 7(1): 123-145.
- Abirami B, Radhakrishnan M, Kumaran S, Wilson A (2021) Impacts of global warming on marine microbial communities. Science of the Total Environment 791: 147905.
- Kumar D, Chaudhary J, Kumar S, Bhardwaj SR, Yusuf M, et al. (2021) Investigation of methylammonium lead bromide hybrid perovskite based photoactive material for the photovoltaic applications. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials & Biostructures (DJNB) 16(1): 205-215.
- Sun Y, Anwar A, Razzaq A, Liang X, Siddique M (2022) Asymmetric role of renewable energy, green innovation, and globalization in deriving environmental sustainability: Evidence from top-10 polluted countries. Renewable Energy 185: 280-290.
© 2022 Mohd Yusuf. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






